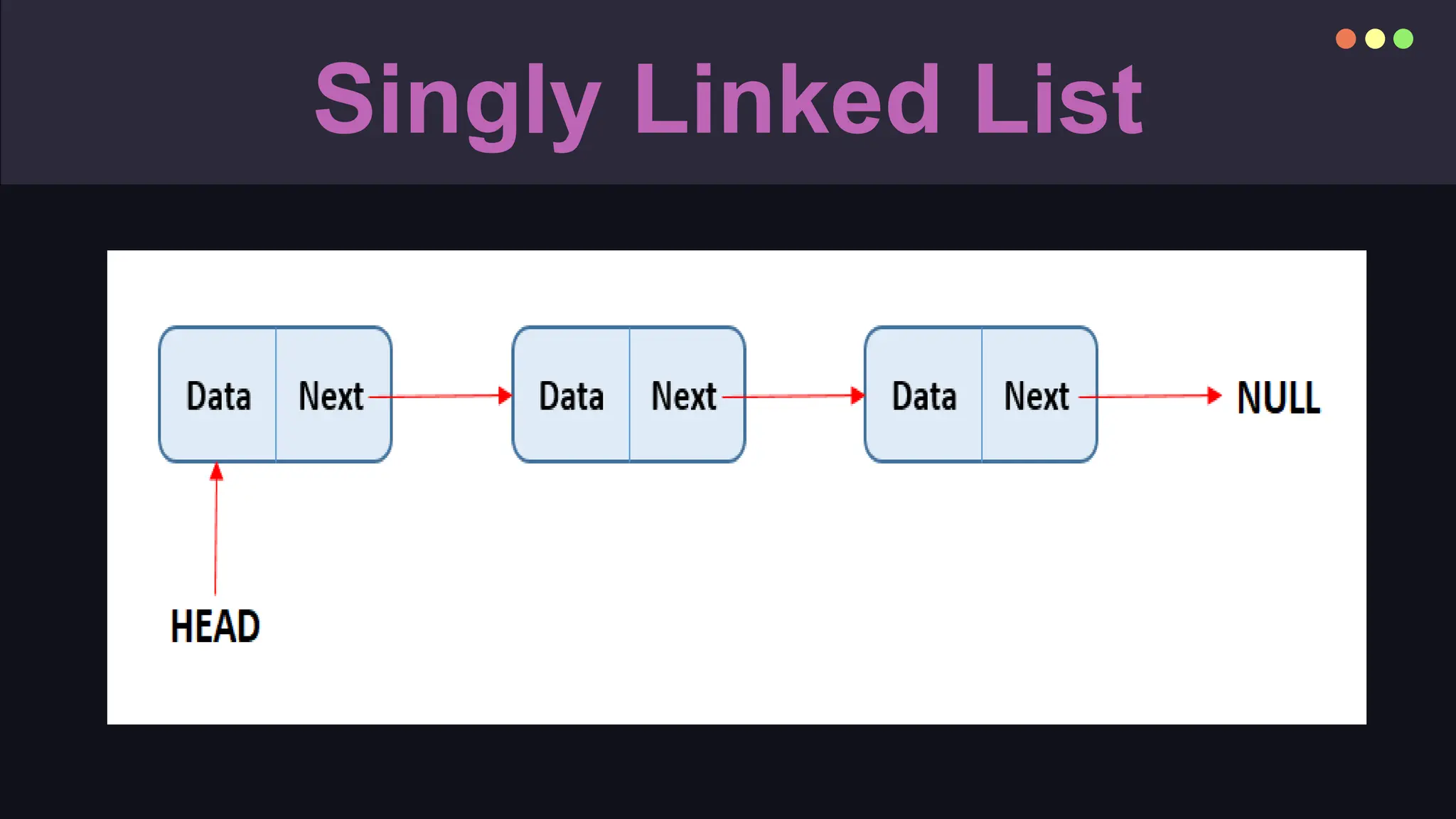
