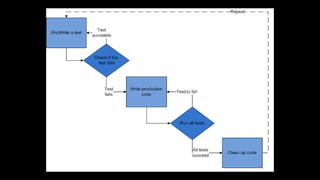
TDD (test-driven development) involves writing unit tests before production code according to three laws: 1) write only enough code to fail a test, 2) write only enough test to fail initially, and 3) write only enough code to pass the test. An example involves testing an add() function by ensuring it handles errors for too few/many arguments and non-numeric values. Benefits of TDD include reduced debugging time, higher code quality, avoiding over-engineering, better interfaces, documentation, and more modular code. Best practices are to keep units small and focused, treat tests as production code, and design for low coupling and isolation.