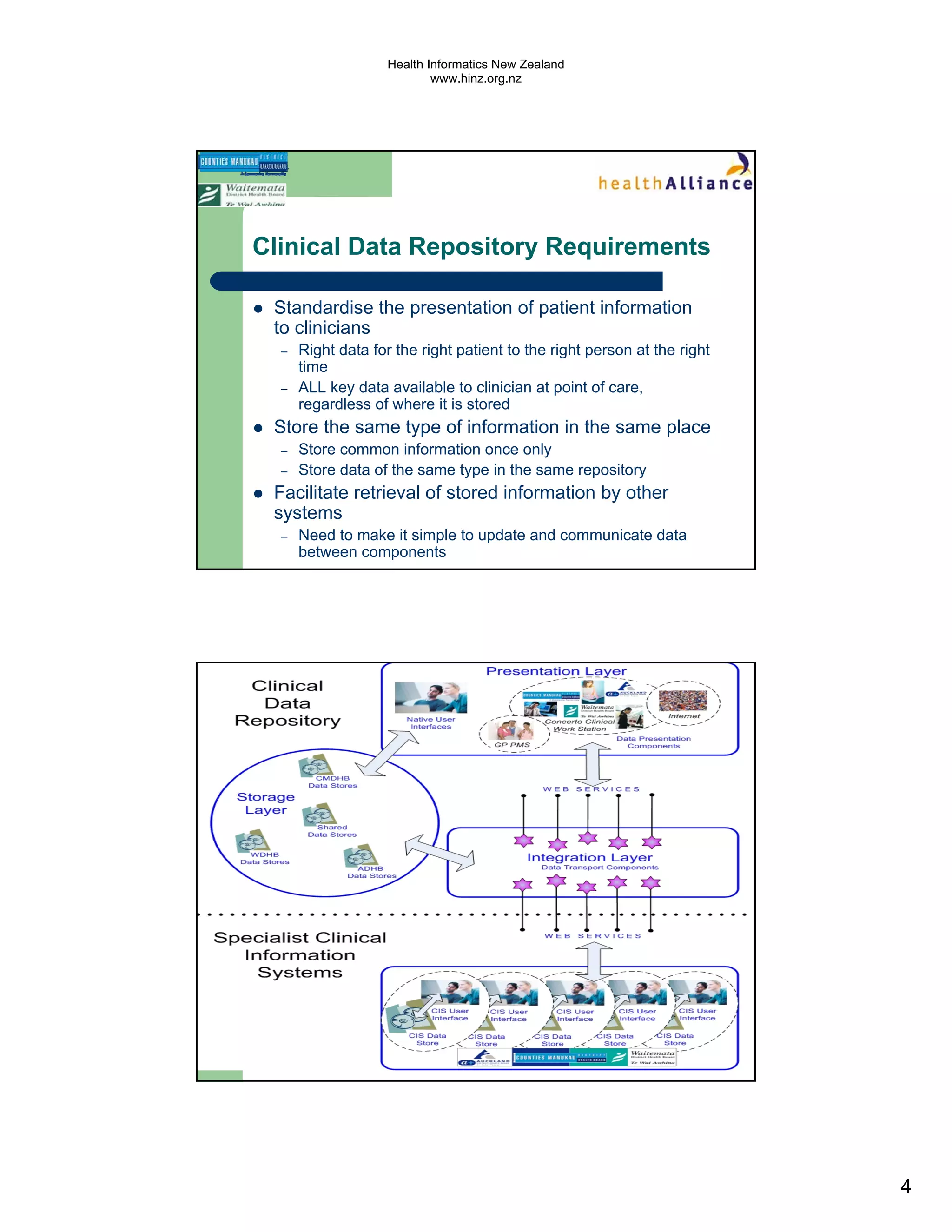
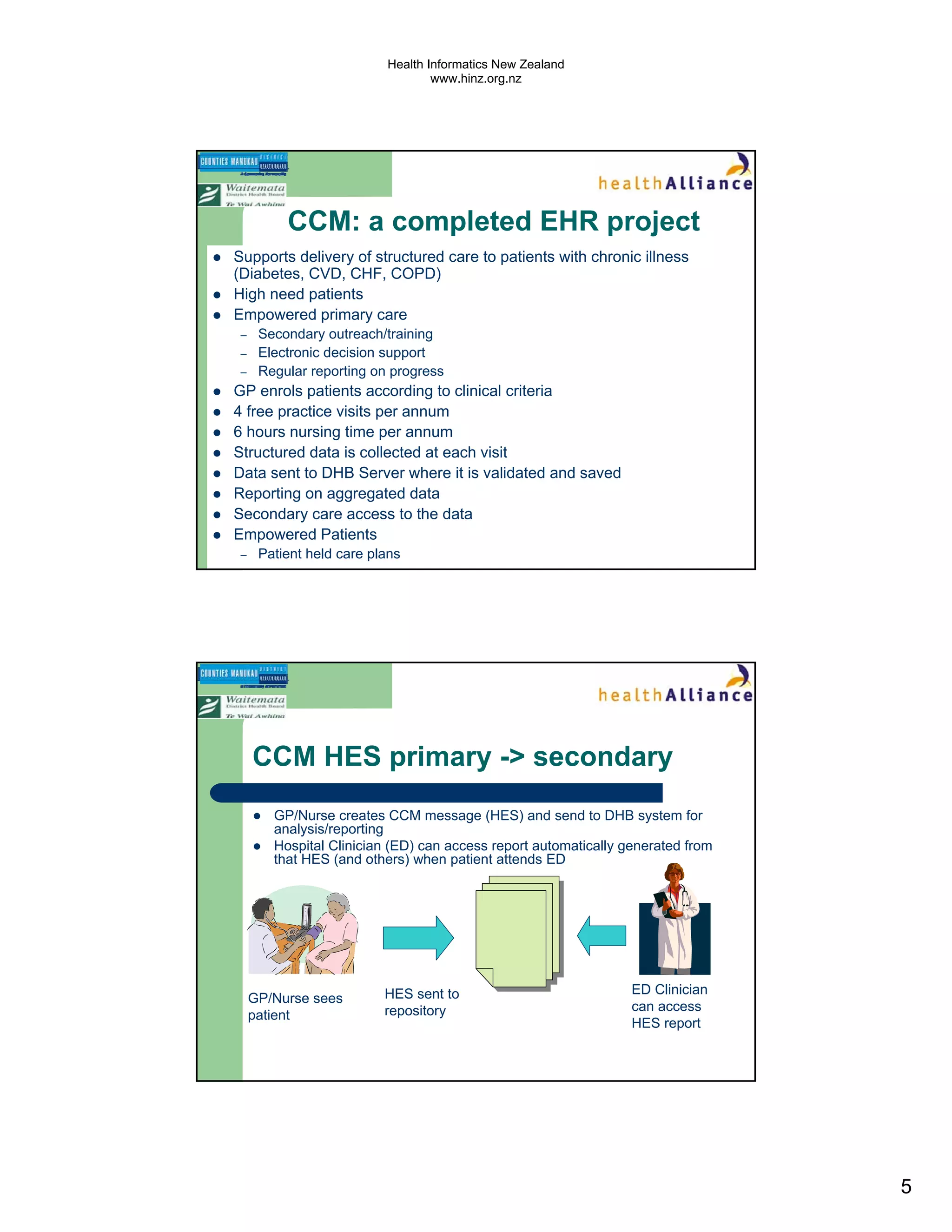
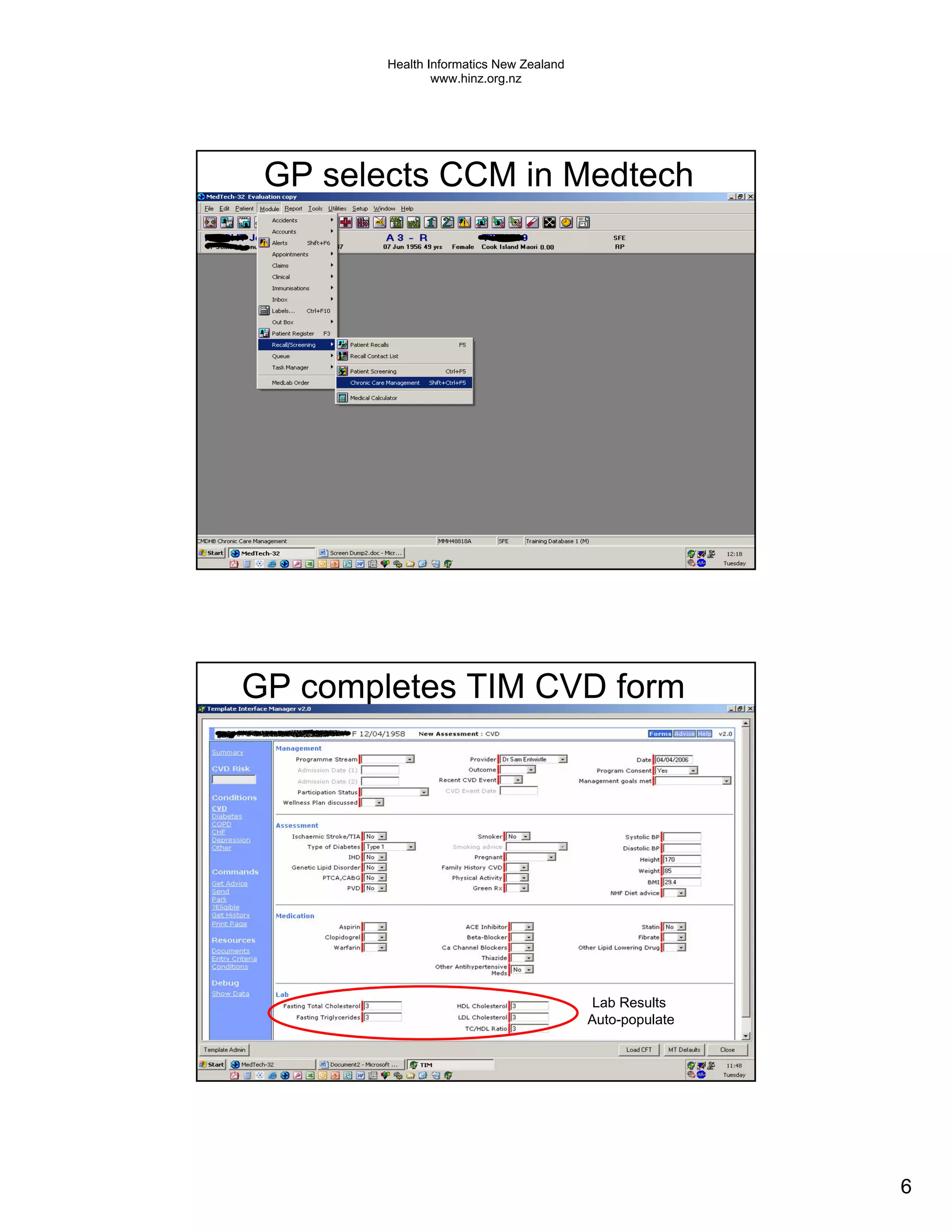
