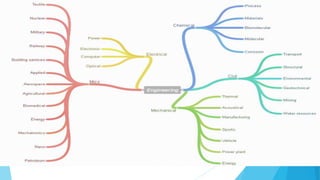
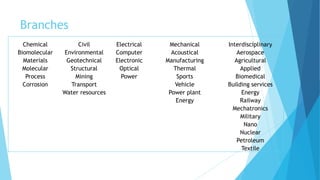
Engineering involves the creative application of scientific principles to design structures, machines, processes, and systems. There are several main branches of engineering including chemical, civil, electrical, and mechanical engineering. Chemical engineering applies physics and chemistry to carry out chemical processes. Civil engineering designs infrastructure and buildings. Electrical engineering designs electrical and electronic systems. Mechanical engineering designs mechanical systems and machines. Within each branch there are many specialized fields that engineers can pursue.