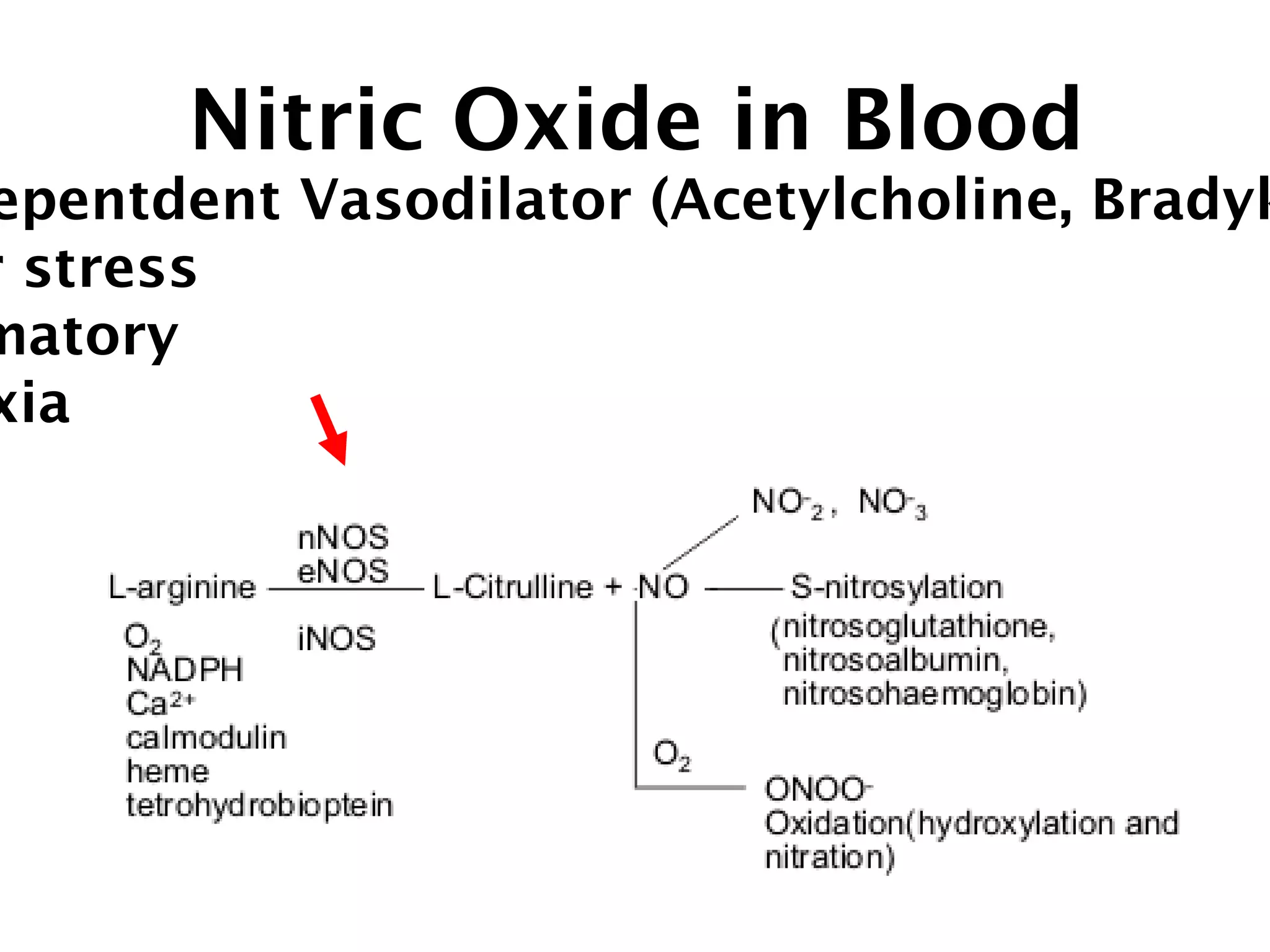
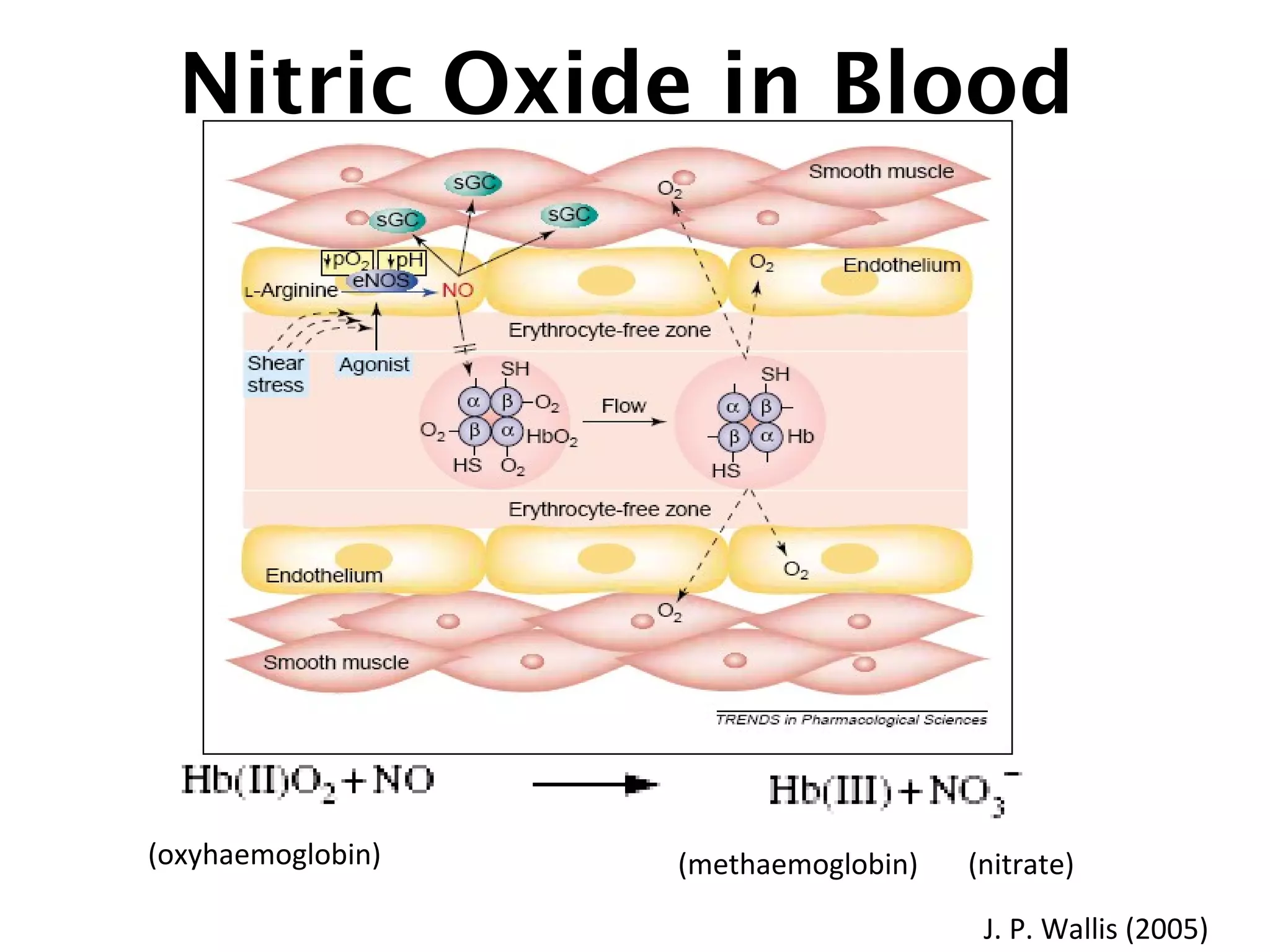
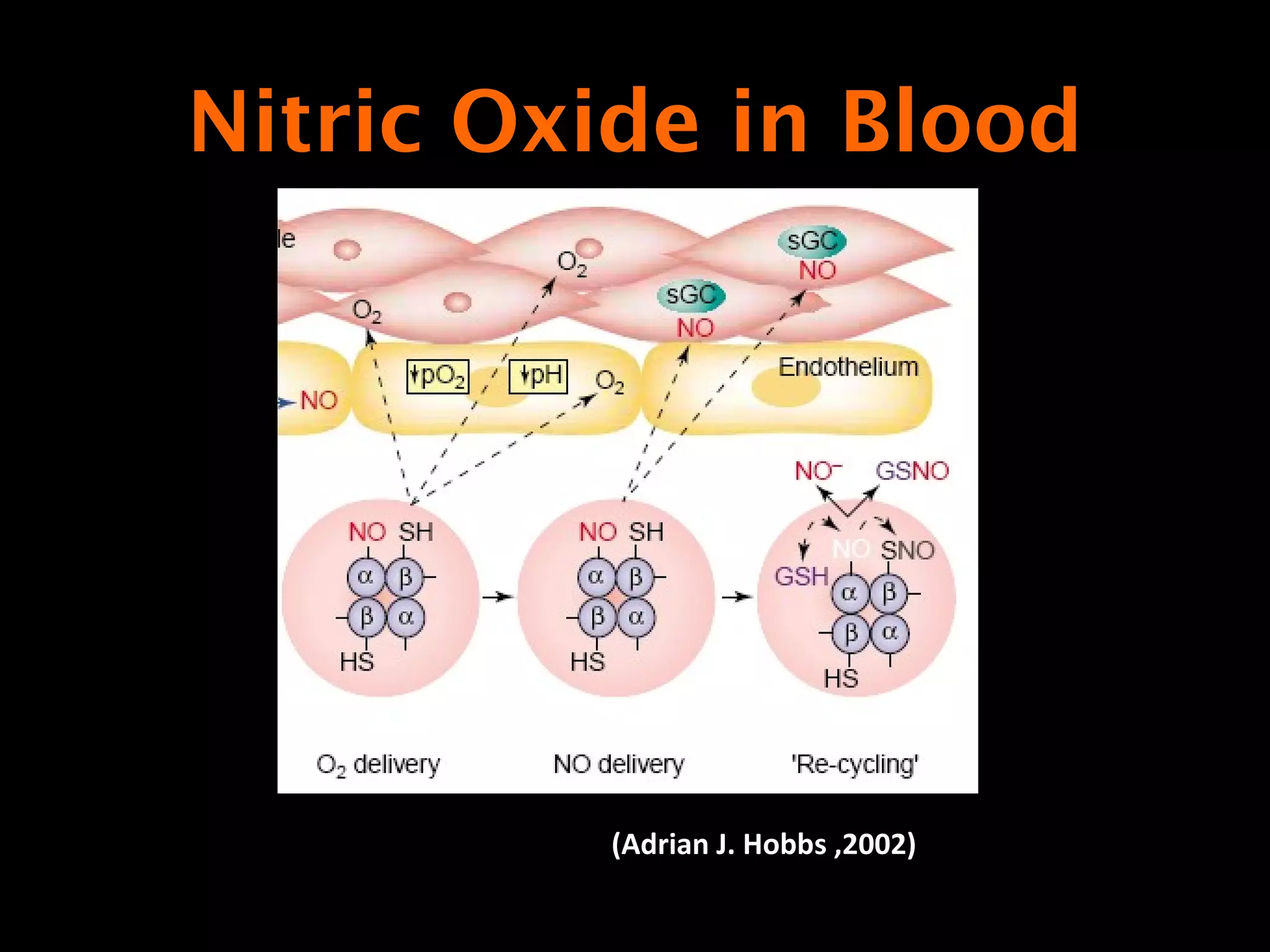
