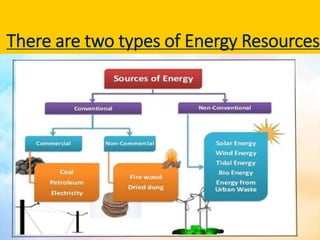
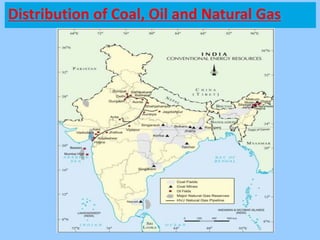
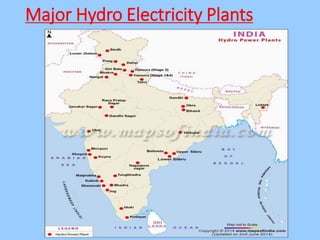
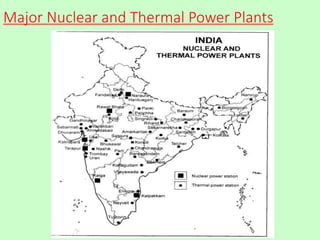
This document discusses different types of energy resources in India. It describes conventional resources like coal, petroleum, natural gas and their distribution in India. It also discusses non-conventional or renewable resources like solar, wind, tidal, biogas energies and their use in India. The document emphasizes the importance of conservation of energy resources for sustainable development and lists some measures to conserve energy.