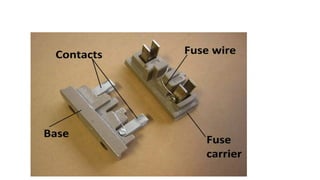
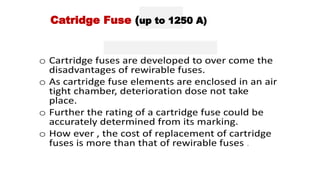
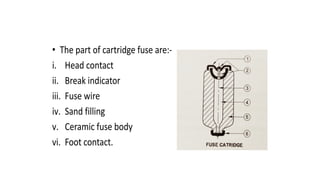
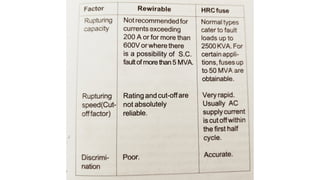
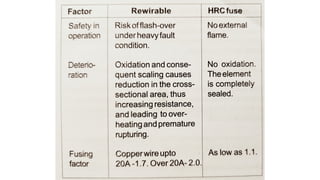
The document discusses protection devices in electric circuits, emphasizing their necessity to prevent damage from excess current. It specifically explains the characteristics of fuses, including fusing current, current rating, cut-off factor, and the materials used. Additionally, it categorizes cartridge fuses based on their rupturing capacity.