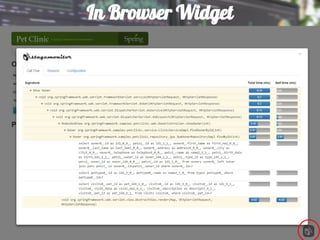
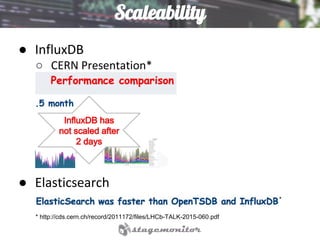
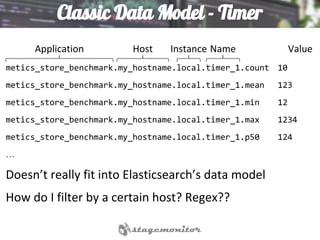
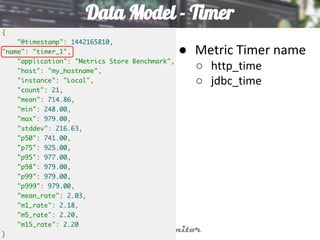
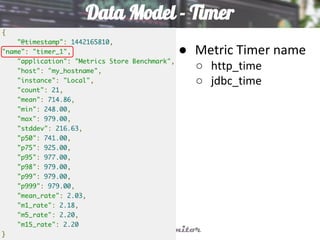
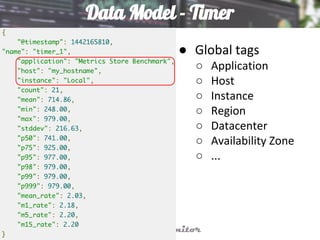
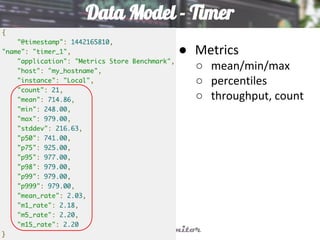
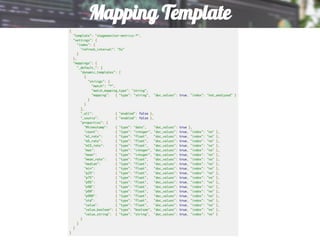
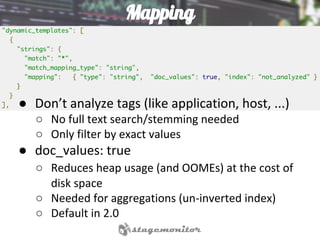
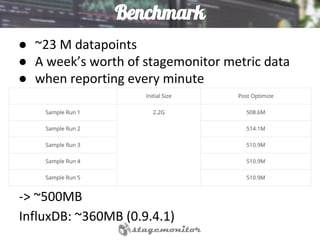
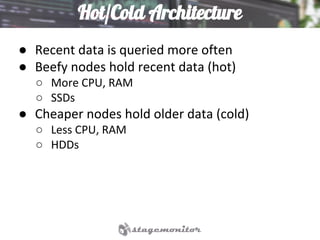
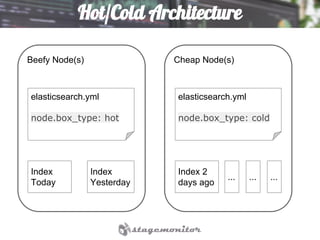
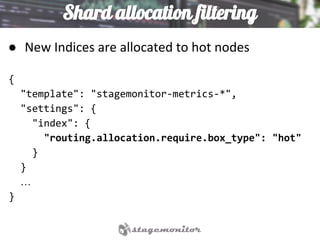
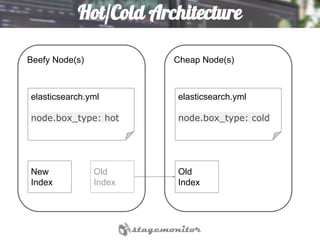
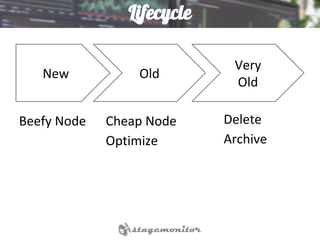
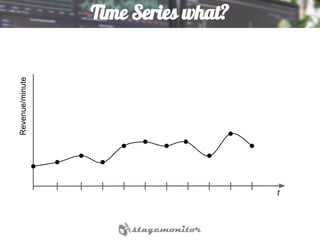This document discusses using Elasticsearch as a time series database. It covers why Elasticsearch was chosen over other options for storing metrics from the open source performance monitoring tool Stagemonitor. The document discusses Elasticsearch's ability to scale, its functions and visualization support in Kibana. It also covers how Stagemonitor's data is modeled in Elasticsearch, including the use of tags, and how index management is handled through a hot/cold node architecture and tools like Curator.