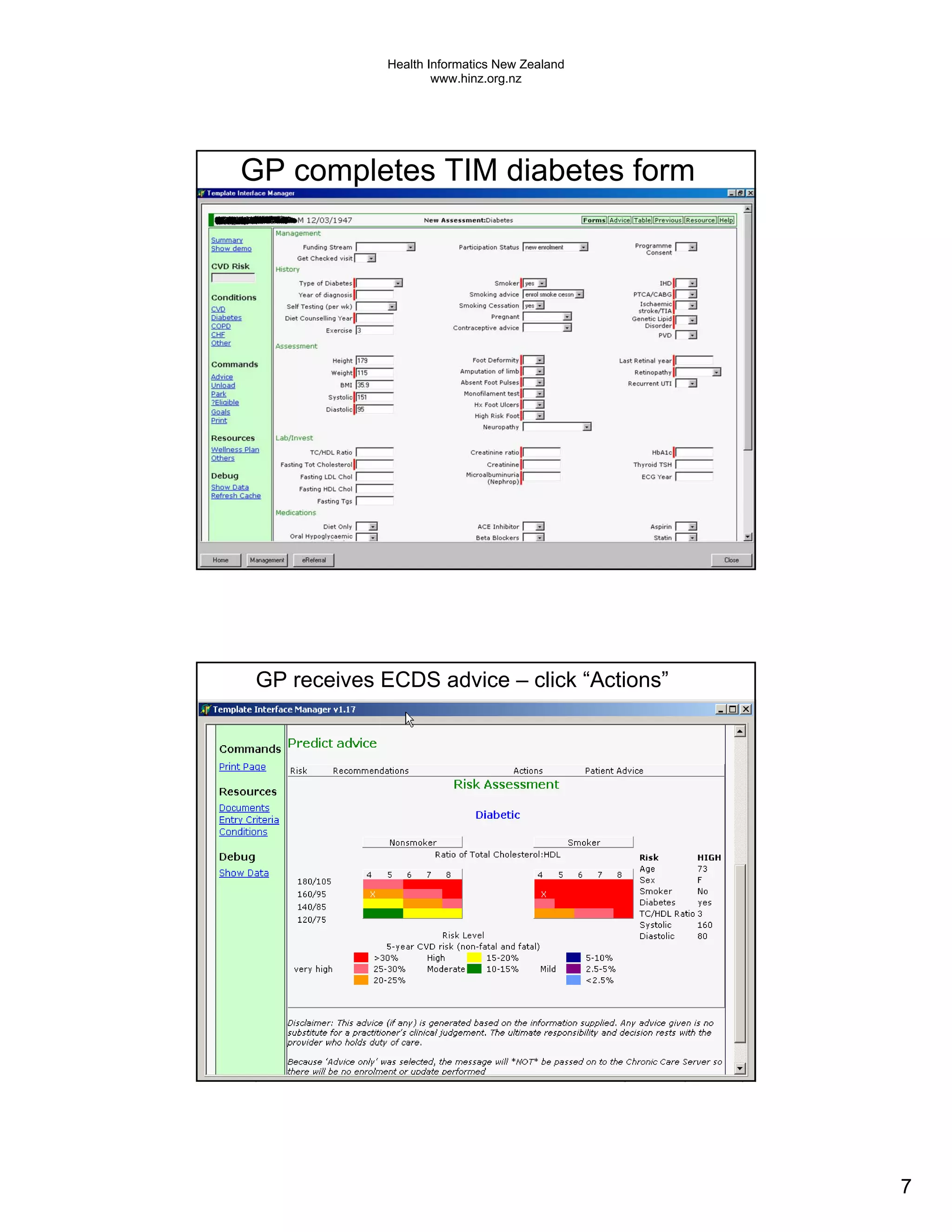
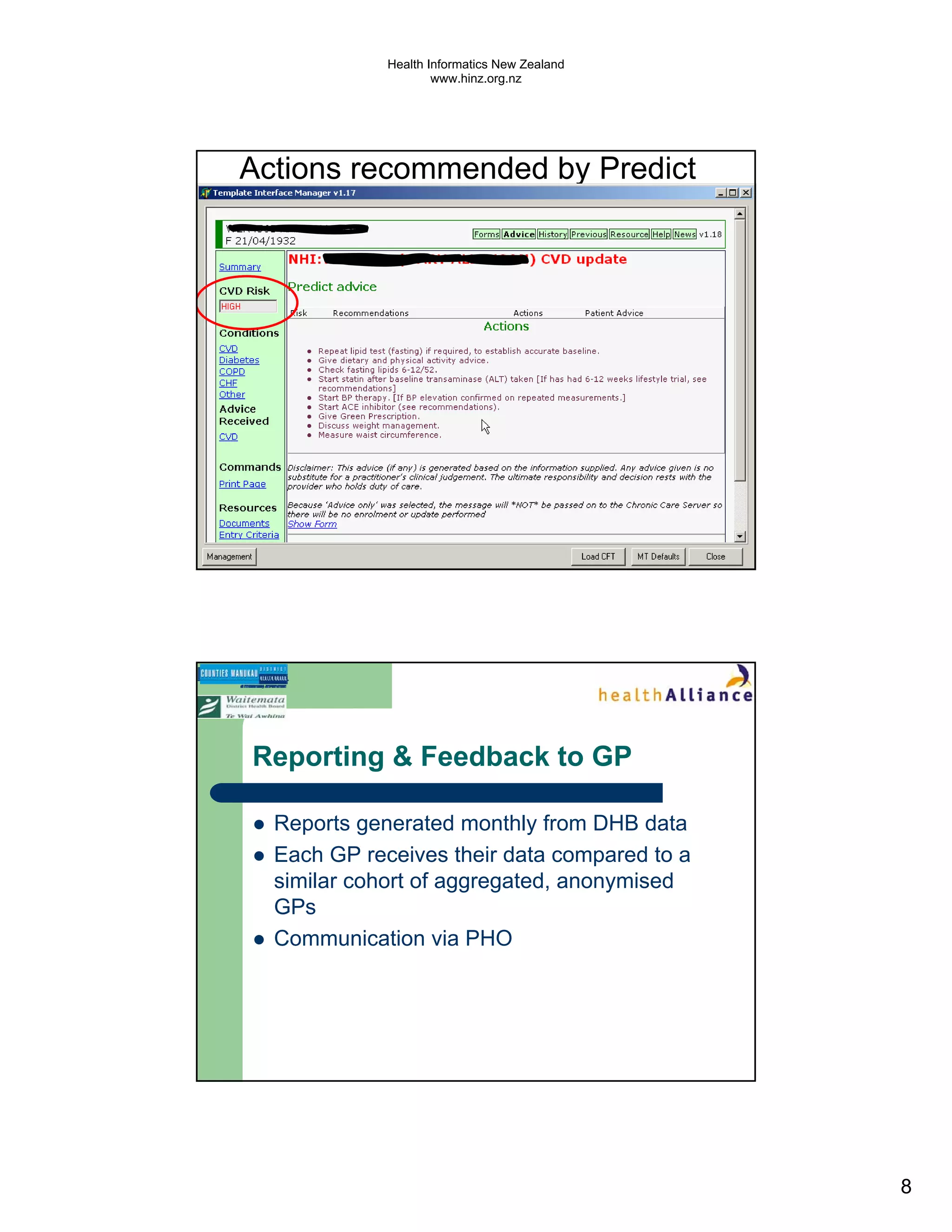
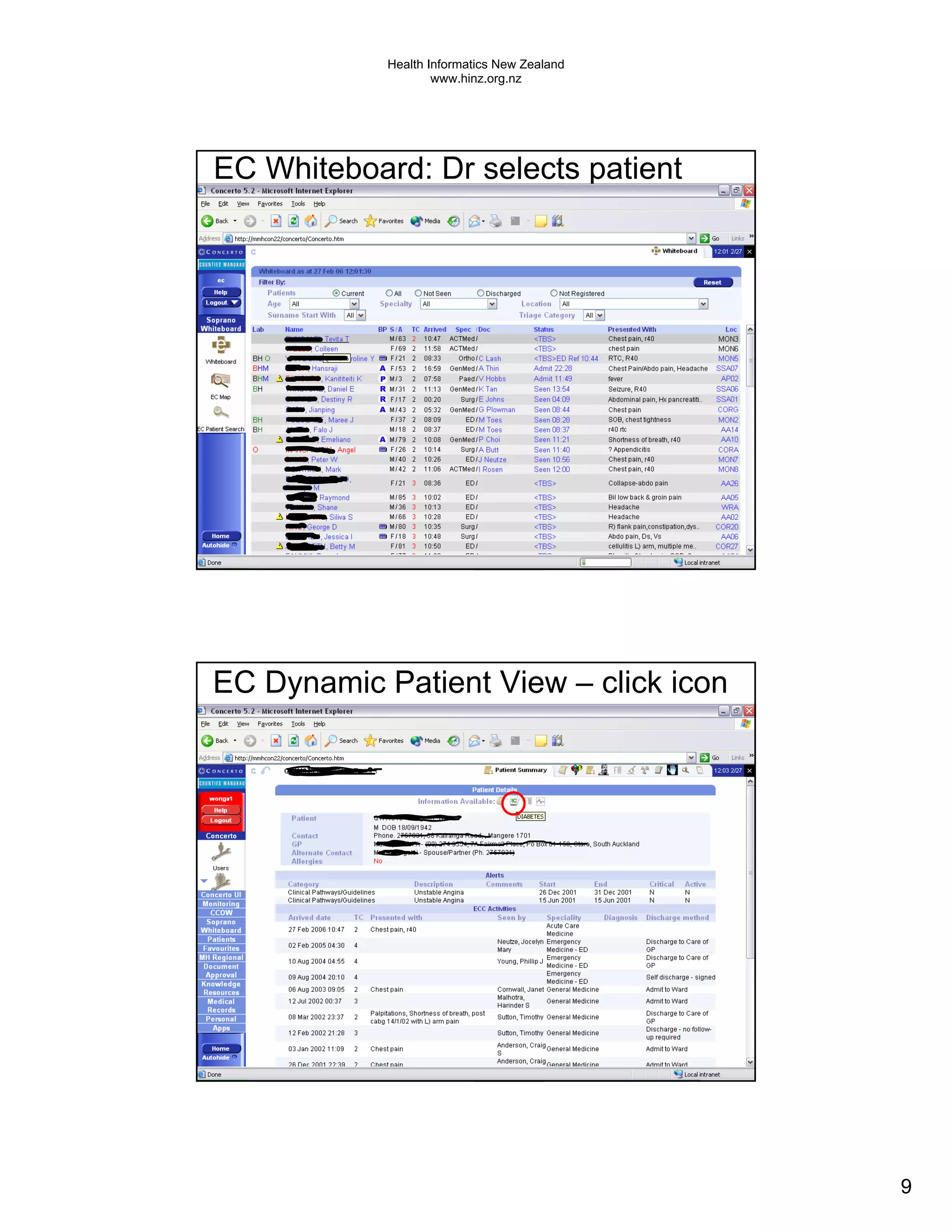
