1) High-probability commands present a sequence of easy requests the learner can comply with before presenting a more difficult, low-probability command. This builds momentum and establishes responding.
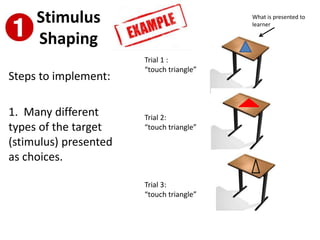
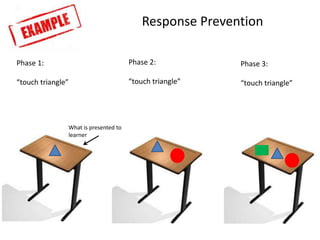
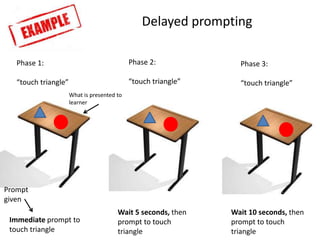
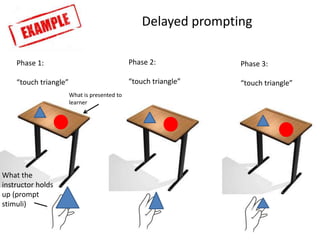
2) Errorless learning presents trials in a way that eliminates mistakes by using prompts and repeated exposure to the correct response. There are four types: stimulus shaping, response prevention, delayed prompting, and superimposition of stimulus fading.
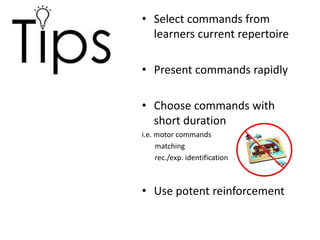
3) The steps to implement high-probability commands are to select easy commands, present them rapidly with reinforcement, then immediately present and reinforce a low-probability command. The steps to implement errorless learning techniques involve systematically fading prompts over time.