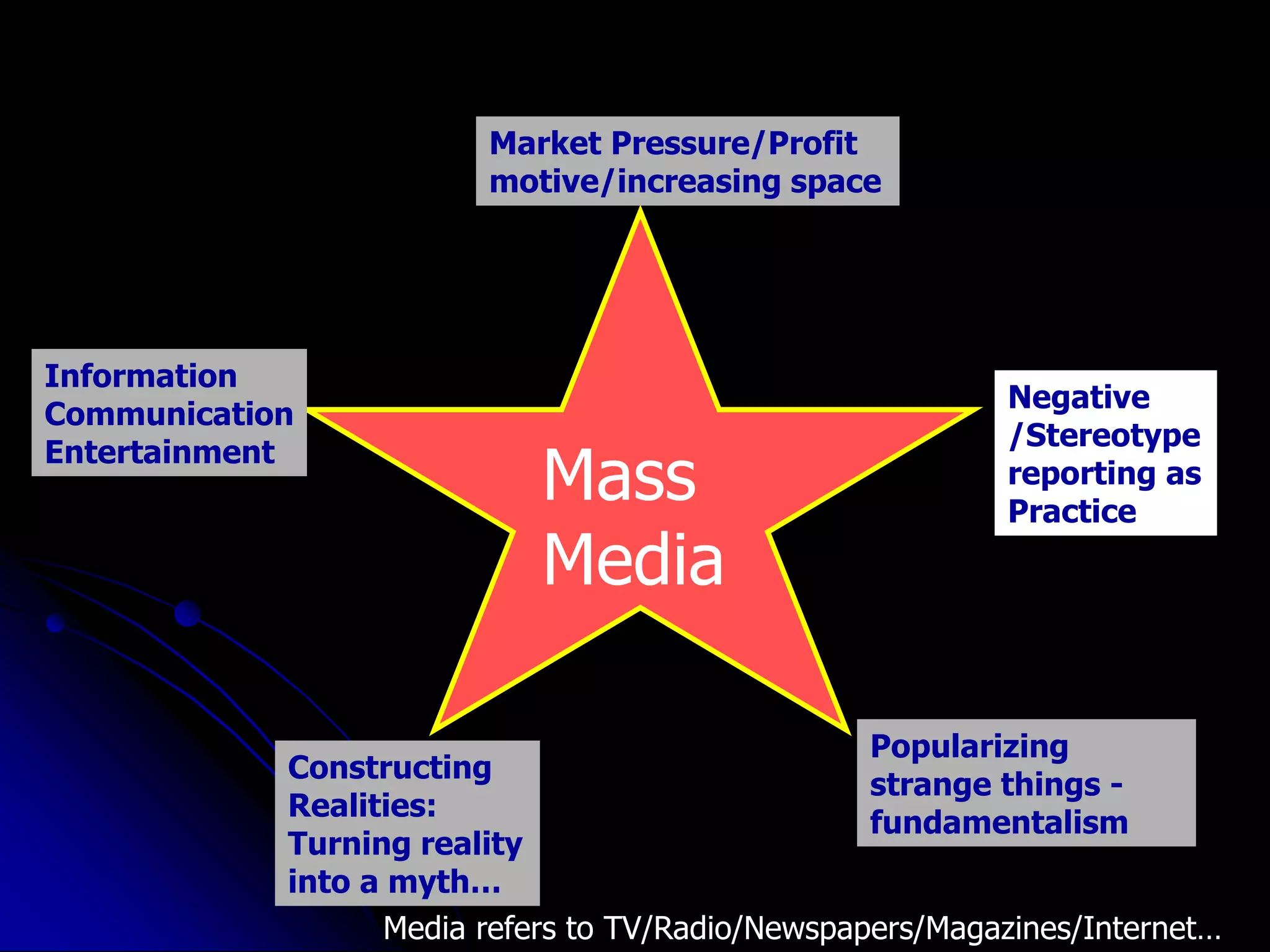
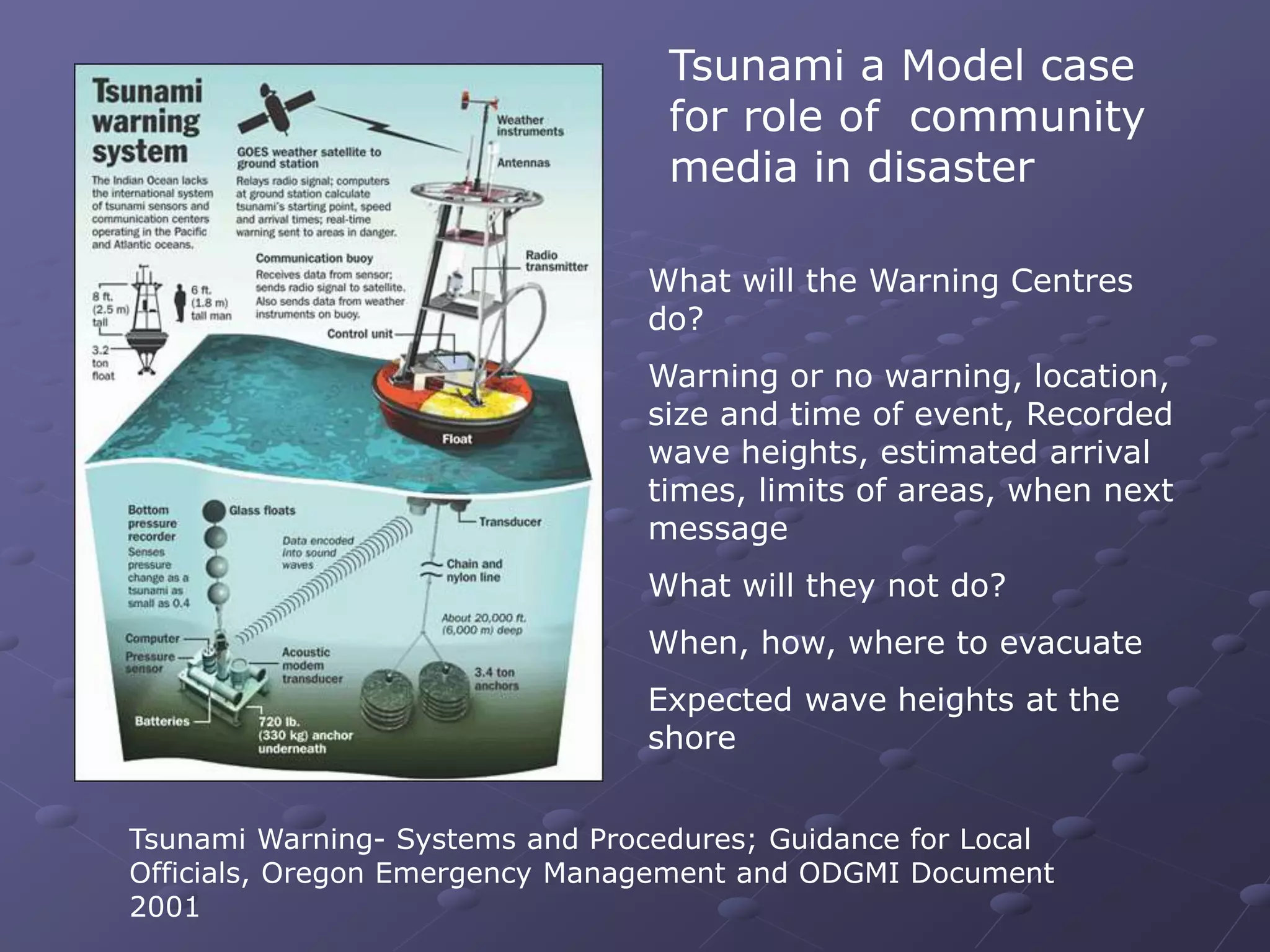
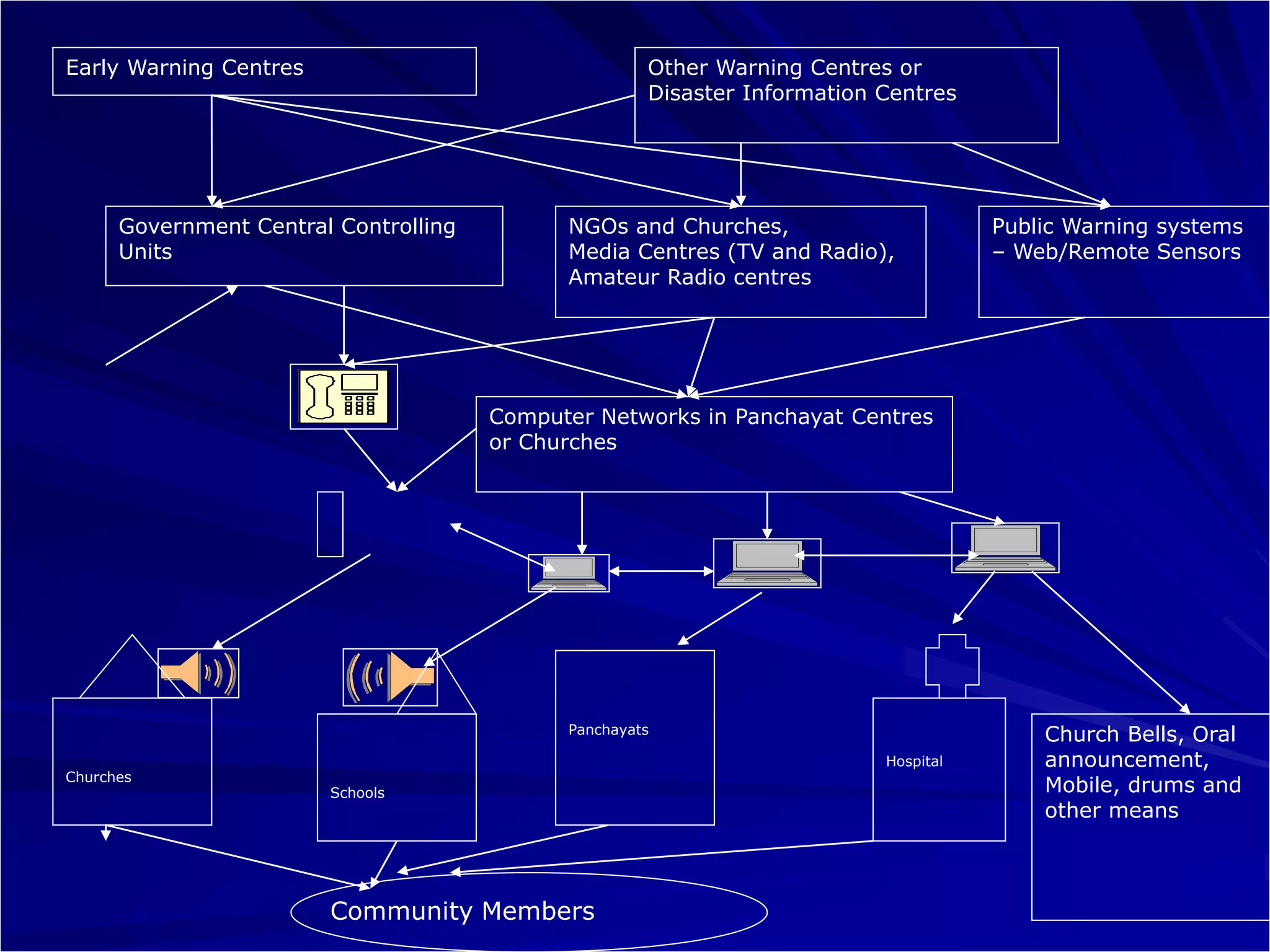
This document discusses the importance of early warning systems and community networks for disaster management. It argues that many lives could have been saved from the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami if information systems were in place to disseminate warnings and facilitate evacuation. The document outlines different approaches for warning dissemination and response coordination, including the roles of mass media, government agencies, NGOs, and community organizations in connecting people through technology and local communication methods. It stresses that technologies should be incorporated into existing community media and designed with sustainability, local language support, and community involvement in mind to effectively serve vulnerable groups.