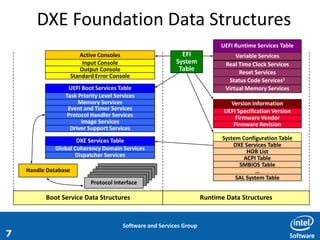
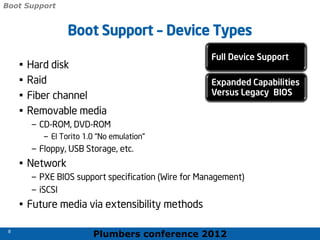
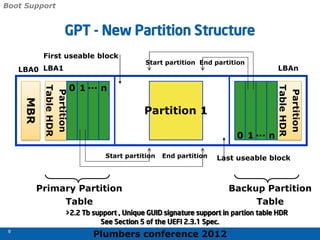
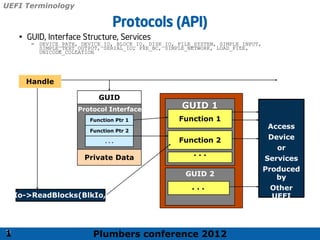
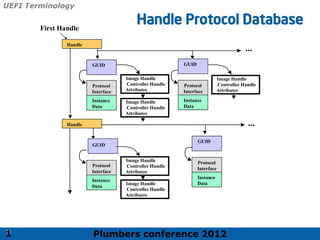
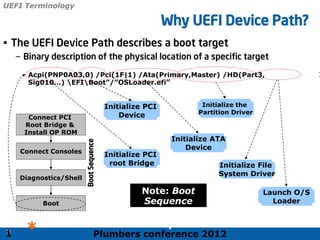
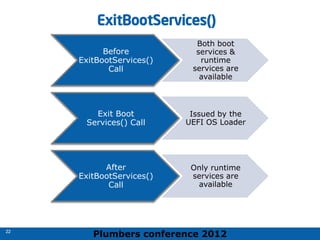
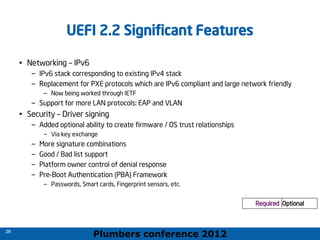
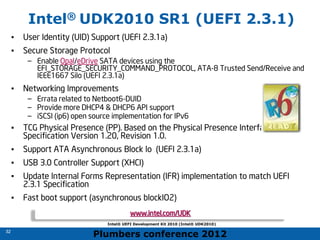
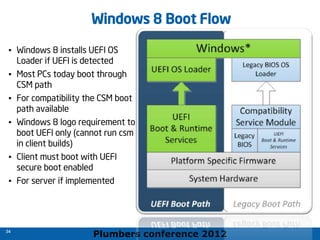
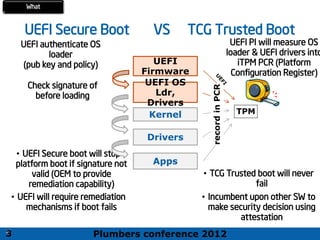
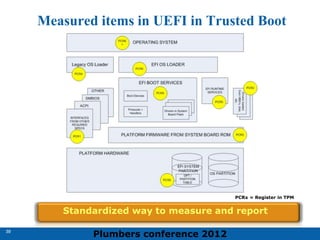
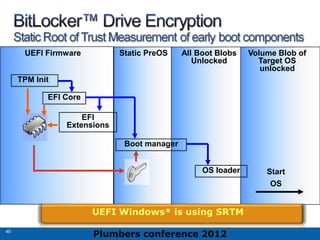
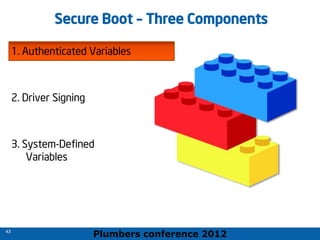
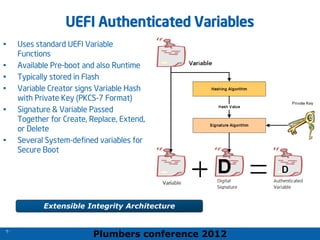
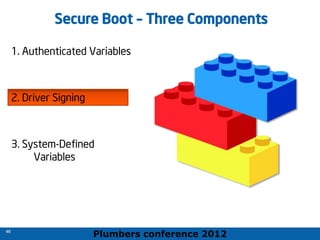
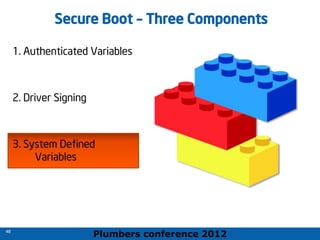
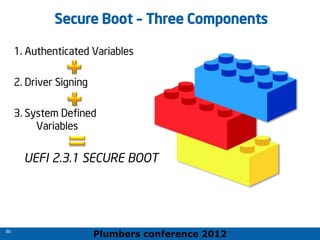
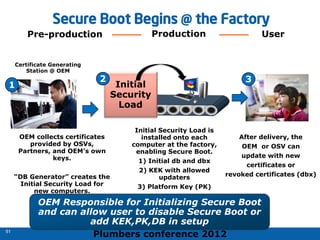
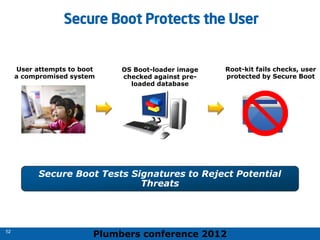
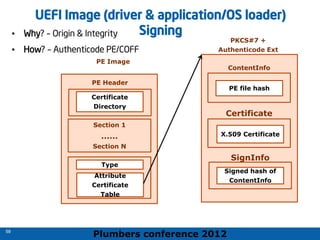
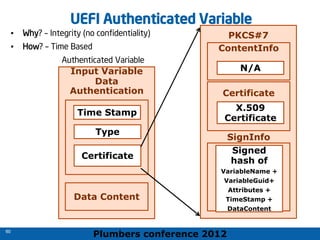
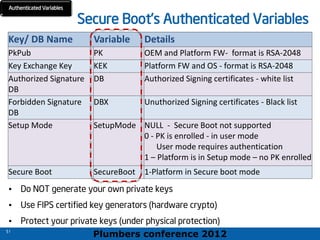
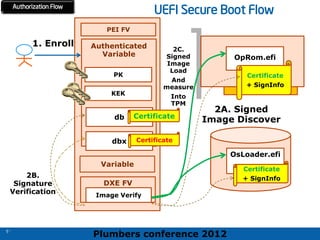
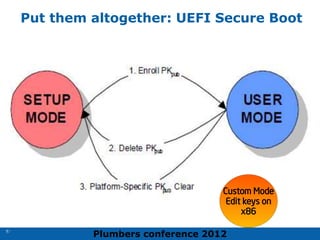
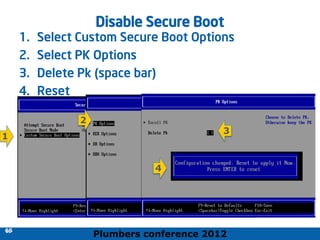
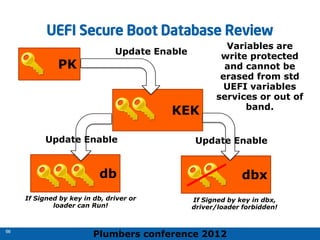
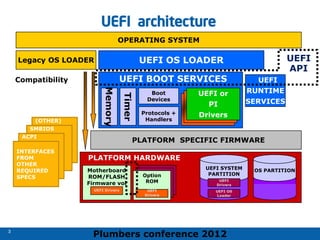
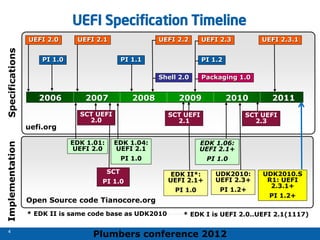
