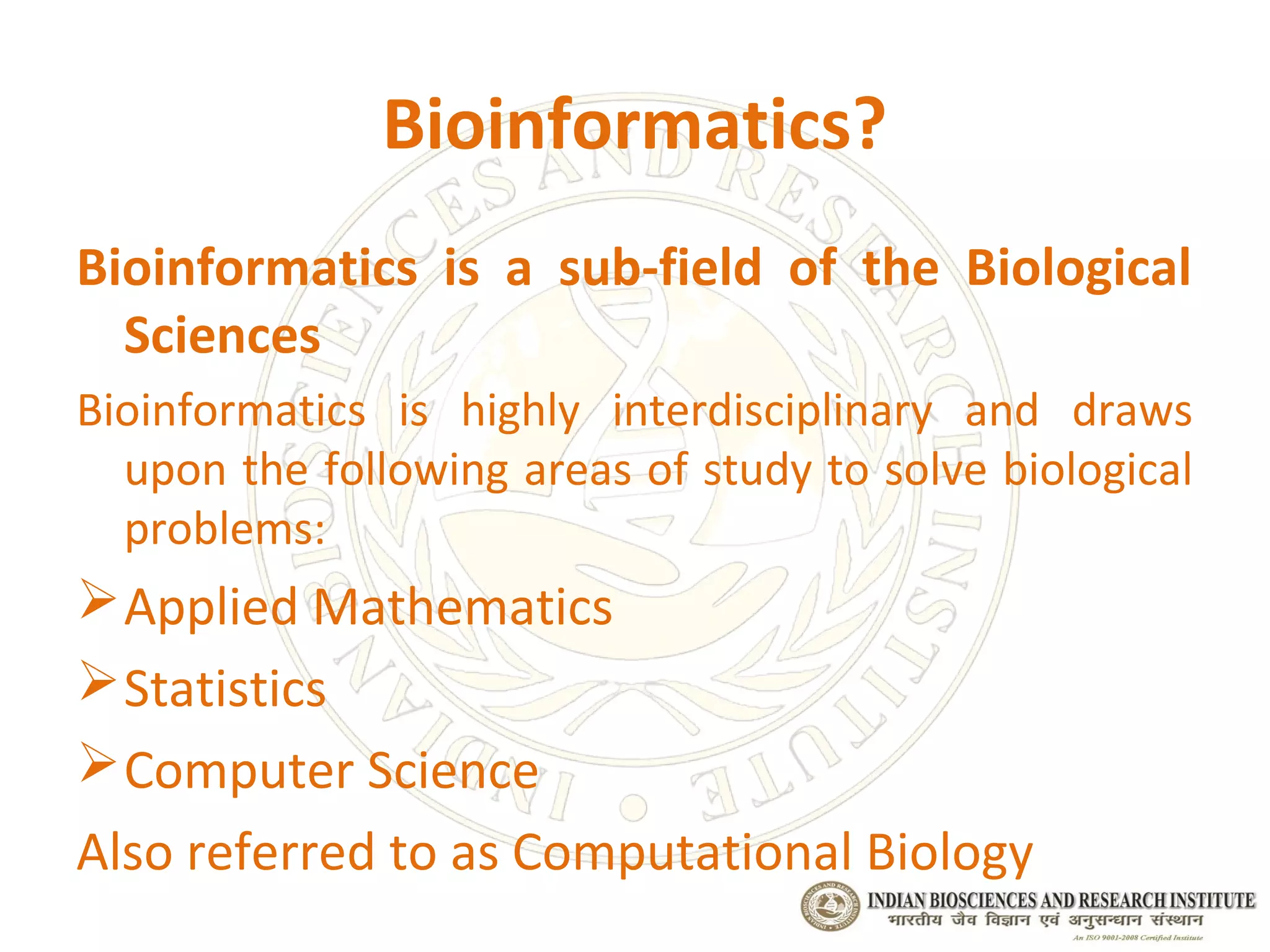
Bioinformatics is an interdisciplinary field combining biology, computer science, and applied mathematics to analyze biological data, notably in genomics and drug discovery. With the growing demand for skilled professionals in this area, various educational courses and job opportunities are emerging across industries like pharmaceuticals and agriculture. The field plays a crucial role in advancing scientific research and technology, particularly in analyzing vast data arising from genomics and molecular biology.










![Certificate Program in Bioinformatics
[6 Months]
Course Content
Module –I Concepts of Bioinformatics
Module -II Structural Biology
Module –II Database Management Systems
and Biological Databases
Module –IV Biostatistics and Algorithms
Module –V Research Study](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edited-bioinformaticscourseatindianbiosciencesandresearchinstitute-130417051420-phpapp02/75/Bioinformatics-Course-at-Indian-Biosciences-and-Research-Institute-12-2048.jpg)
![Certificate Program in Bioinformatics
[3 Months]
Course Content
Module-I Concepts of Bioinformatics
Module-II Database Management Systems
and Biological Databases
Module-III Research Study](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edited-bioinformaticscourseatindianbiosciencesandresearchinstitute-130417051420-phpapp02/75/Bioinformatics-Course-at-Indian-Biosciences-and-Research-Institute-13-2048.jpg)

