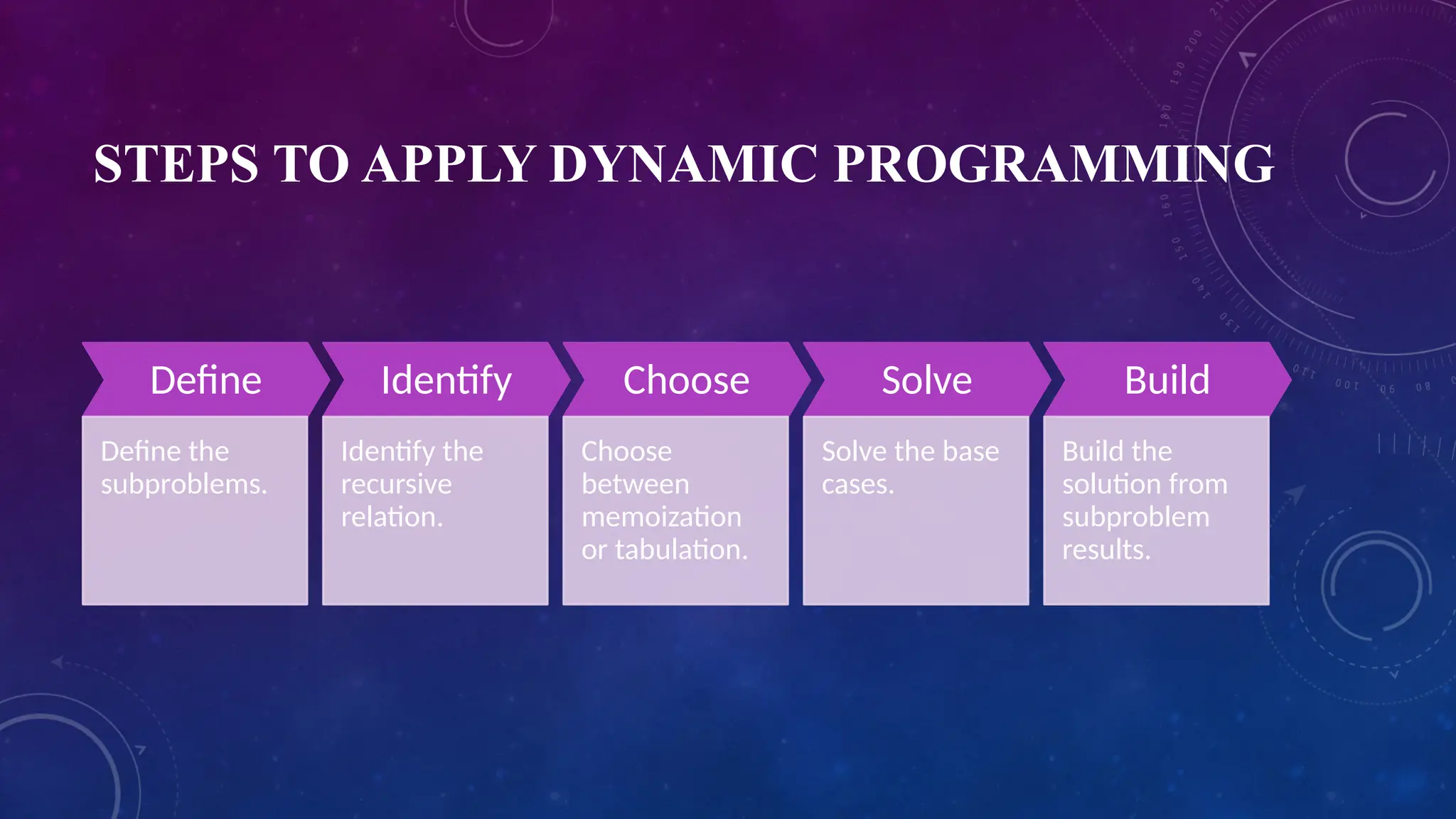
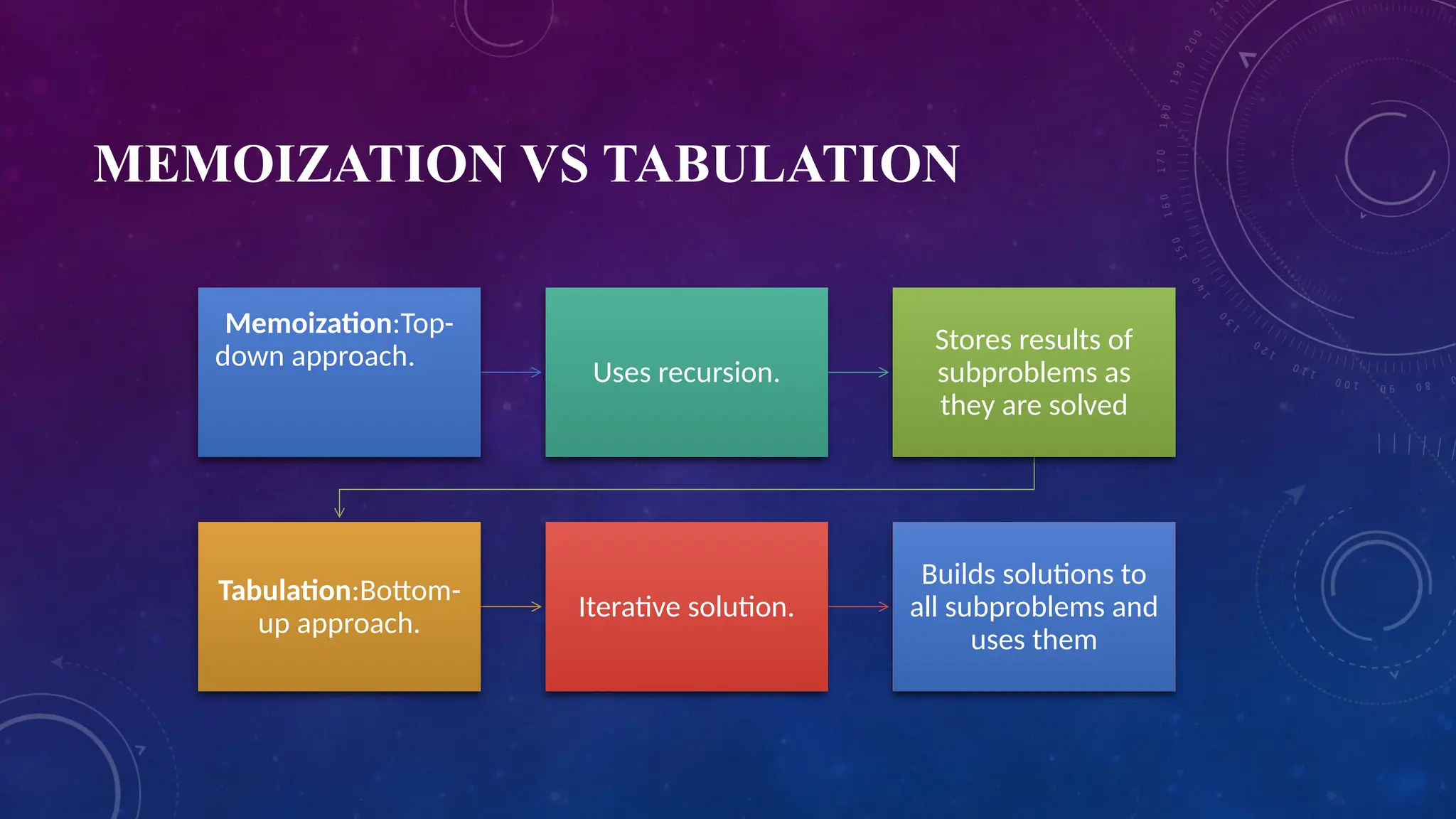
Dynamic programming is a method for solving complex problems by breaking them down into simpler overlapping subproblems with optimal substructure. It is often preferred over greedy methods for optimization problems due to its efficient use of previously solved subproblems through approaches like memoization (top-down) and tabulation (bottom-up). While it can reduce time complexity and avoid redundant calculations, dynamic programming may require significant memory and necessitates the identification of suitable subproblems.





