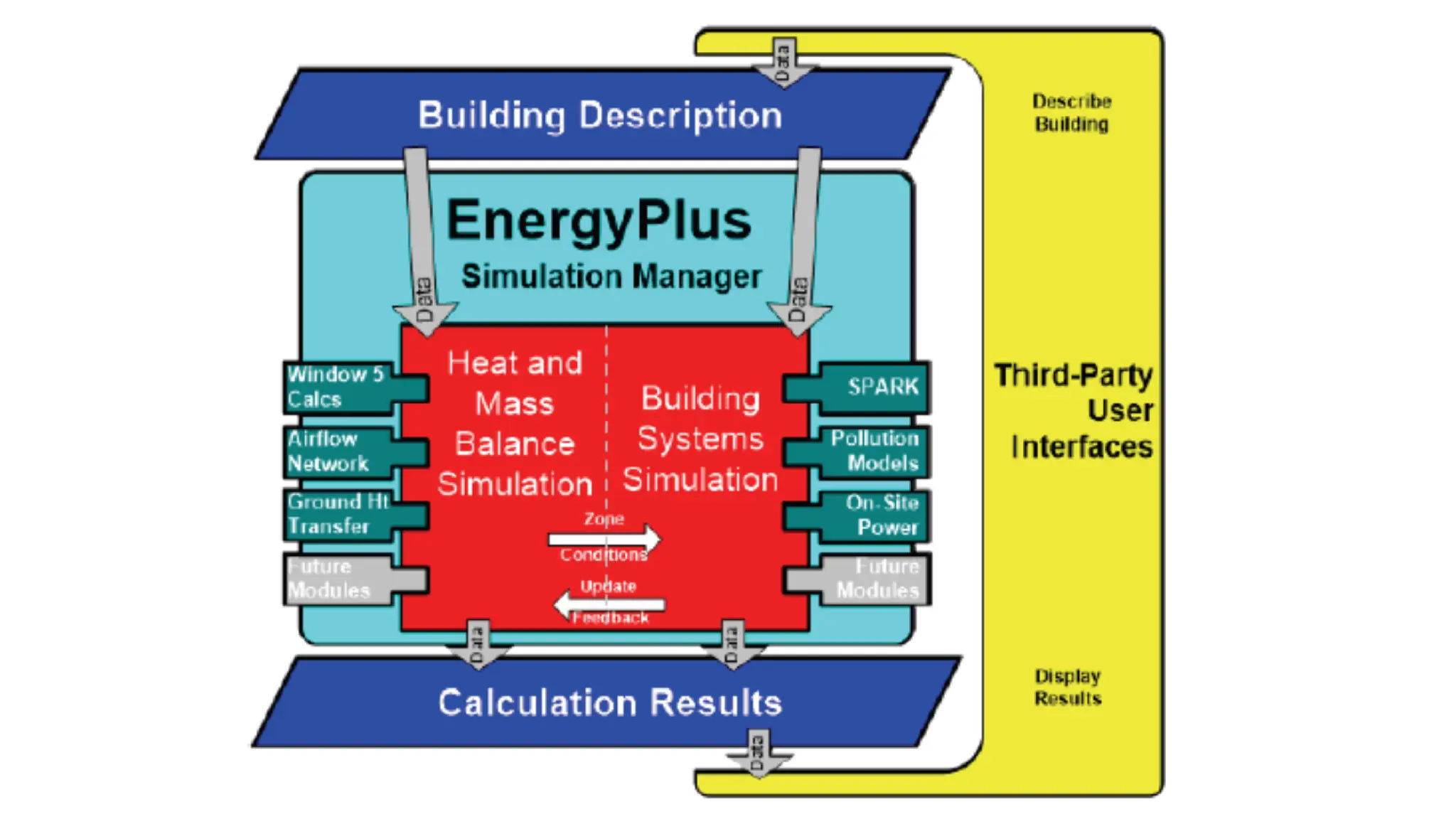
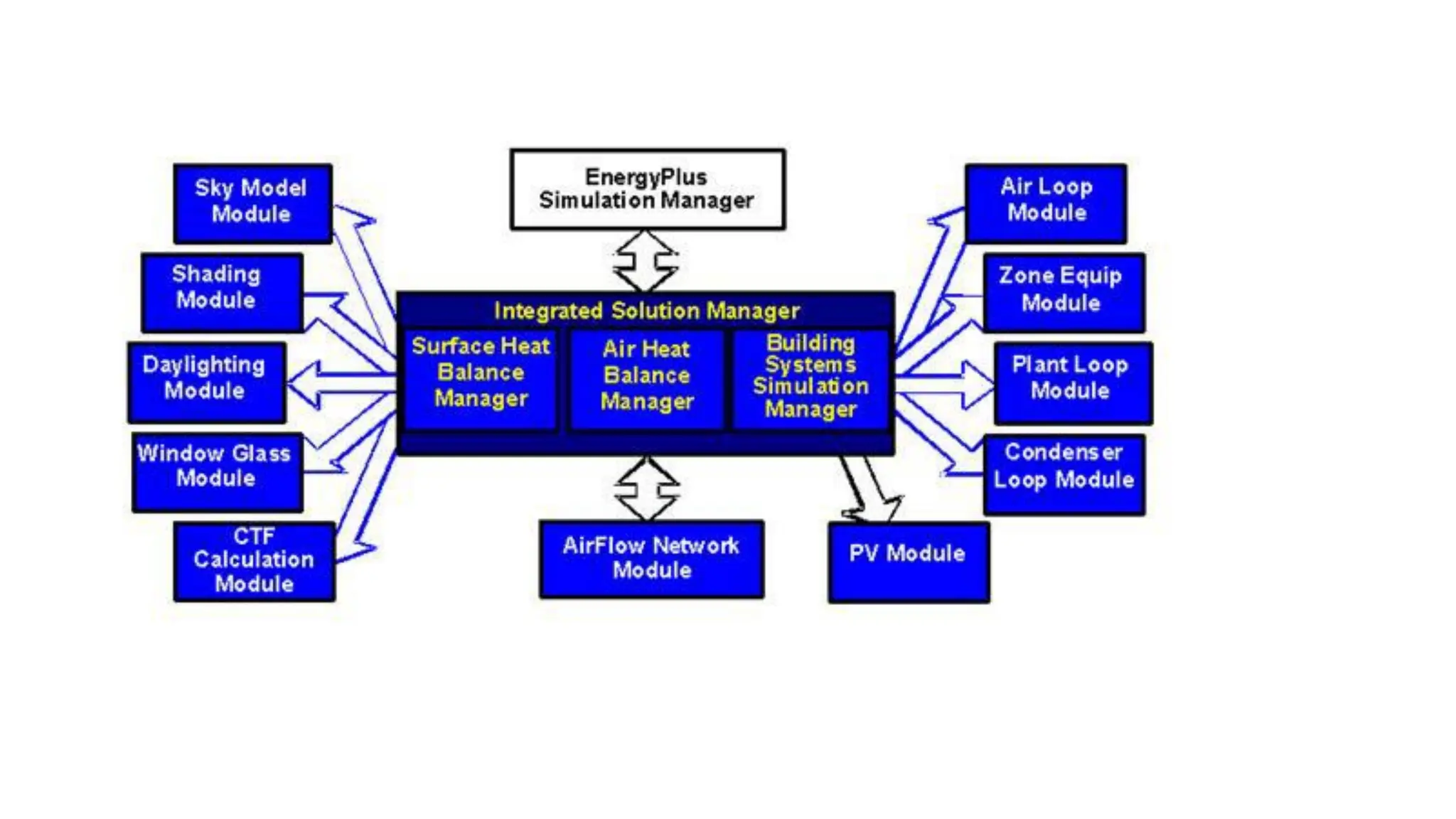
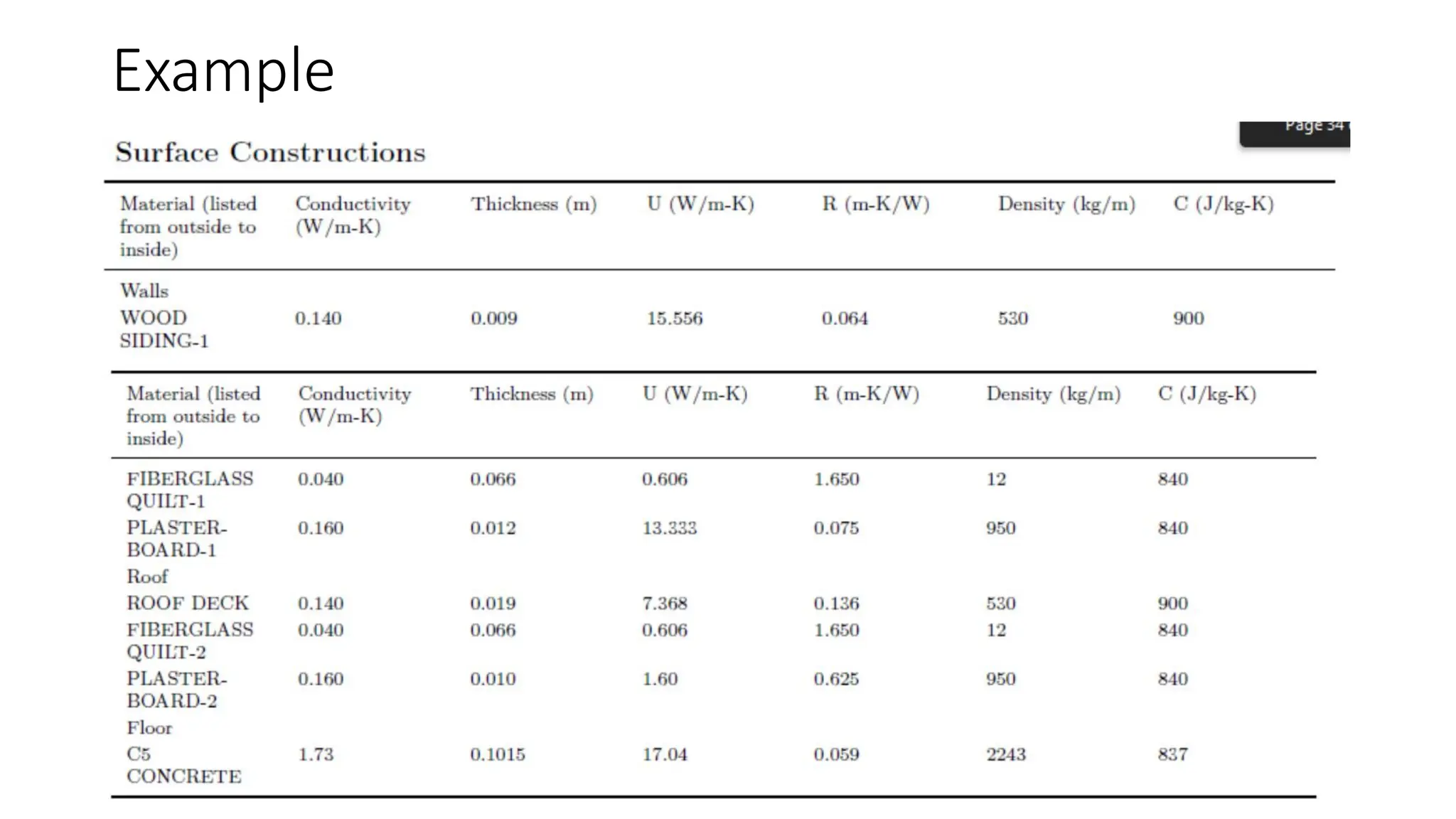
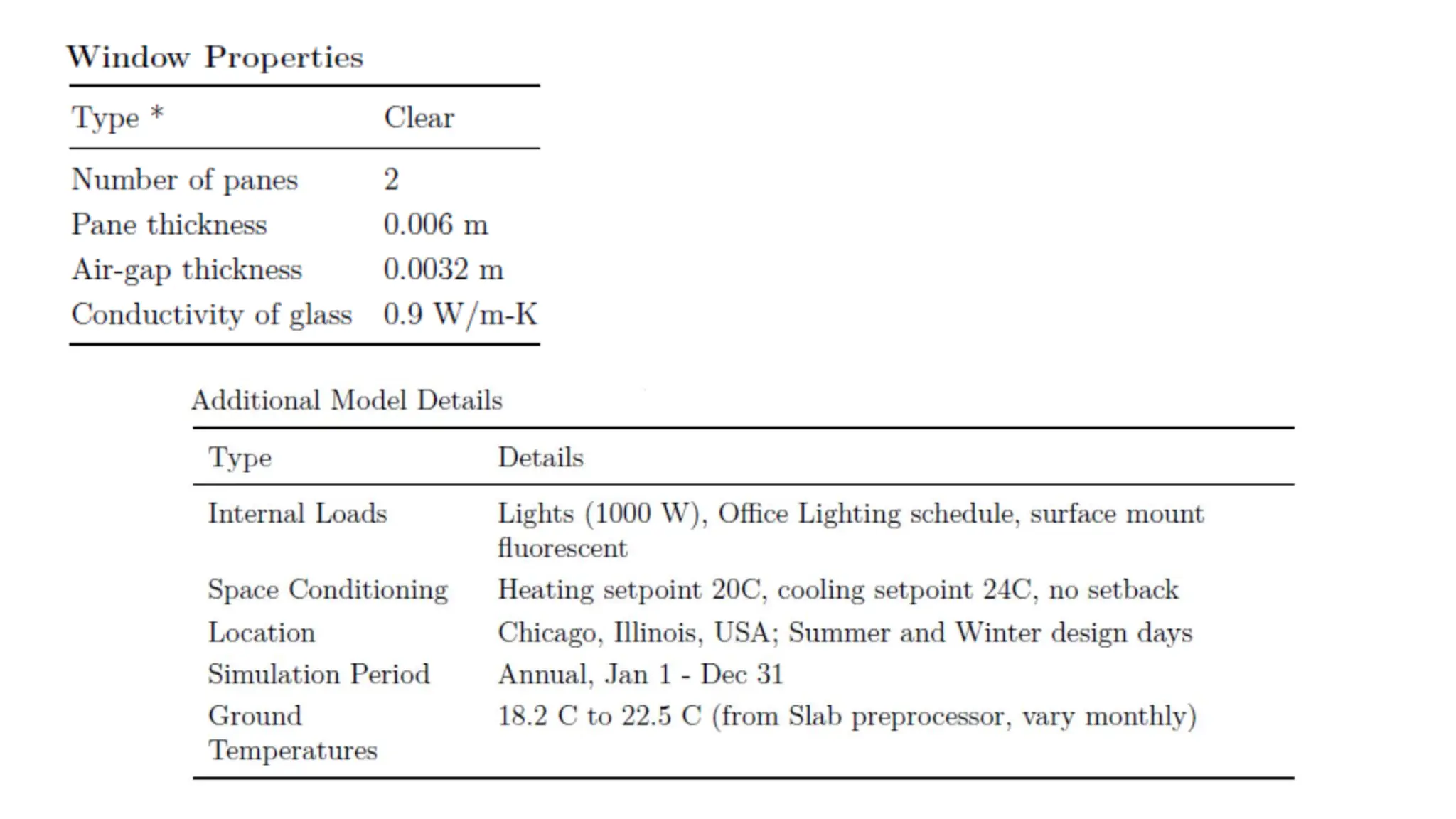
EnergyPlus is a whole building energy simulation program that engineers and architects use to model energy and water use in buildings. It has roots in earlier programs BLAST and DOE-2. EnergyPlus allows users to size HVAC equipment, conduct retrofit studies, and optimize energy performance. It features integrated modeling of building systems and components like fenestration, daylighting, HVAC systems, and more. It uses heat balance-based and finite difference techniques to model thermal loads, heat transfer, and moisture transport at multiple time steps.