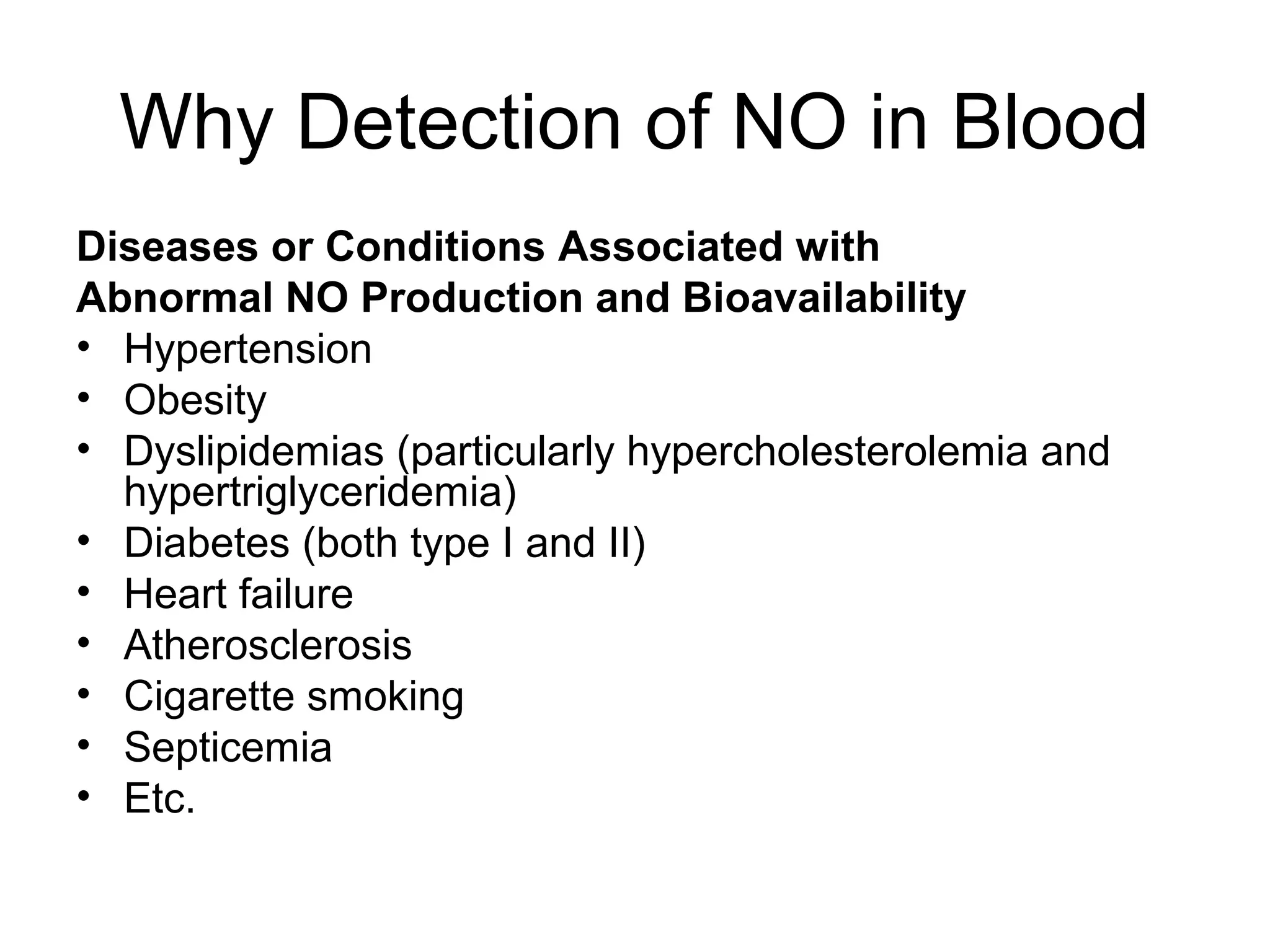
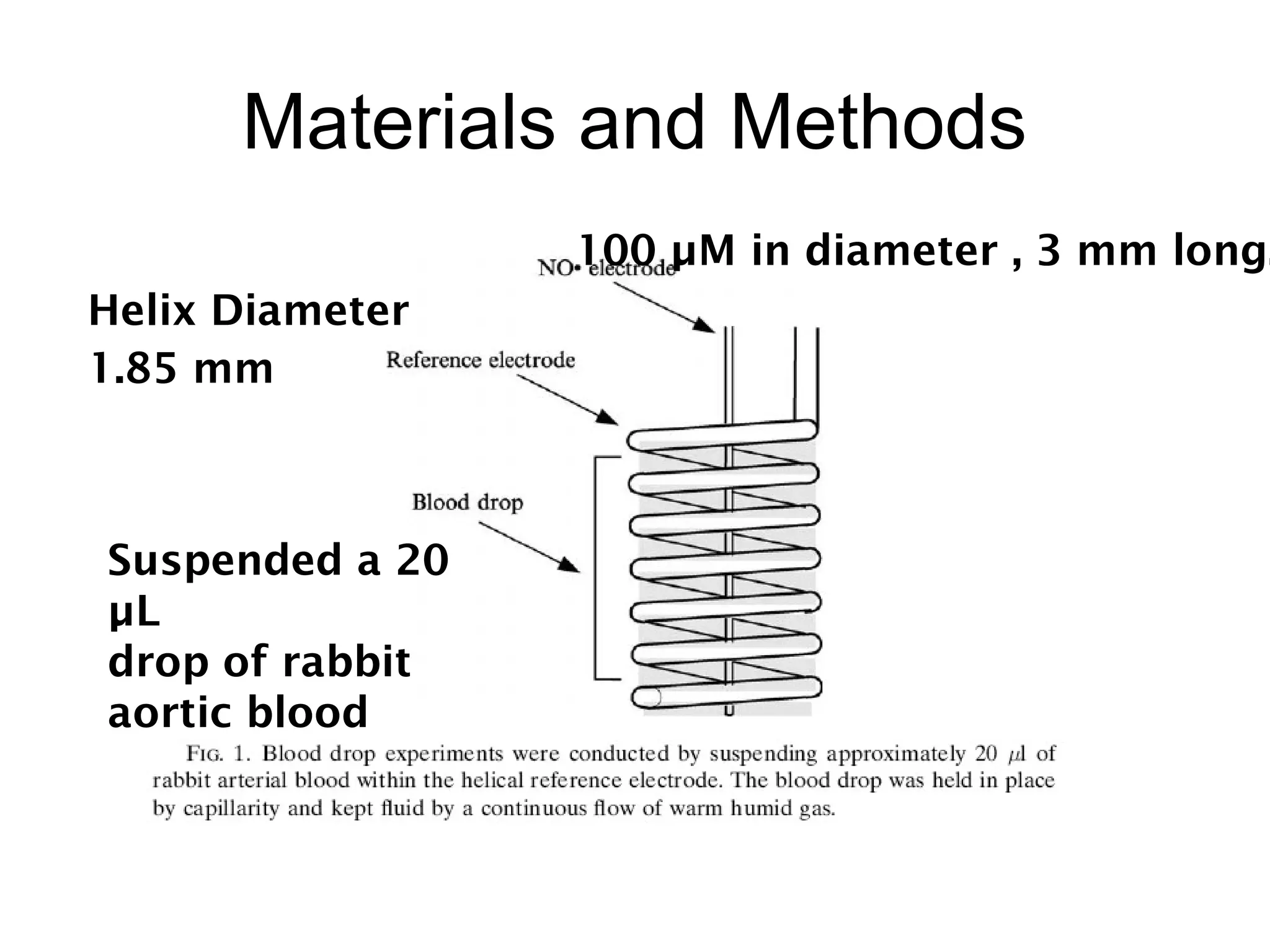
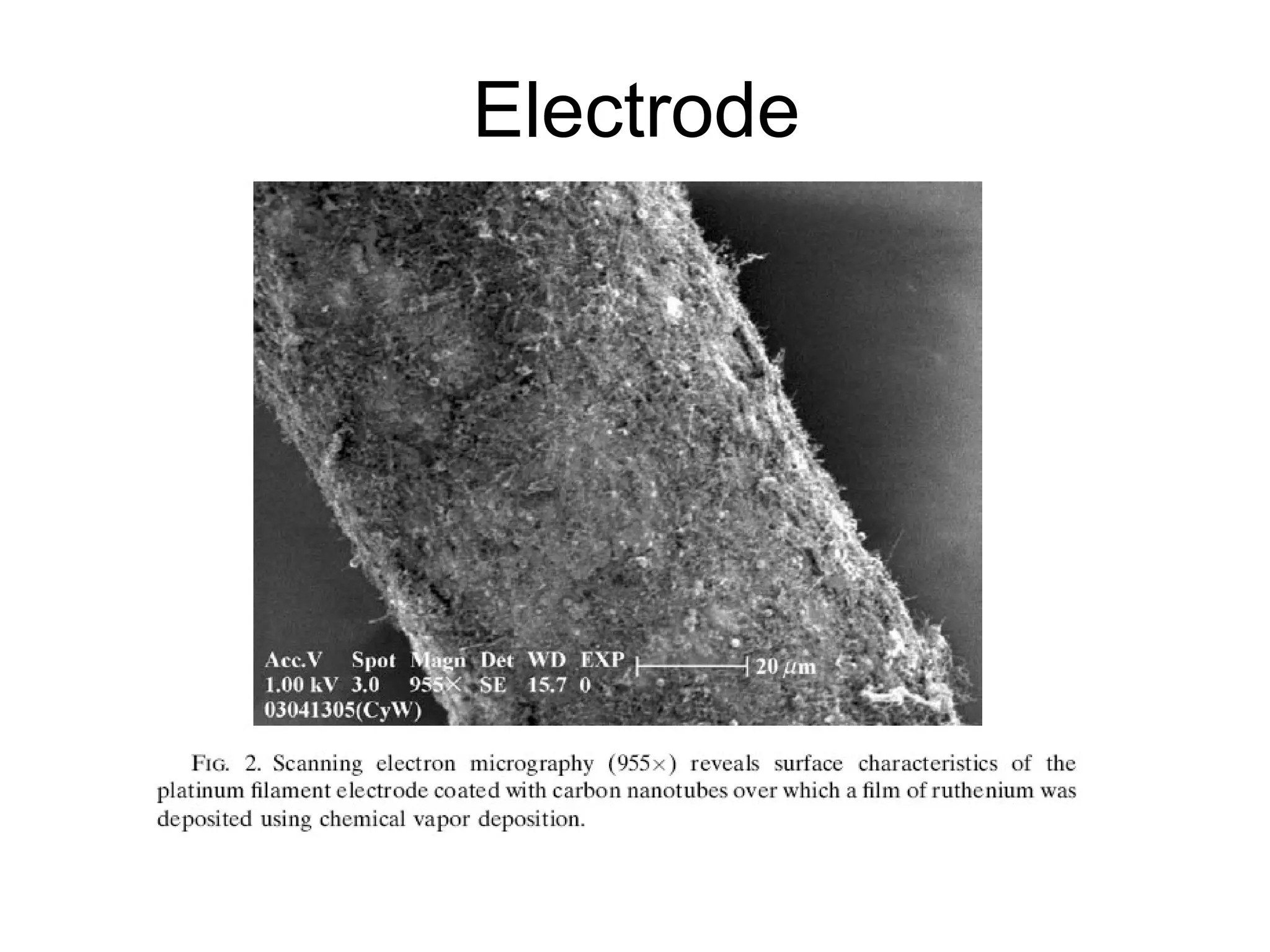
