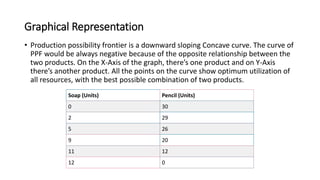
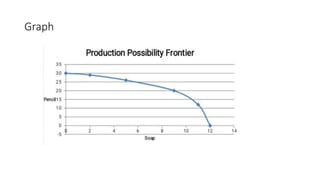
This document provides an introduction to economics, including definitions of key terms. It discusses how human wants can be economic or non-economic, and defines goods and services. It also defines microeconomics and macroeconomics, positive and normative economics, the four factors of production (land, labor, capital, enterprise), and illustrates the production possibility frontier graphically. The production possibility frontier shows the different combinations of two goods an economy can produce with limited resources.