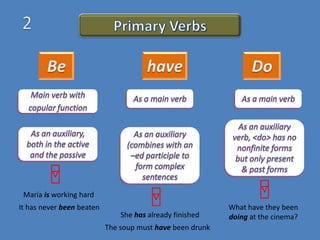
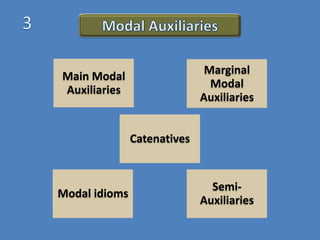
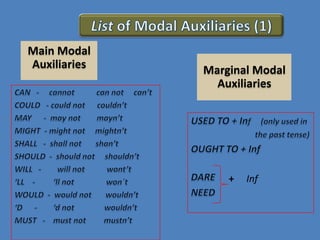
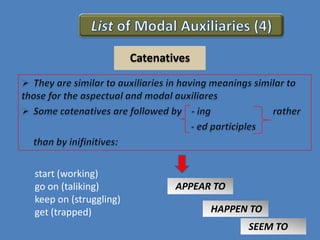
This document discusses different verb classes in English grammar. It defines a verb as having two main senses: as a finite verb in clauses like "she calls" and as a nonfinite verb in constructions like "to call". It then explains the different verb forms - the base form, third person -s form, past/-ed form, and -ing participle. These forms serve different functions in finite and nonfinite verb phrases. The document also discusses main modal auxiliaries, marginal modal auxiliaries, modal idioms, catenatives, and semi-auxiliaries. It provides examples and notes about the uses of different types of verbs.