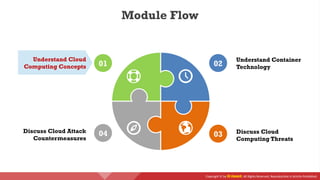
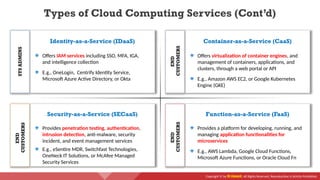
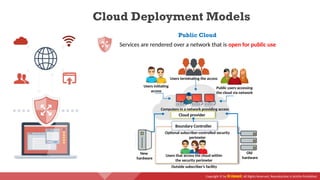
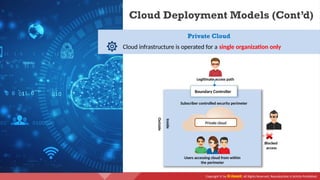
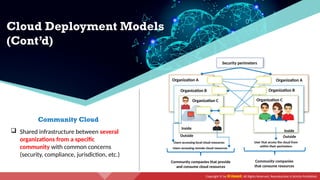
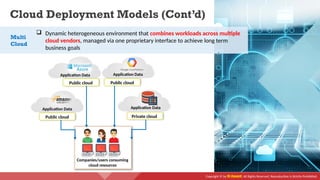
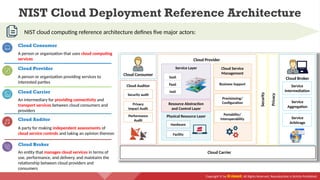
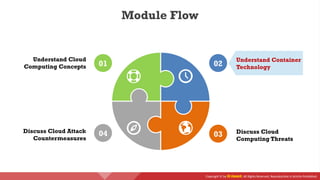
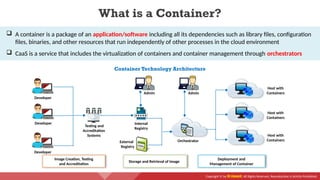
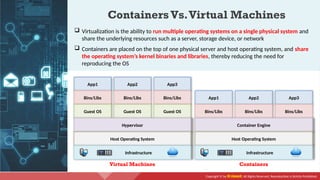
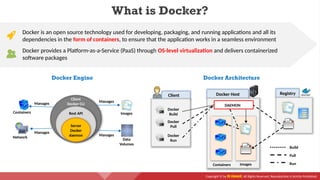
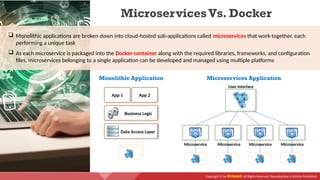
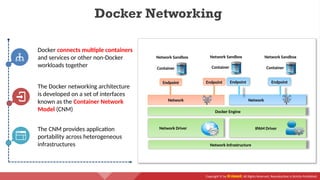
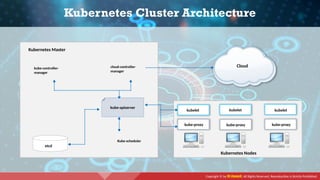
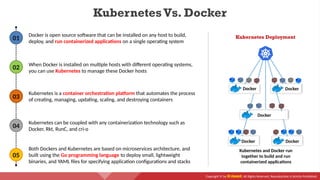
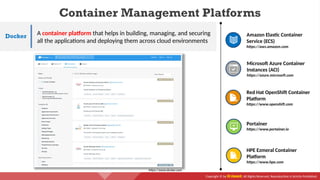
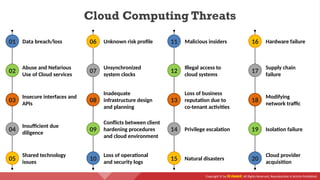
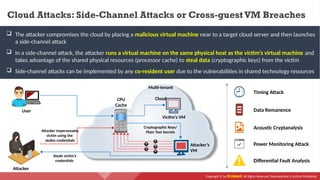
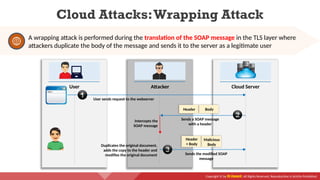
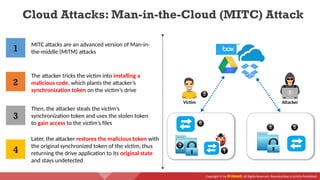
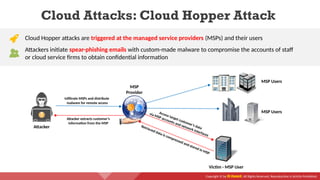
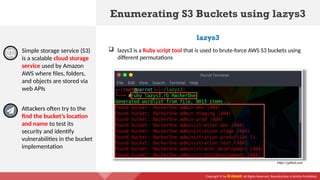
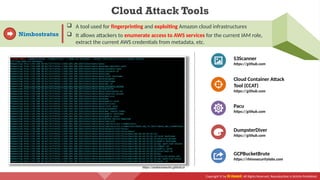
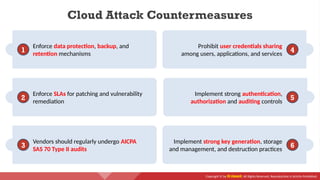
The document provides an overview of cloud computing concepts, including various service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) and deployment models (public, private, hybrid). It discusses threats and countermeasures associated with cloud computing, emphasizing the importance of security tools and practices in managing cloud environments. Additionally, it highlights container technology and orchestration platforms like Docker and Kubernetes for managing applications in the cloud.