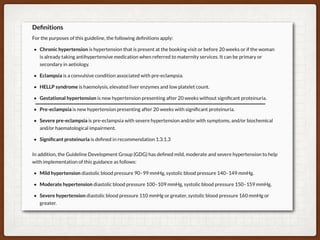
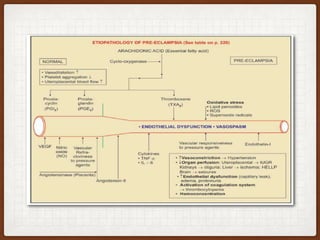
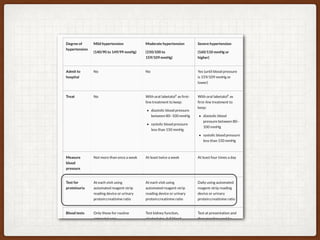
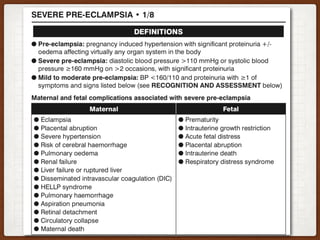
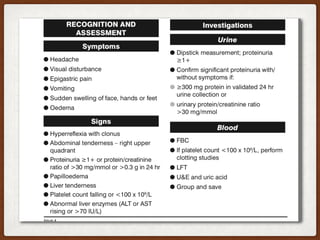
1. This case involves a 38-year-old pregnant woman at 41+1 weeks gestation with gestational hypertension who was induced with Propess. She developed eclampsia during her cesarean section under spinal anesthesia.
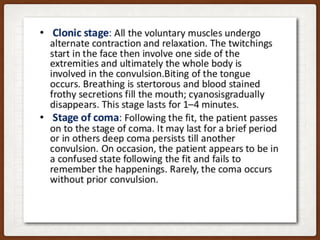
2. She experienced seizures immediately after the spinal was administered and required intubation and general anesthesia to complete the emergency c-section. Her baby had low APGAR scores but did not require resuscitation.
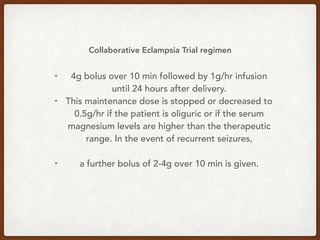
3. She was treated per protocol with magnesium sulfate bolus and infusion to prevent further seizures. Both mother and baby recovered well post-operatively. The team reflected on areas that went well and aspects of management that could be reviewed further.