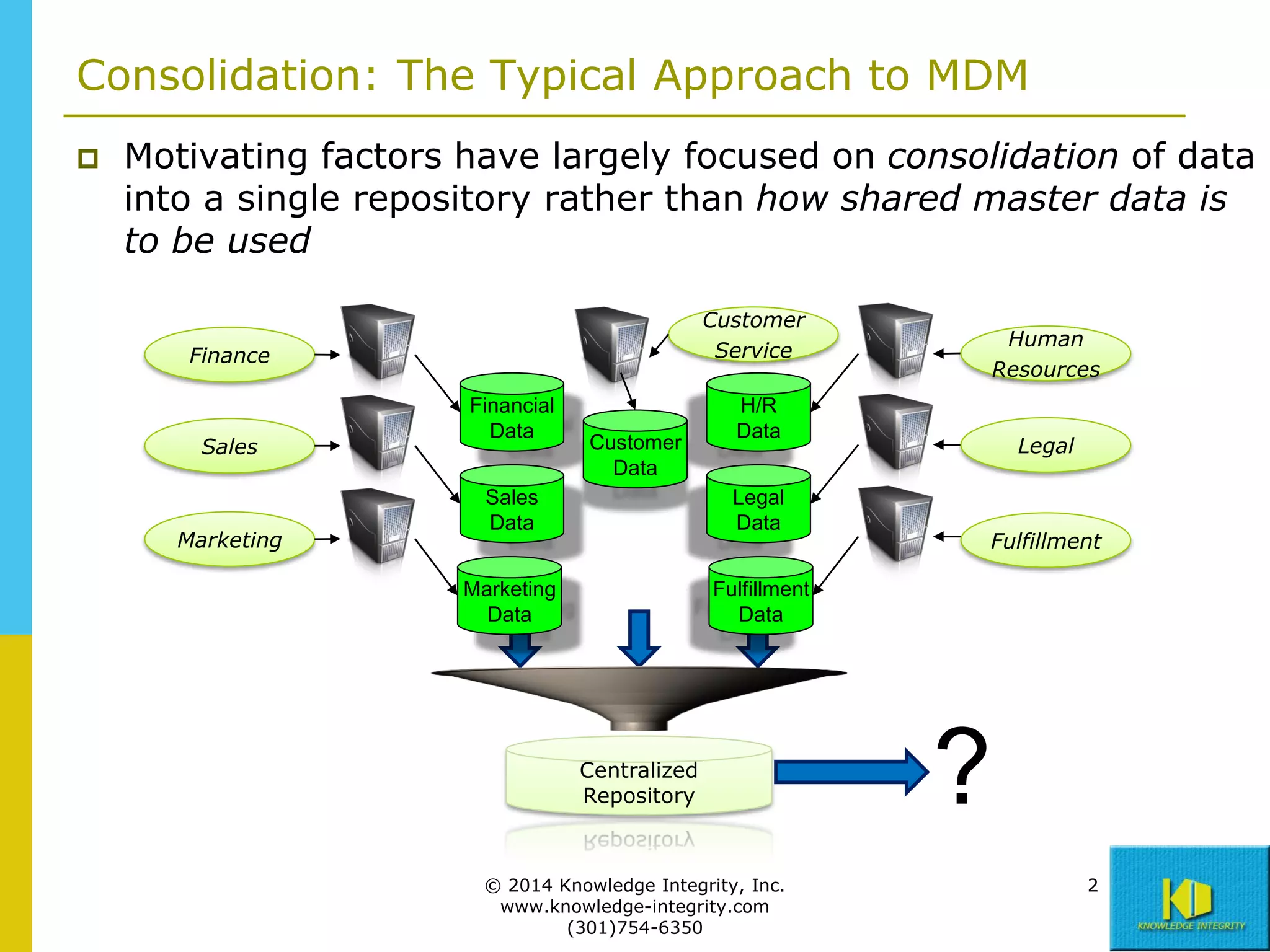
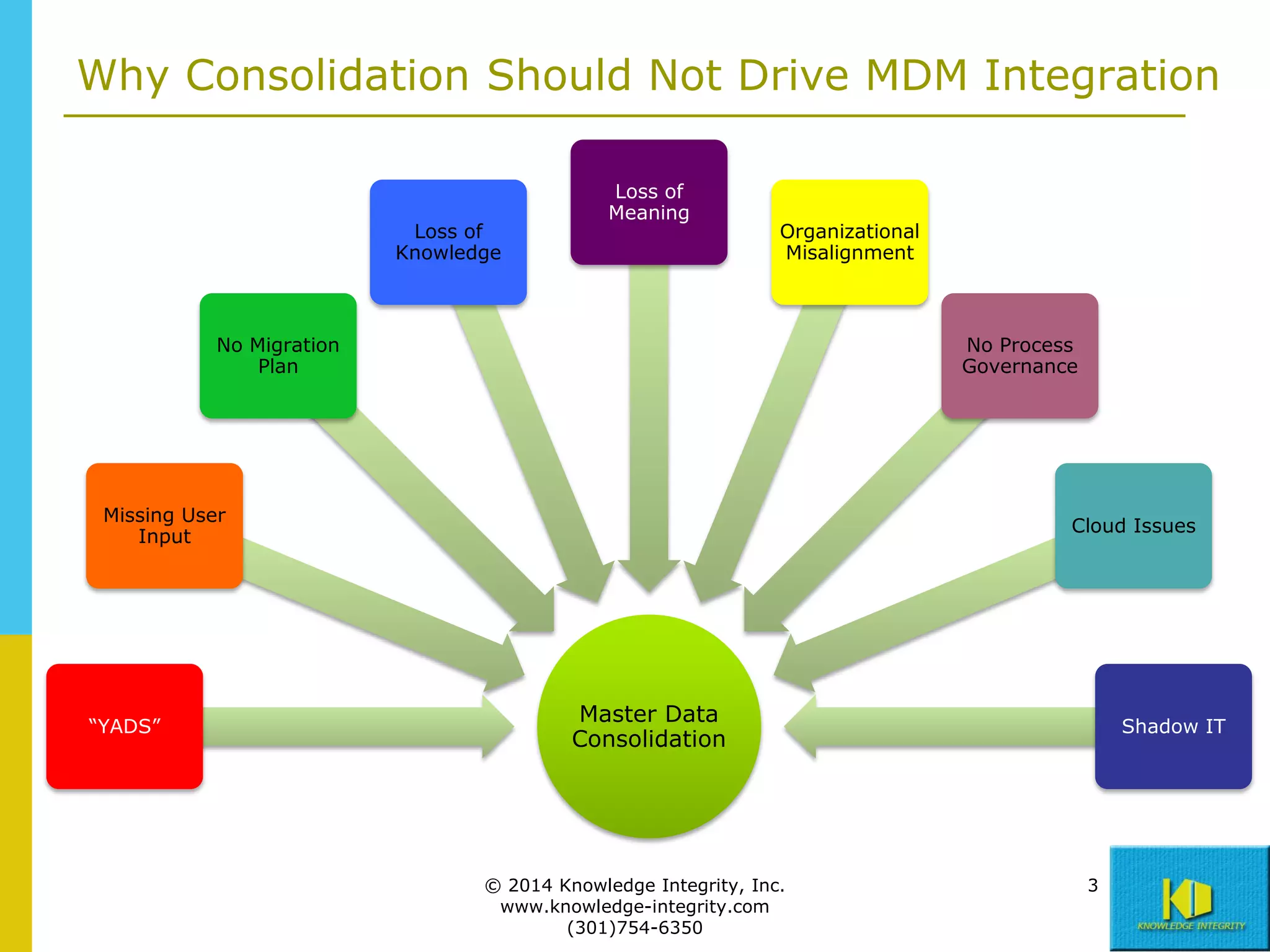
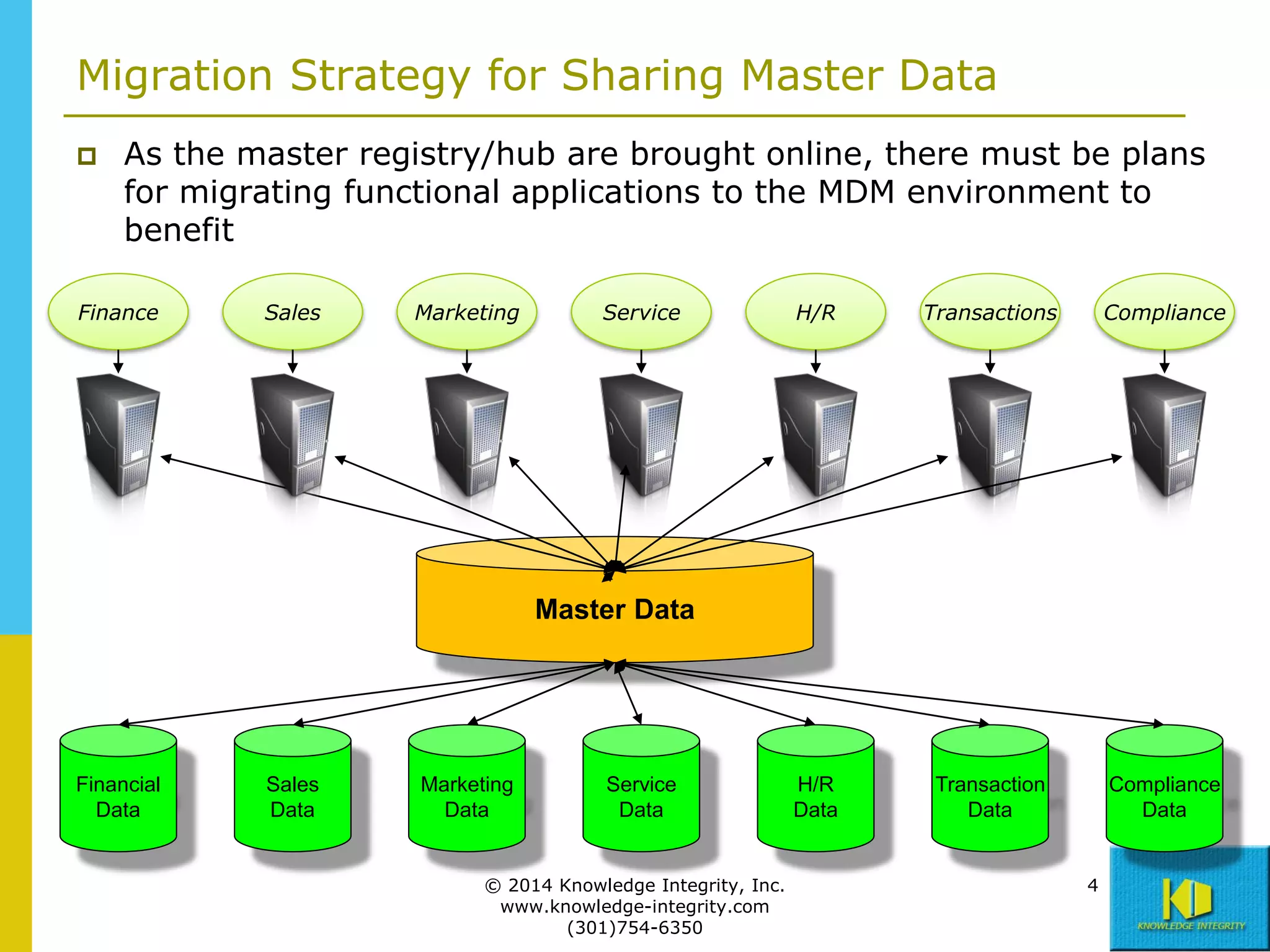