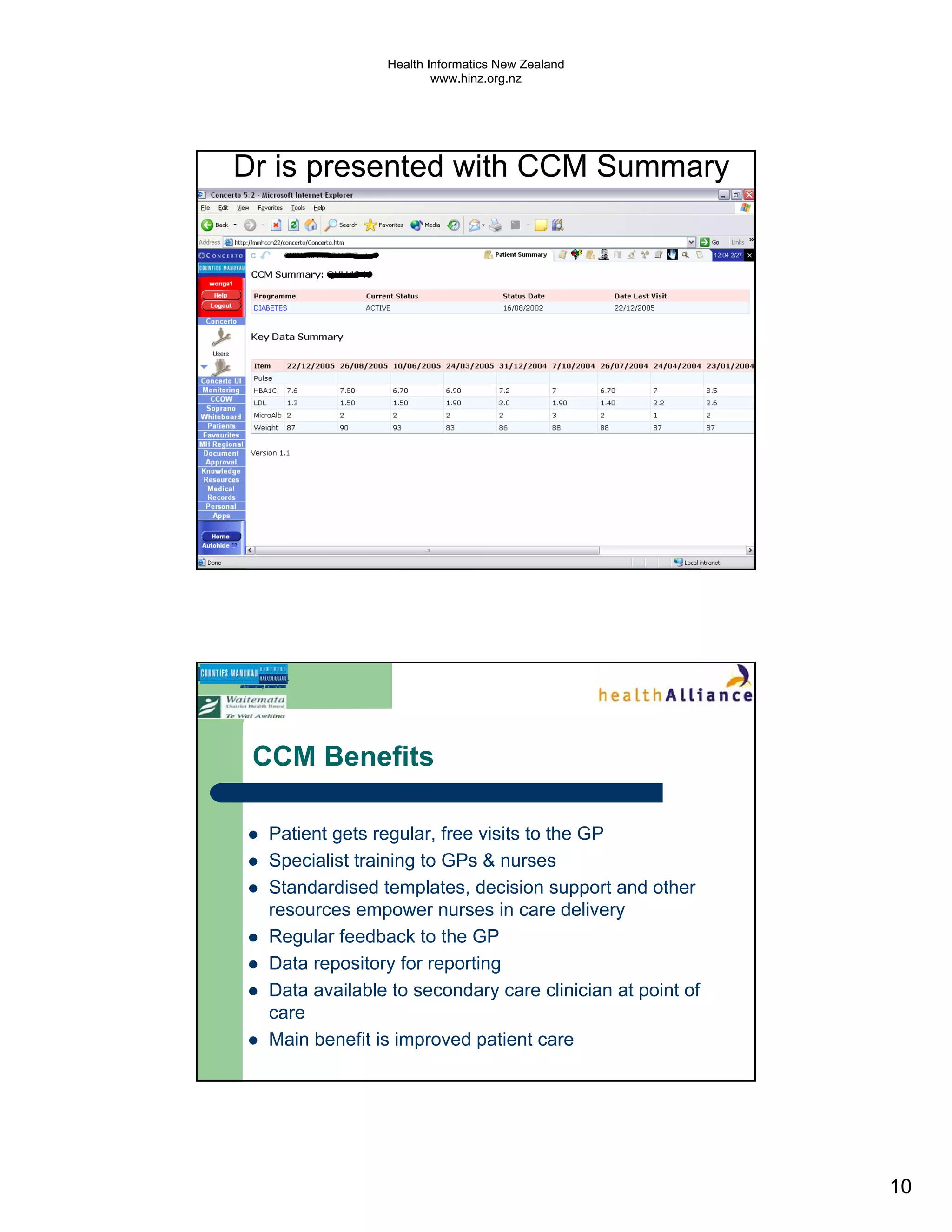
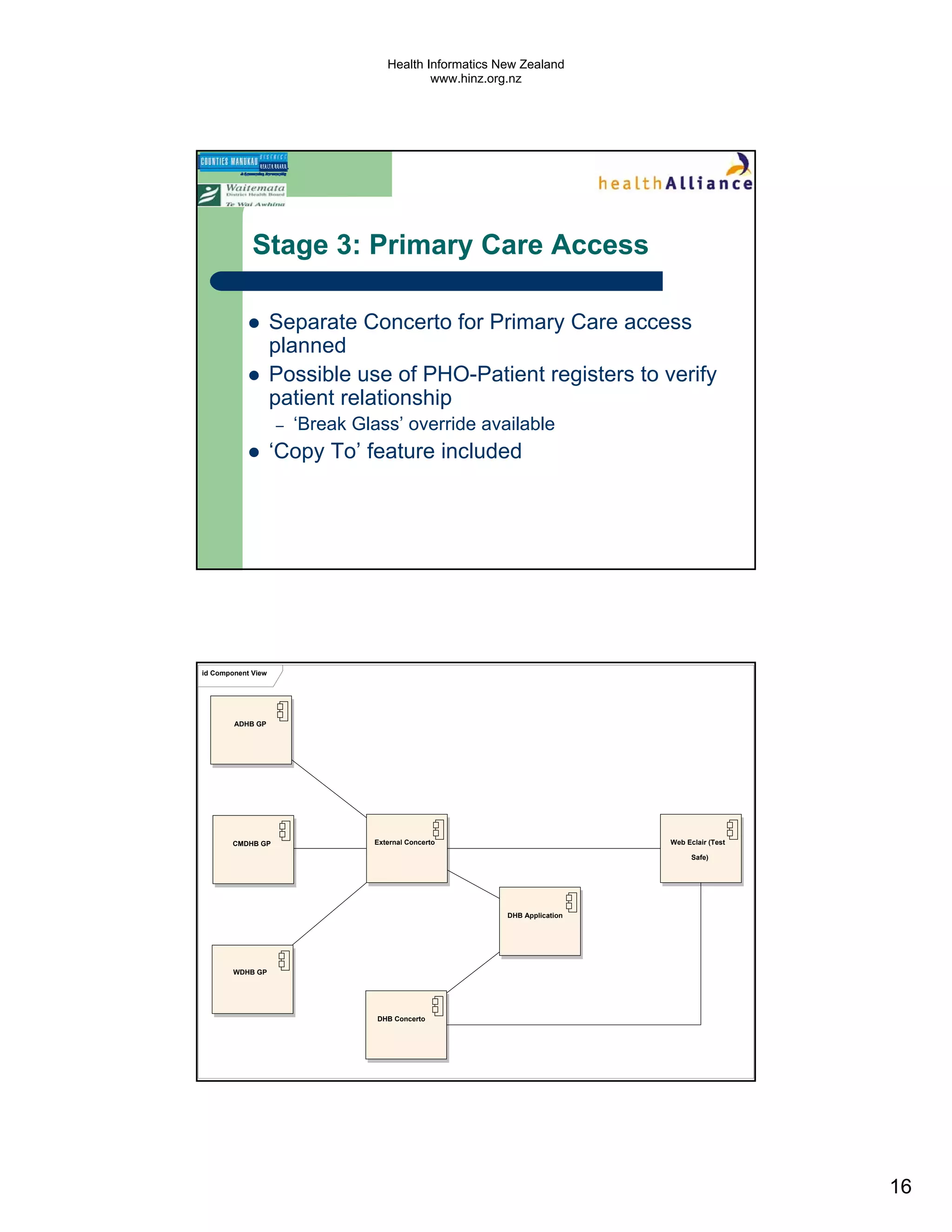
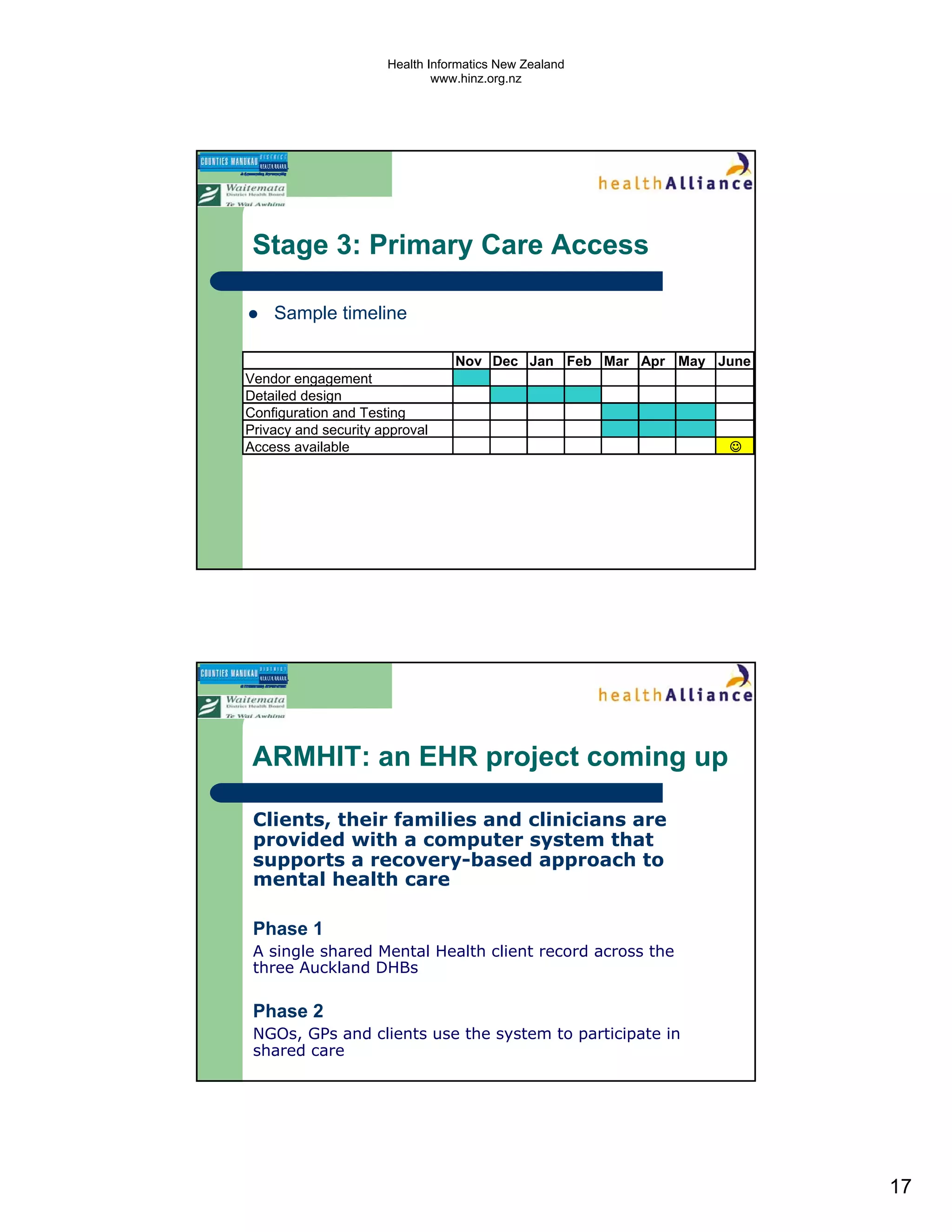
