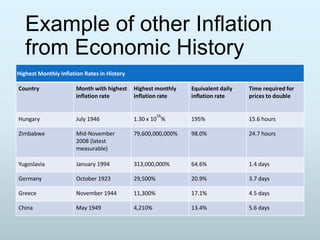
This document provides information on economic concepts such as inflation, deflation, multipliers, and examples from history. It discusses:
1) What inflation and deflation are, examples from Zimbabwe and Germany, and problems high inflation can cause like worsening poverty and reduced savings incentives.
2) What multipliers represent and examples from economic history like Quesnay's formulation in the 18th century.
3) Examples of inflation drivers like the oil crisis of 1973 which led to recessions, energy shortages, and a move to more fuel efficient vehicles and alternative energy sources.
4) Keynes' views on preventing booms and recessions through countercyclical fiscal policies like increasing taxes during bo