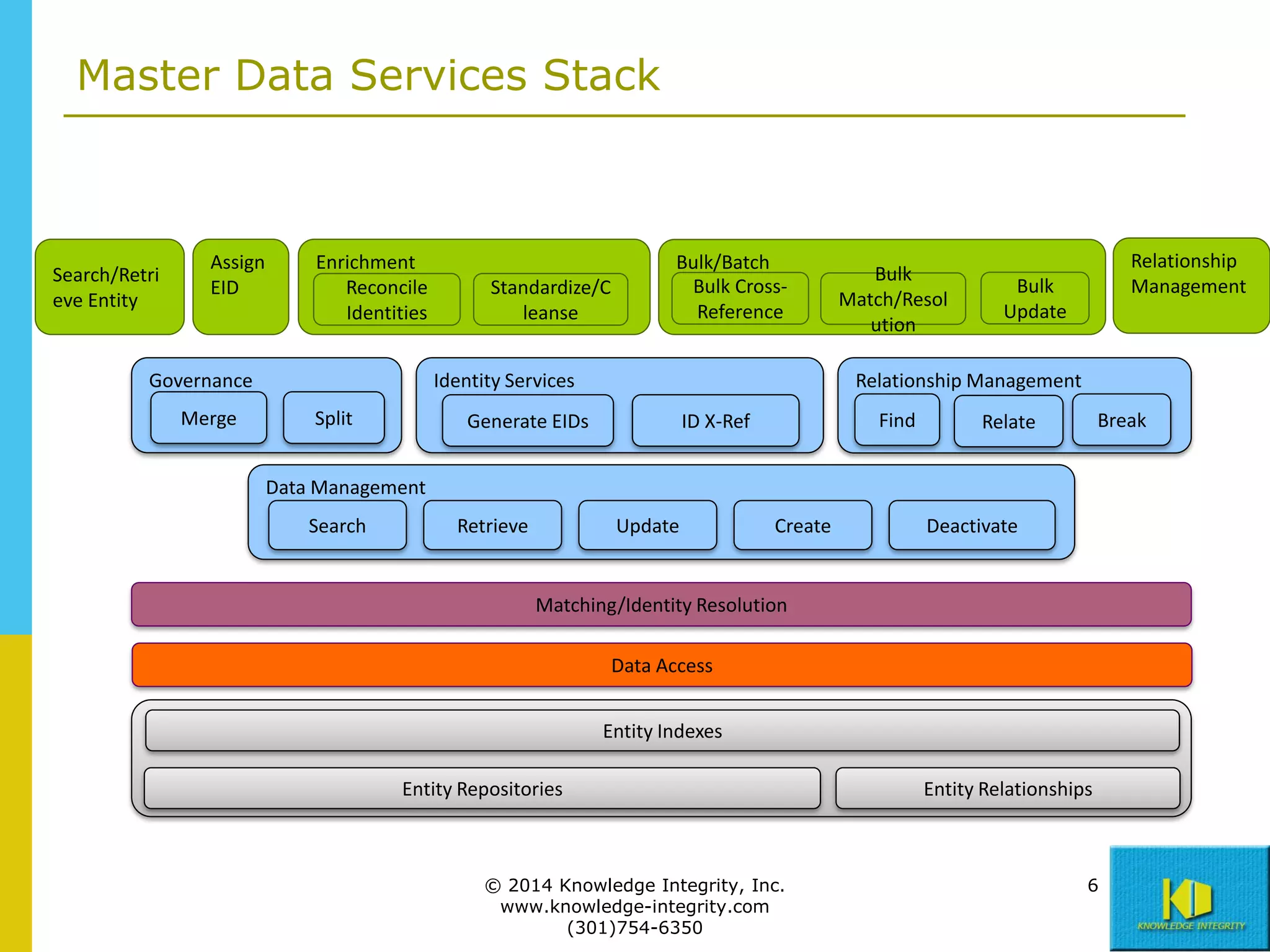
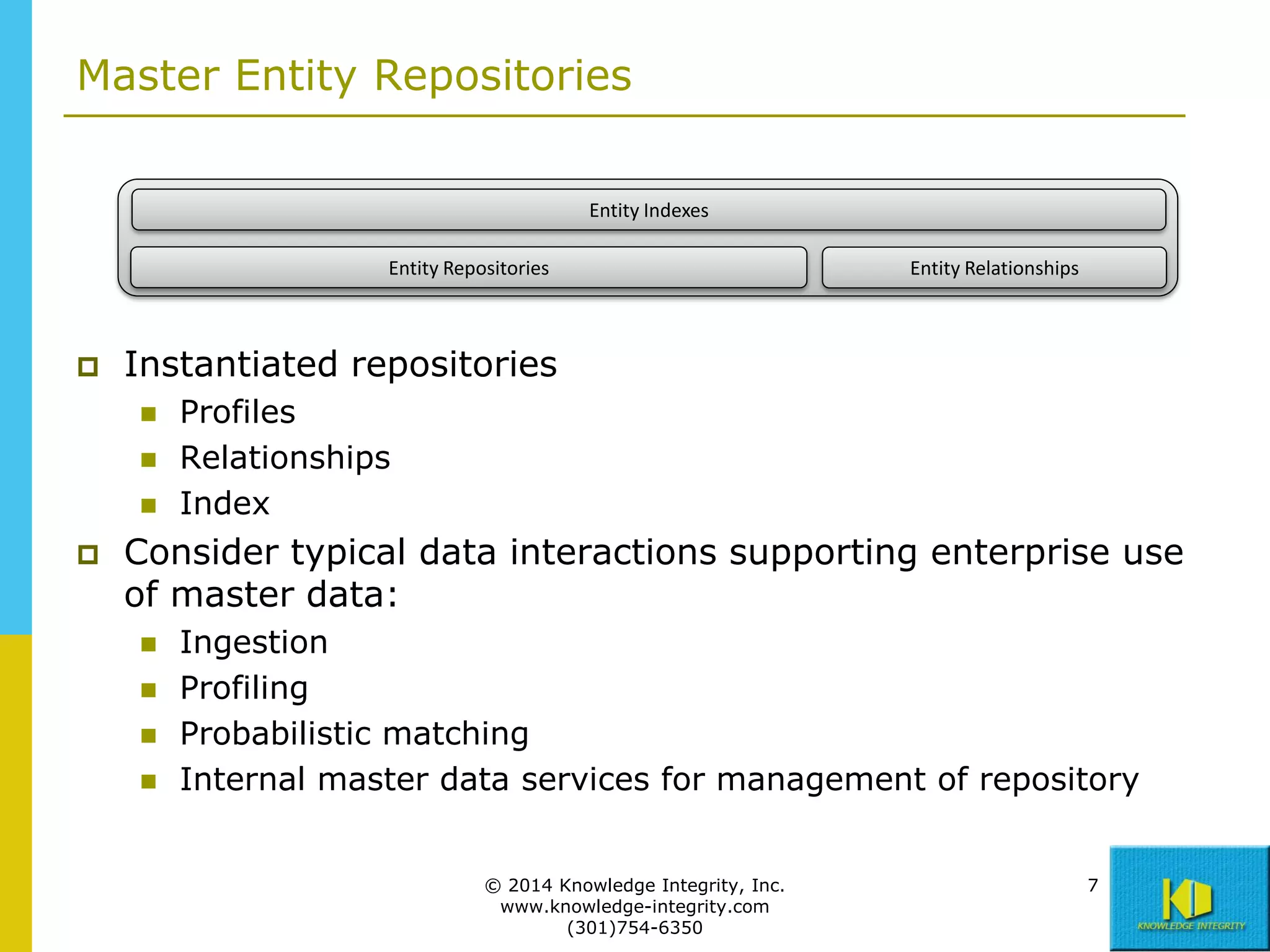
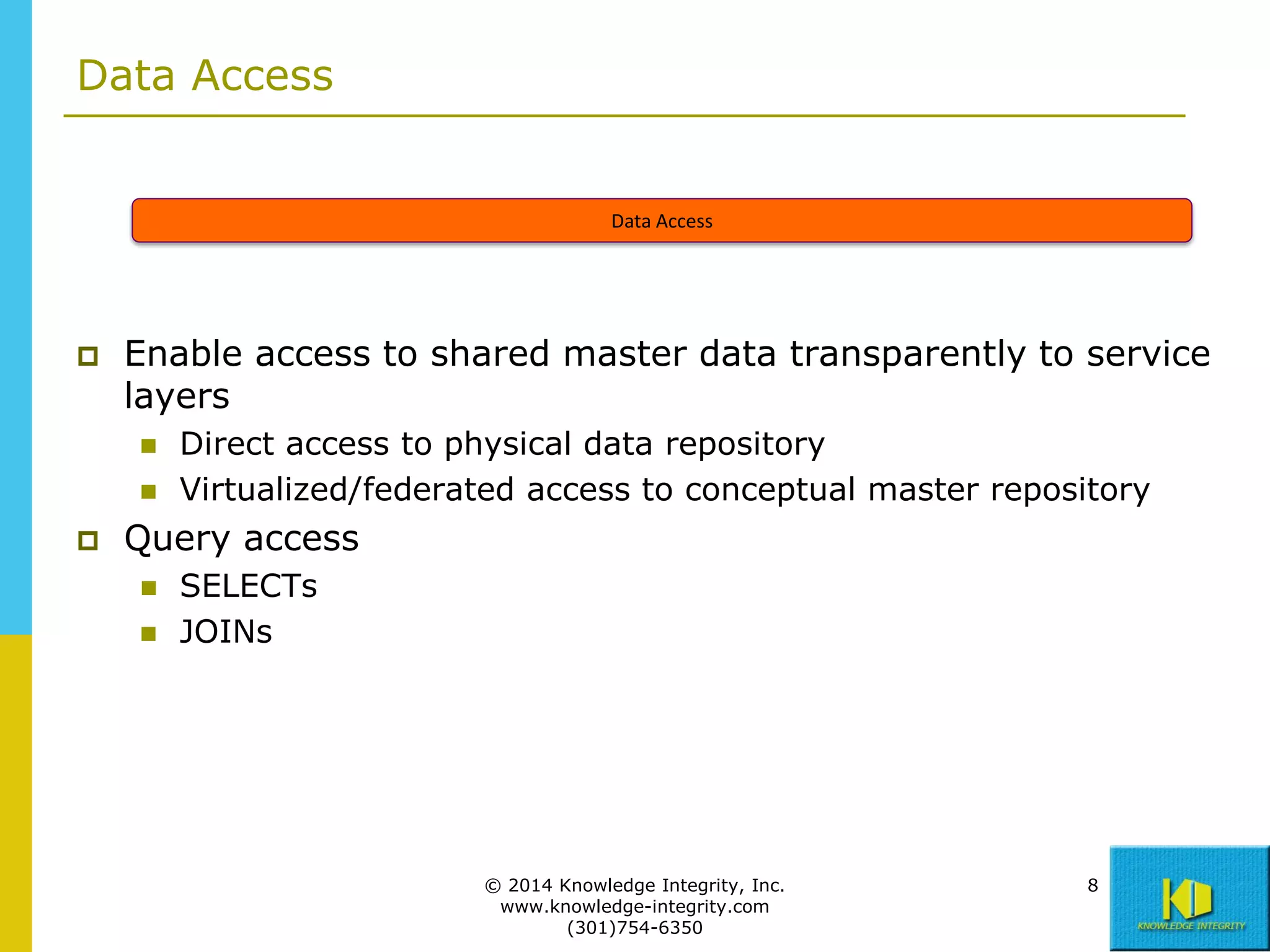