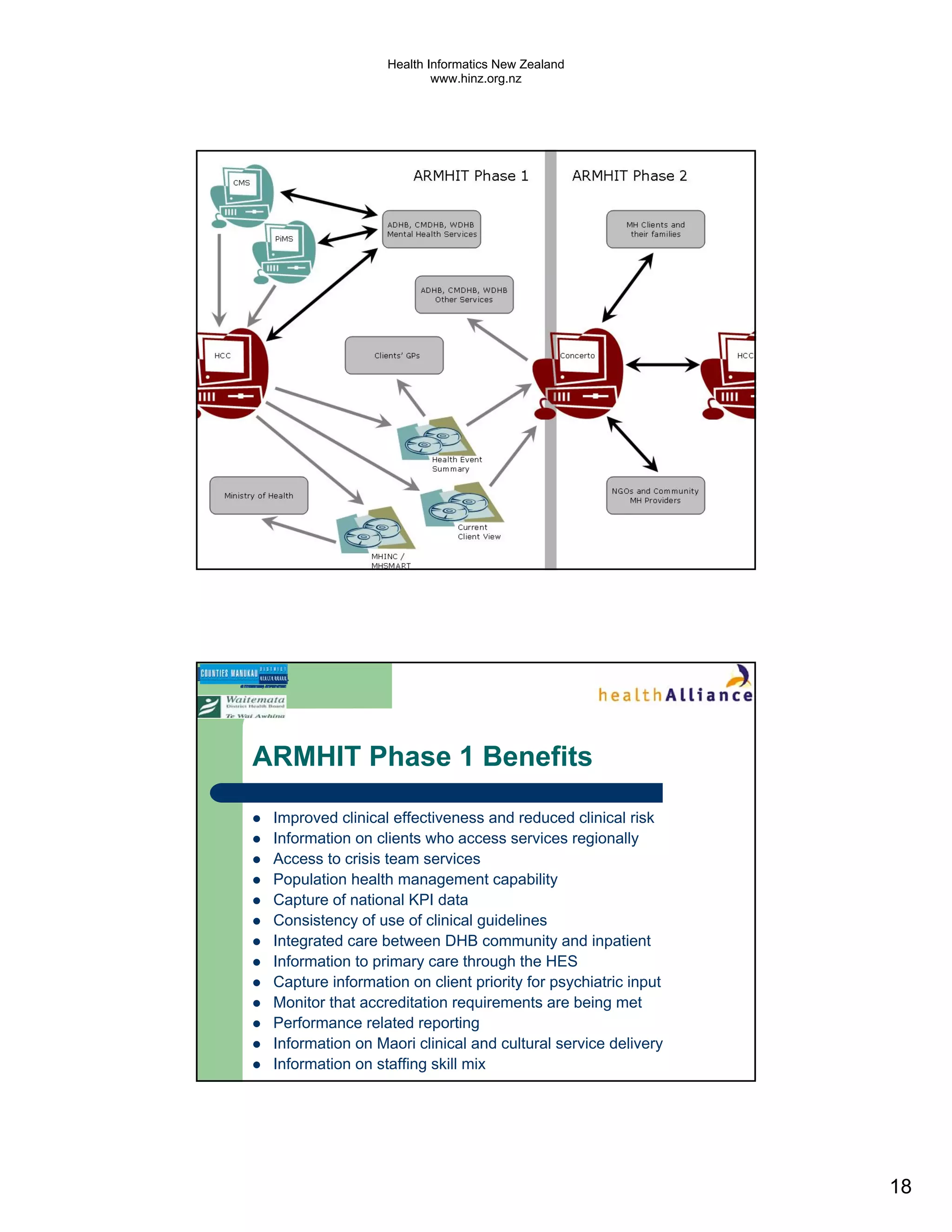
The document discusses several electronic health record projects in Auckland, New Zealand. It describes the Chronic Care Management project, which supports structured care for patients with chronic illnesses through electronic tools. It also outlines the TestSafe project, which aims to give clinicians access to all laboratory test results for their patients across multiple healthcare organizations. Finally, it discusses plans for the ARMHIT project to create a single shared mental health record across three Auckland District Health Boards.