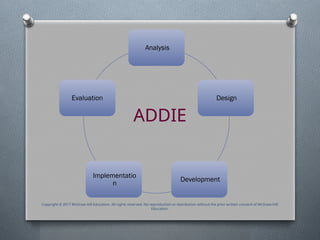
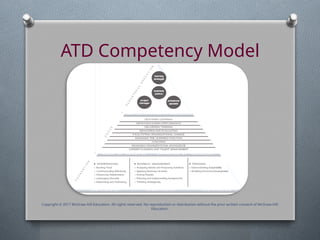
Behavioral training programs are designed to address a wide range of areas, including communication, problem-solving, conflict resolution, leadership, and teamwork. These programs utilize various techniques such as workshops, simulations, role-playing, and feedback sessions to facilitate the learning and application of new behaviors.