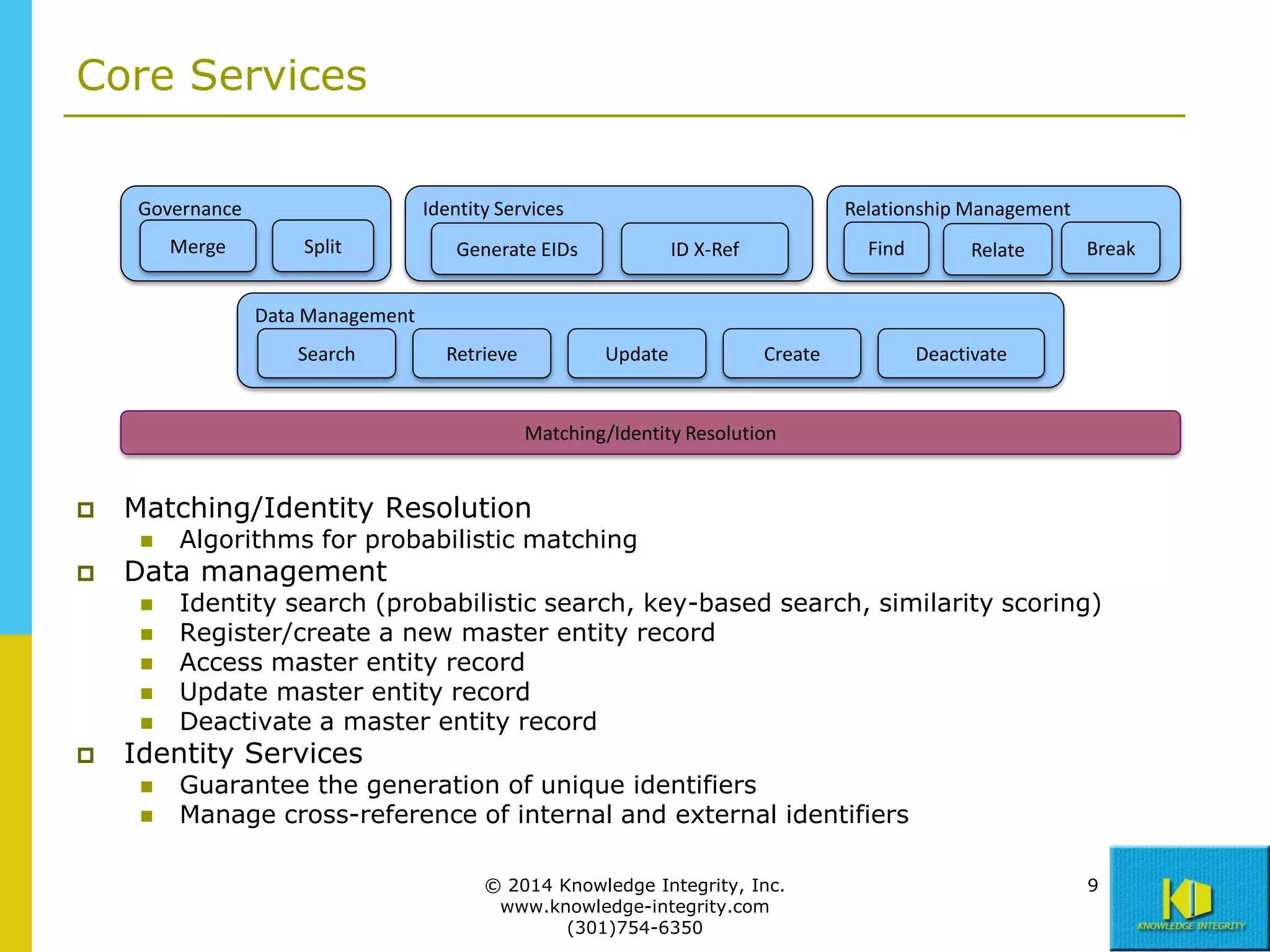
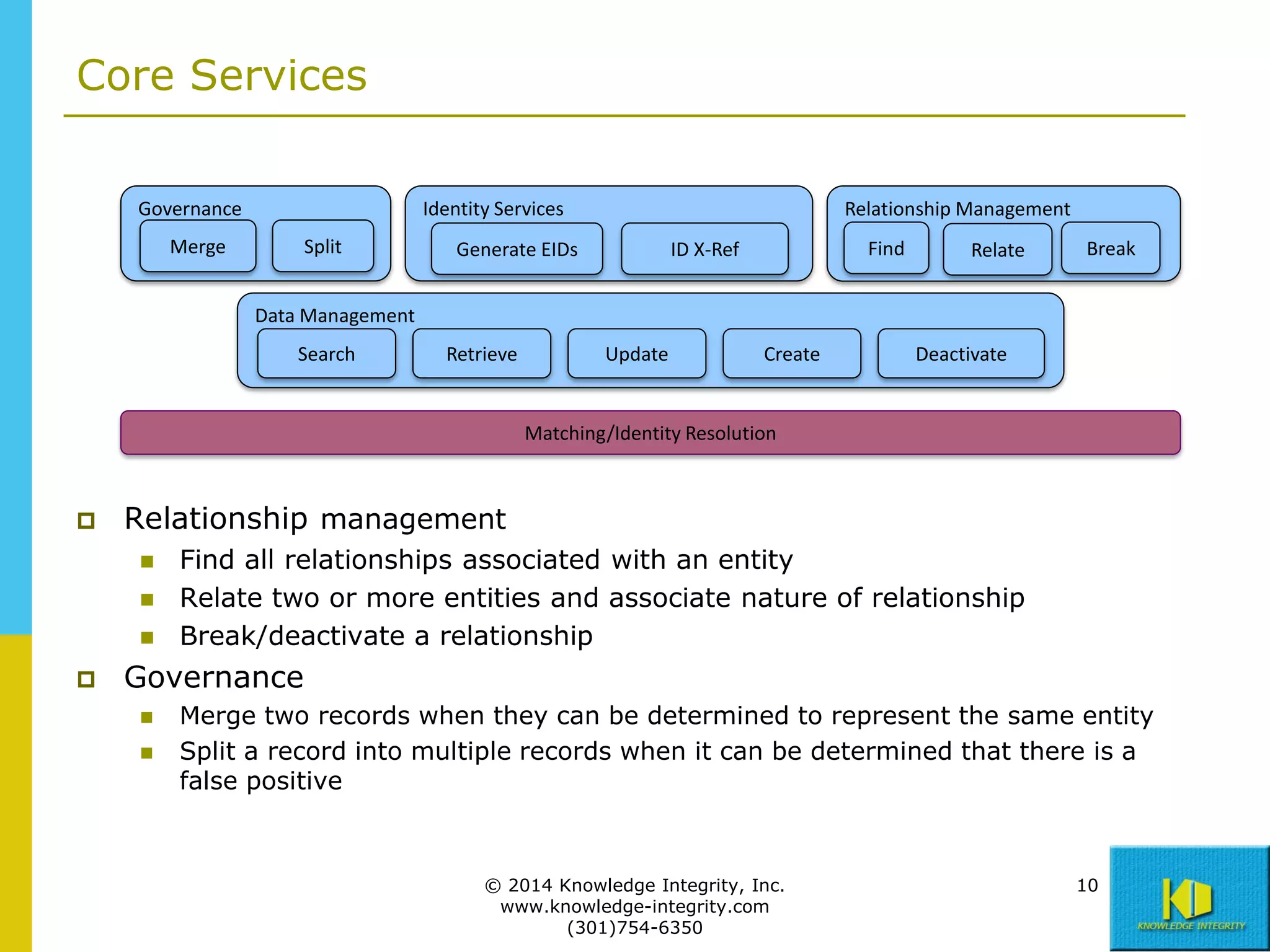
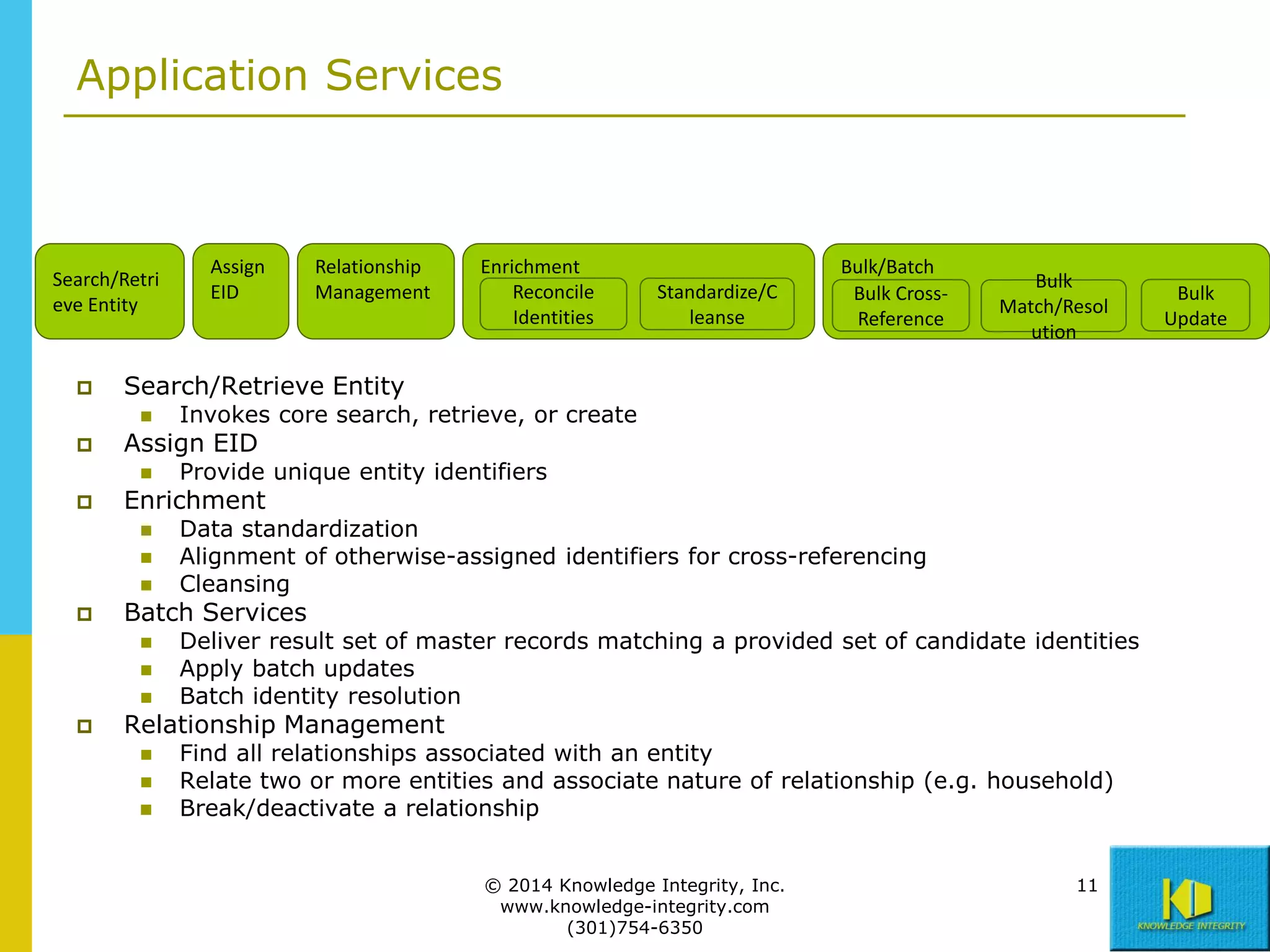