![TABULATION
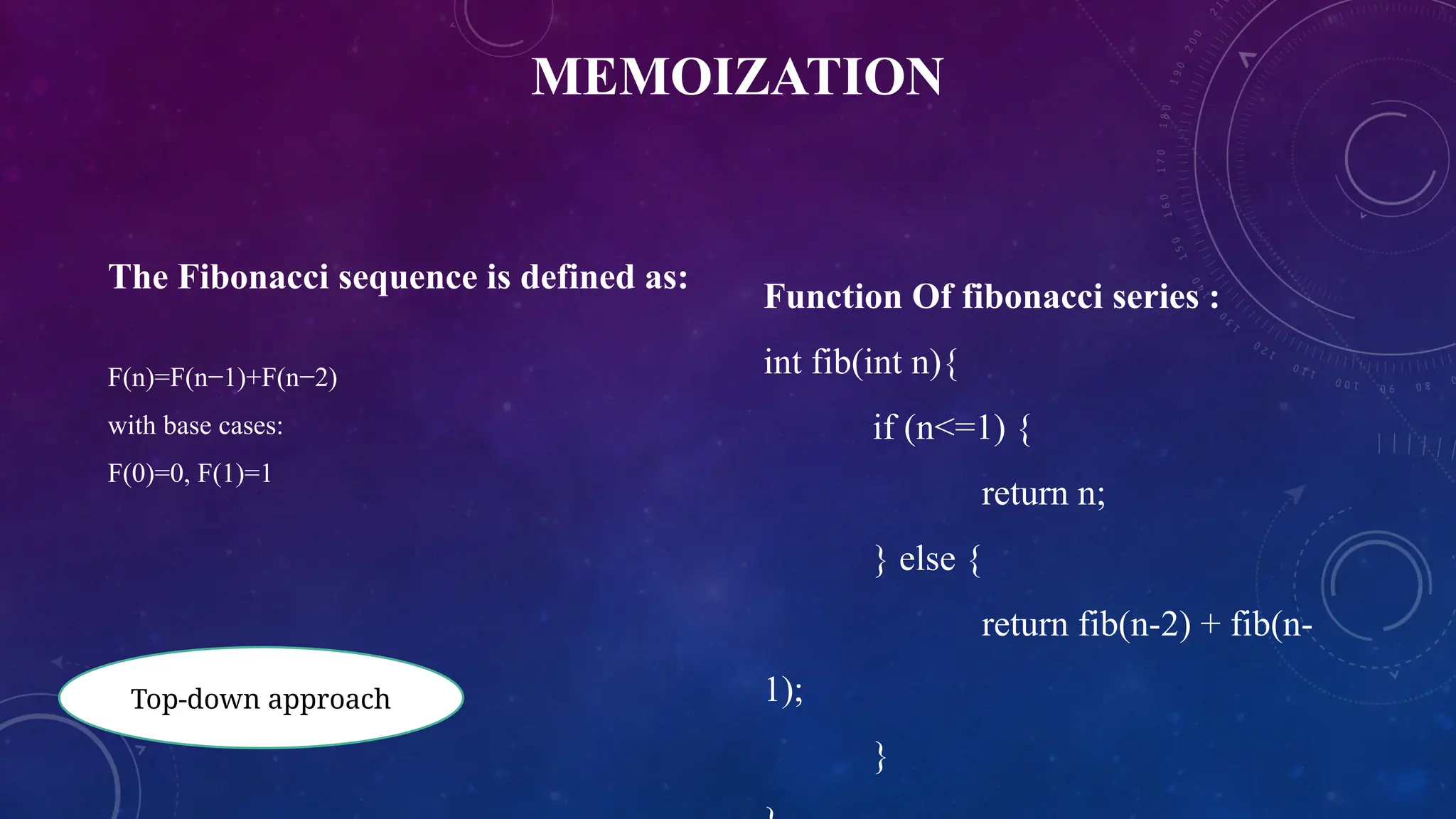
Function Of fibonacci series:
int fib(int n){
if (n<=1) {
return n;
F[0]=0;F[1]=1;
}
for(int i=2; i<=n; i++){
F[i] = F[i-2]+F[i-1];
}
return F[n];
}
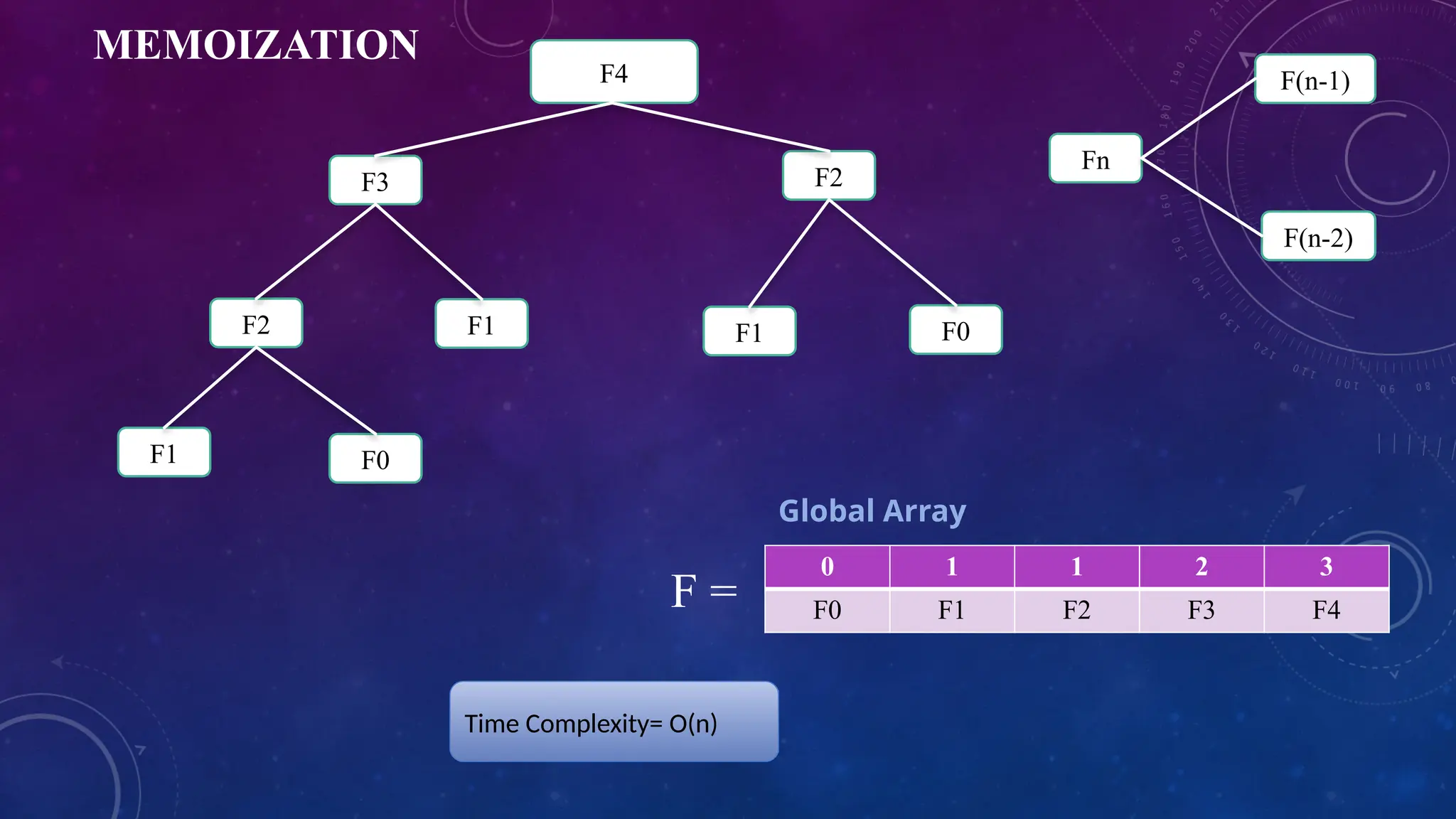
0 1 1 2 3
F0 F1 F2 F3 F4
F =
Time Complexity= O(n)
Global Array
Bottom-up
approach
F1 F0
F2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamicprogramming-240909083819-dc0f77bd/75/DYNAMIC_________________________PROGRAMMING-pptx-9-2048.jpg)