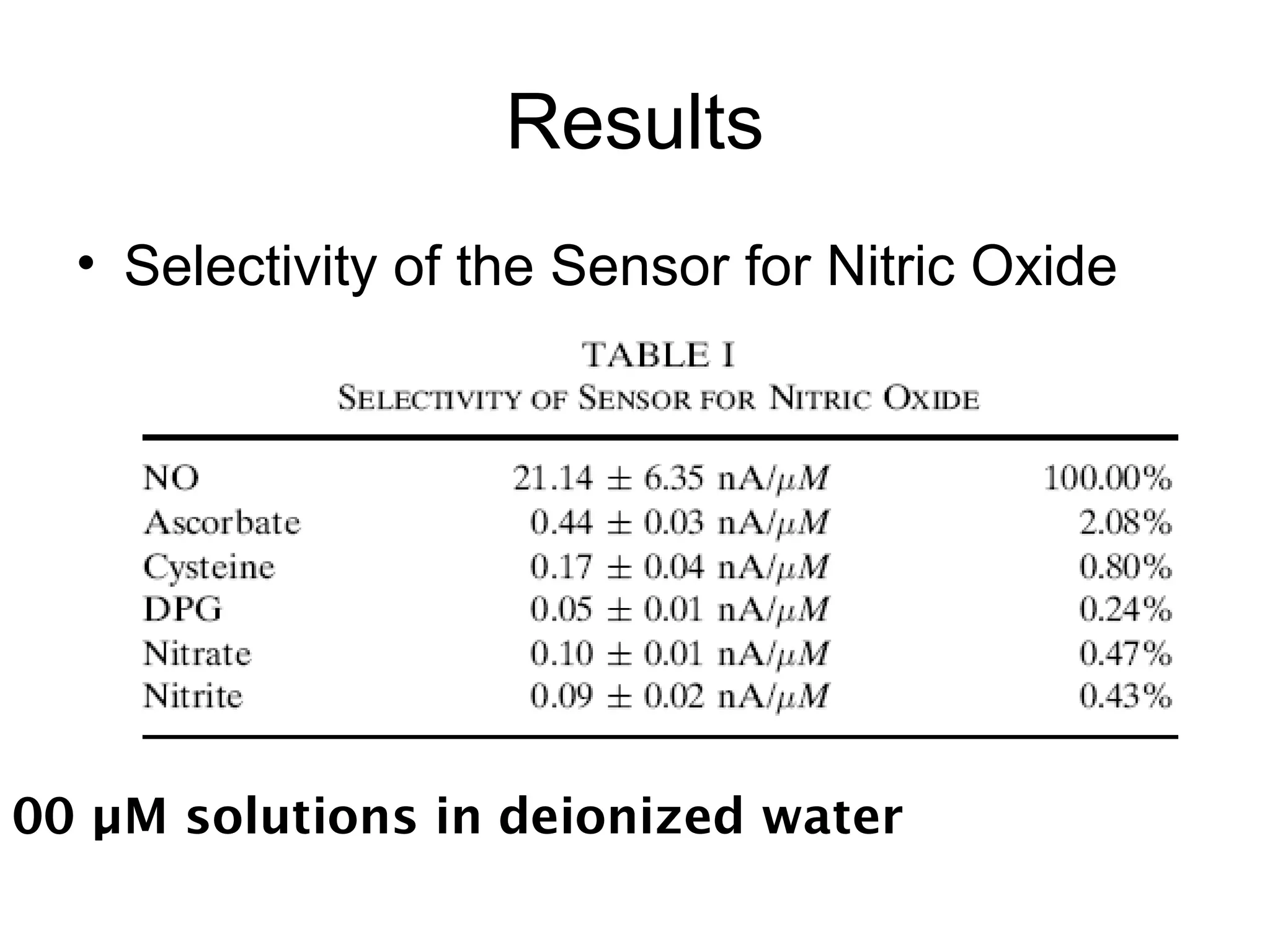
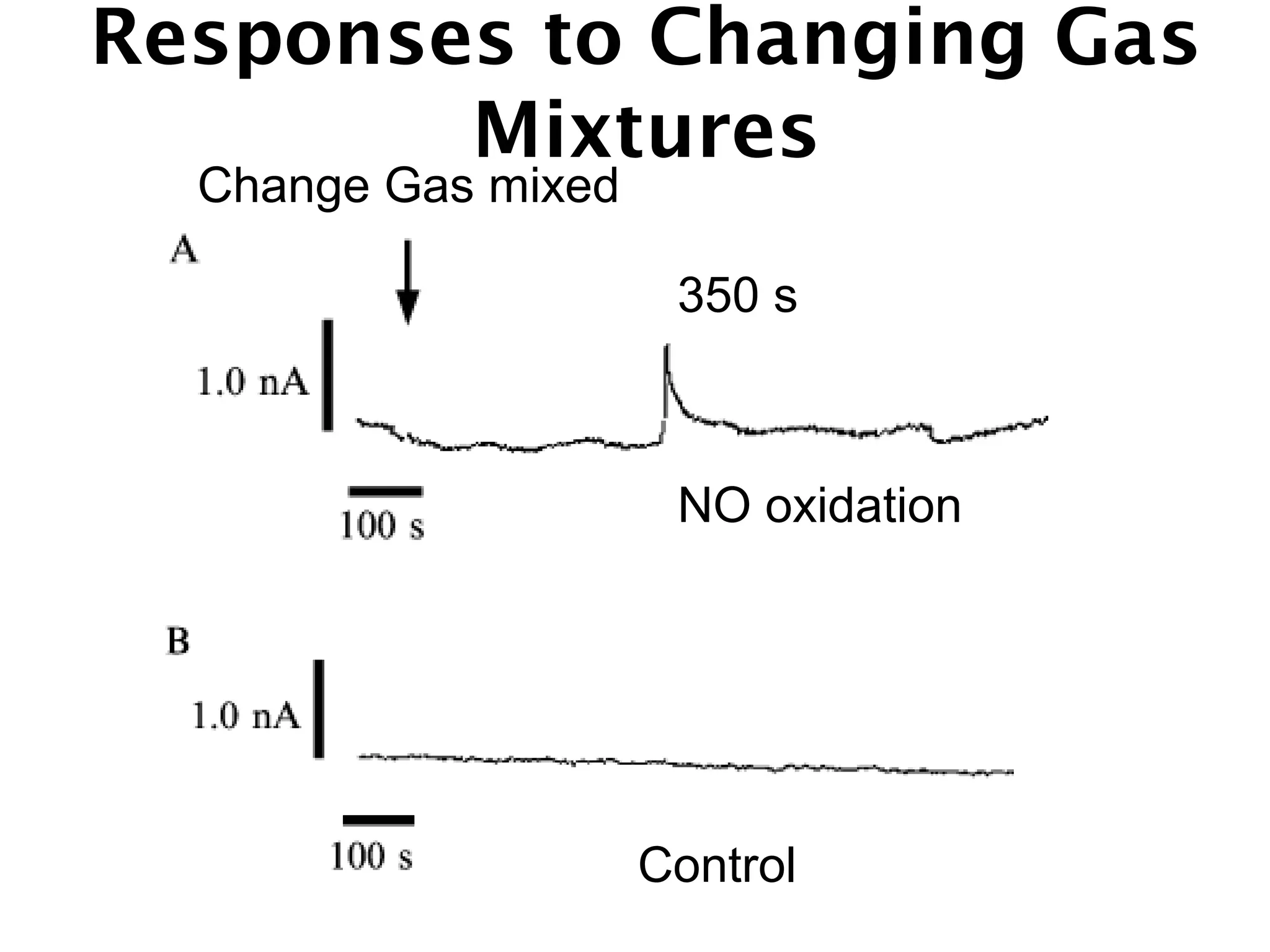
This document describes a method for electrochemically detecting nitric oxide (NO) in biological fluids using platinum wire electrodes coated with ruthenium and Nafion. Rabbit aortic blood was suspended in drops and exposed to changing gas mixtures. The electrodes detected NO oxidation signals 200-400 seconds after exposure to decreased oxygen, indicating NO release from blood cells in response to lower oxygen levels. While the study demonstrated sensitive NO detection, further validation is needed to confirm results using other methods and better control experimental conditions.