The 2012 Plumbers Conference presented a tutorial on UEFI, covering its basics, security features, and development platforms, alongside a detailed exploration of UEFI architecture and boot services. The conference highlighted UEFI's advantages over legacy BIOS, including improved partitioning and support for advanced features like secure boot. Key UEFI specifications and timeline updates were discussed, emphasizing the transition to UEFI 2.3.1 and its significance in supporting modern operating systems like Windows 8.



![Plumbers conference 2012
6
6
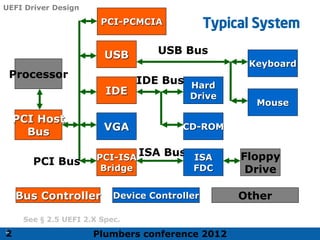
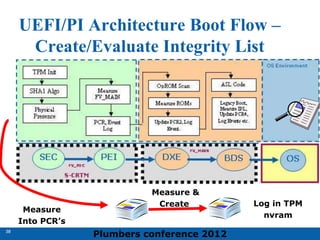
Architecture Execution Flow
6
Pre EFI
Initializati
on (PEI)
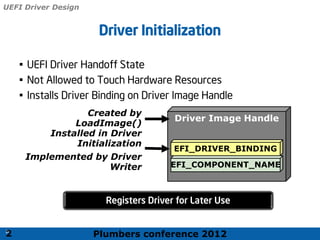
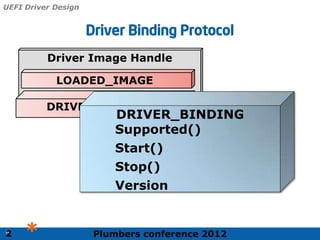
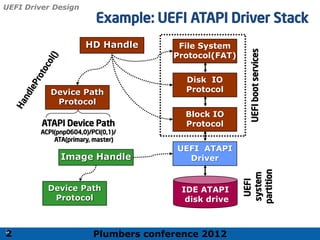
Driver
Execution
Environment
(DXE)
Boot
Dev
Select
(BDS)
Transient
System Load
(TSL)
After
Life
(AL)
Power
on
[ . . Platform initialization . . ] [ . . . . OS boot . . . . ] Shutdown
Run Time
(RT)
?
OS-Present
App
Final OS
Environment
Final OS
Boot Loader
OS-Absent
App
Transient OS
Environment
Transient OS
Boot Loader
Boot
Manager
Proces
sor
Init
Chipse
t Init
Board
Init
verif
y
Device,
Bus, or
Service
Driver
UEFI
Interface
Pre
Verifier
EFI Driver
Dispatcher
Intrinsic
Services
Security
(SEC)
Boot Execution Flow](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/efiarchitecturetutorial-241030194904-f47c098e/85/EFI-Architecture-tutorial-related-to-UEFI-6-320.jpg)