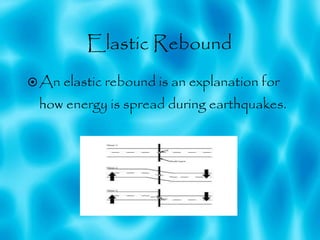
The document summarizes information about earthquakes, including how they are caused by movement of rock beneath the earth's surface. It describes the different types of seismic waves produced by earthquakes and discusses the major 2011 Tohoku earthquake in Japan. This earthquake, measured at magnitude 9.0, caused widespread damage through tsunamis, landslides and collapsed buildings. It severely impacted the Japanese economy by damaging factories and disrupting the auto industry, and also caused problems for nearby nuclear power plants.