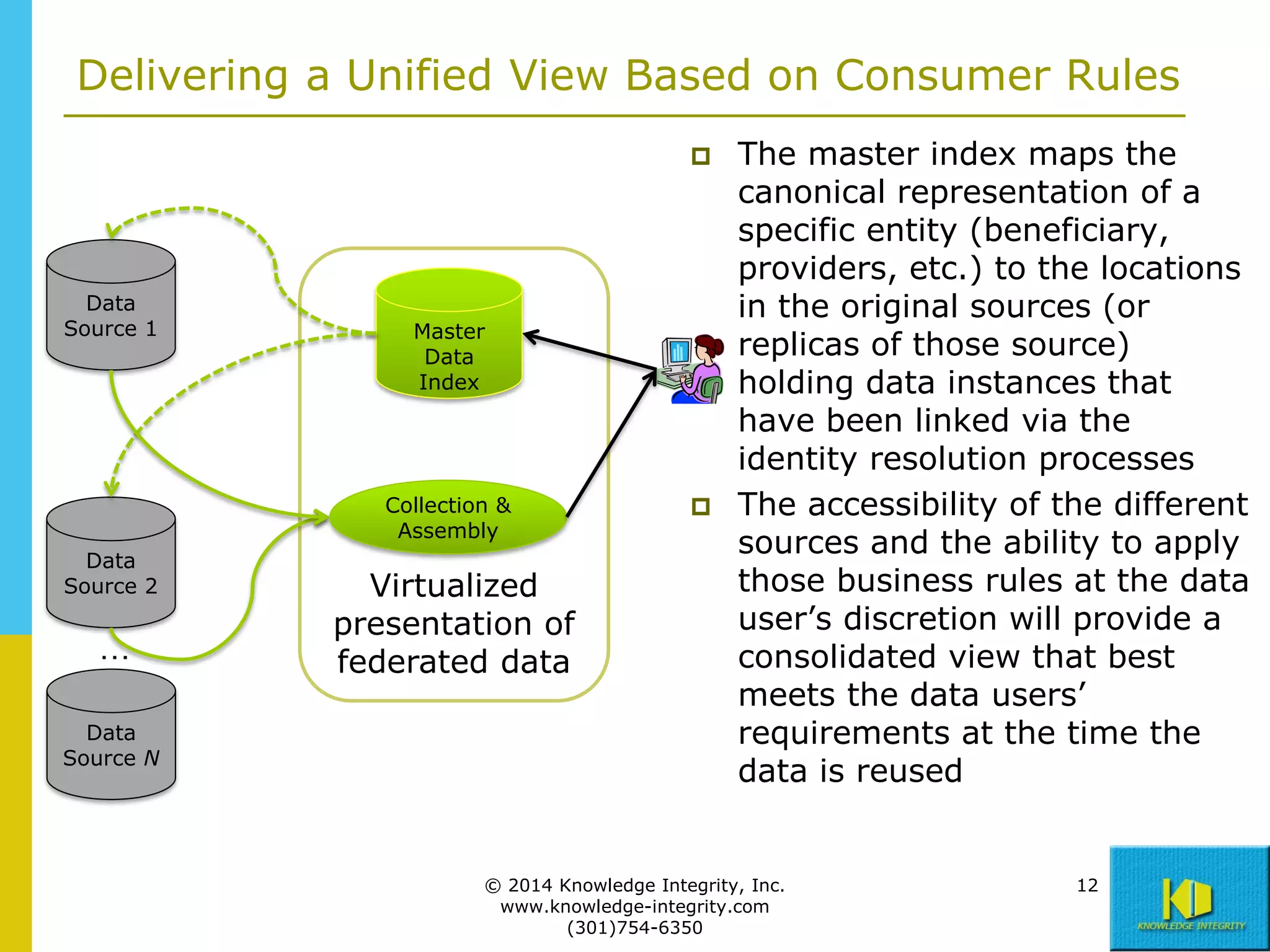
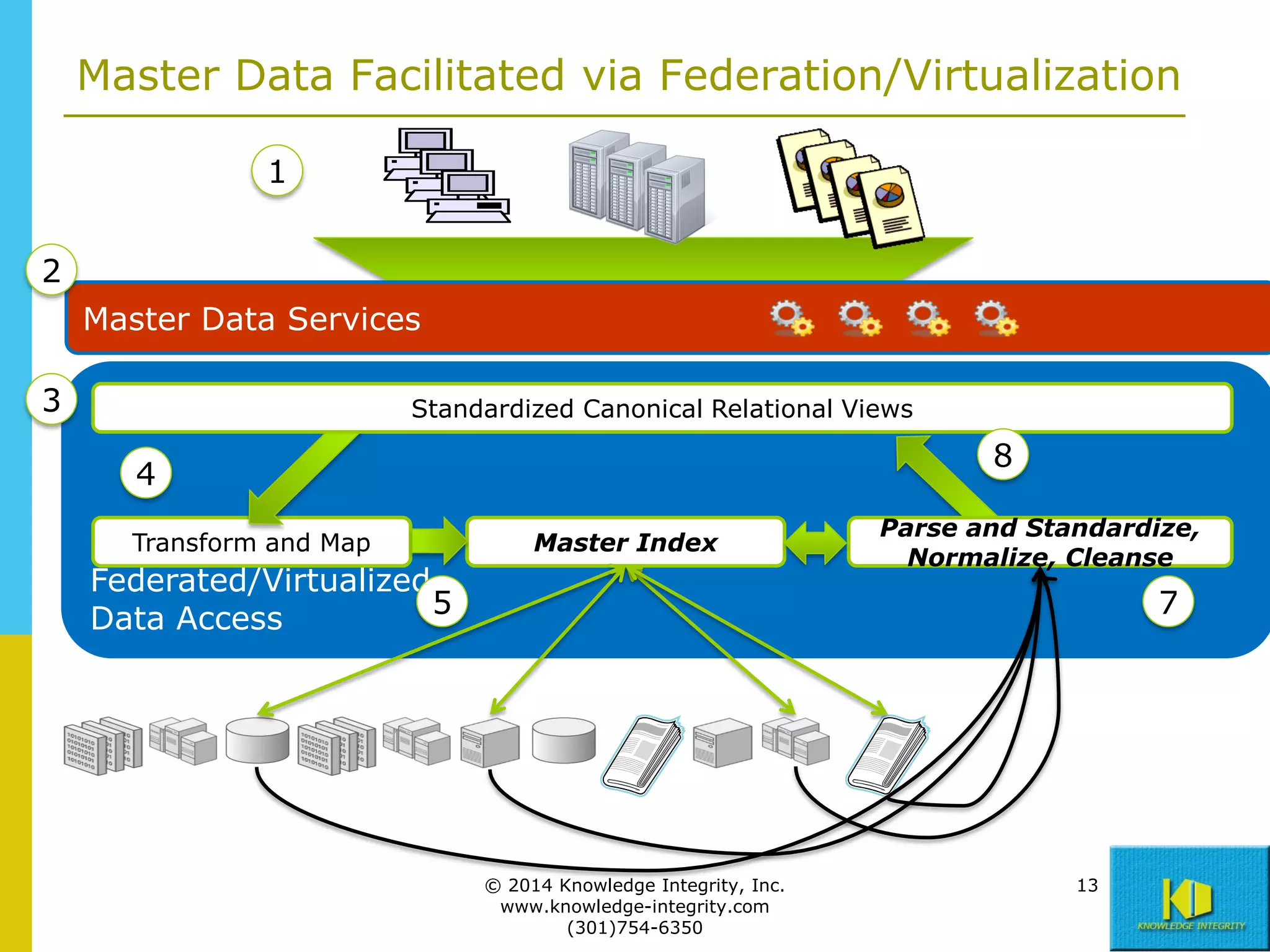
The document discusses the importance of master data management (MDM) in application integration, emphasizing that consolidation of data should not be the sole driving factor. It outlines strategies for migrating master data services and emphasizes the need for a comprehensive understanding of data usage scenarios, integration points, and required functionalities for effective MDM. Additionally, it provides an overview of core services and operational processes necessary to manage and access shared master data effectively.