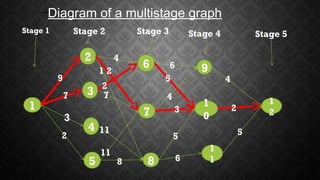
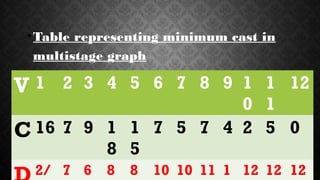
Dynamic programming is an algorithm design technique for solving complex problems defined by overlapping subproblems. It works by solving each subproblem only once and storing the results for future use, avoiding the work of recomputing results. The principle of optimality states that optimal solutions can be constructed from optimal solutions of subproblems. Dynamic programming algorithms involve characterizing the optimal substructure, recursively defining the optimal value, computing the optimal value in a bottom-up manner, and constructing an optimal solution. It is generally applied to optimization problems and provides efficient solutions, though it may not always find a global optimum. An example is finding the minimum cost path through a multistage graph.