SIP is a signaling protocol that is enabling unified communications applications by allowing IP-based communications to be extended across different networks, devices, and transport mediums. Key advantages of SIP include supporting mobility, virtual numbers, and business continuity. SIP trunking provides cost benefits like reduced network service costs by converging voice and data on a single IP connection. Considerations for SIP implementation include ensuring interoperability between systems, implementing security measures like encryption, and properly provisioning E911 services for mobile users.







![Energize Your Unified Communications with SIP XO Communications
9
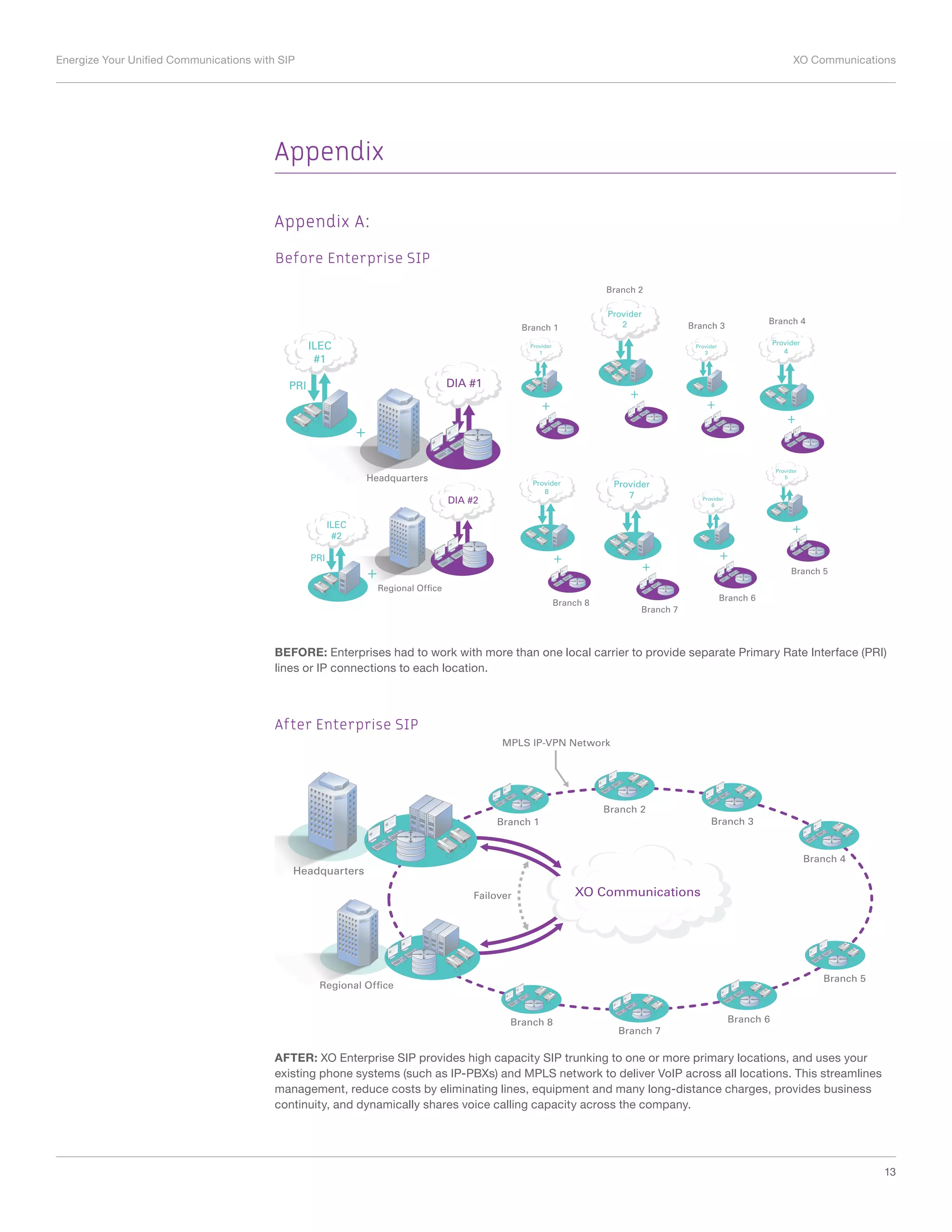
Reduced Network Service Costs
Convergence implies that a single connection can serve multiple access requirements. With SIP
trunks:
• Voice and data applications ride over one IP connection, instead of separate voice and data
services.
• The connection is highly efficient because unallocated SIP bandwidth is automatically and
dynamically made available for other uses and applications as required (see Figure 3). Added
voice compression is available from some service providers, such as XO Communications,
enabling higher throughput and efficiency as well.
• With centralized SIP trunking, companies can provide high-capacity connections between
their IP-PBX phone systems in one or more primary locations that serve as demarcation
points to the service provider’s core network and the universal Public Switched Telephone
System. This reduces the costs associated with managing separate networks, eliminates
local telephone lines and equipment at many locations, and eliminates long-distance charges
among headquarters and branch offices. [see Appendix A].
Figure 3. Real-time IP dynamic bandwidth allocation gives priority to voice traffic but makes additional data
bandwidth capacity available when phone lines are not in use.
Centralized SIP trunking
reduces the costs associated
with managing separate
networks, eliminates
local telephone lines
and equipment at many
locations, and eliminates
long-distance charges
among headquarters
and branch offices.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/energize-your-unified-communications-with-sip-140617151549-phpapp02/75/Energize-your-Unified-Communications-with-SIP-9-2048.jpg)