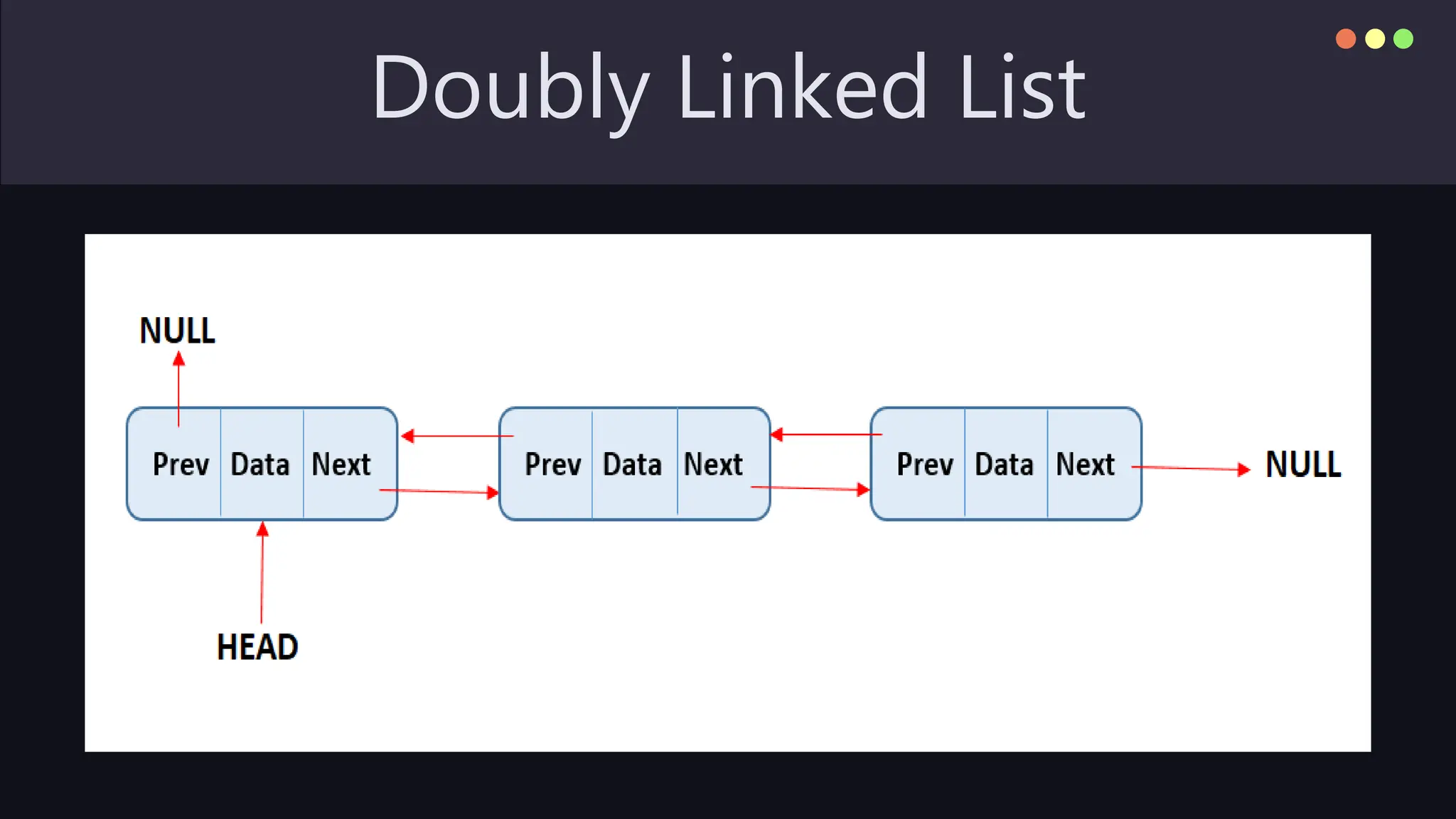
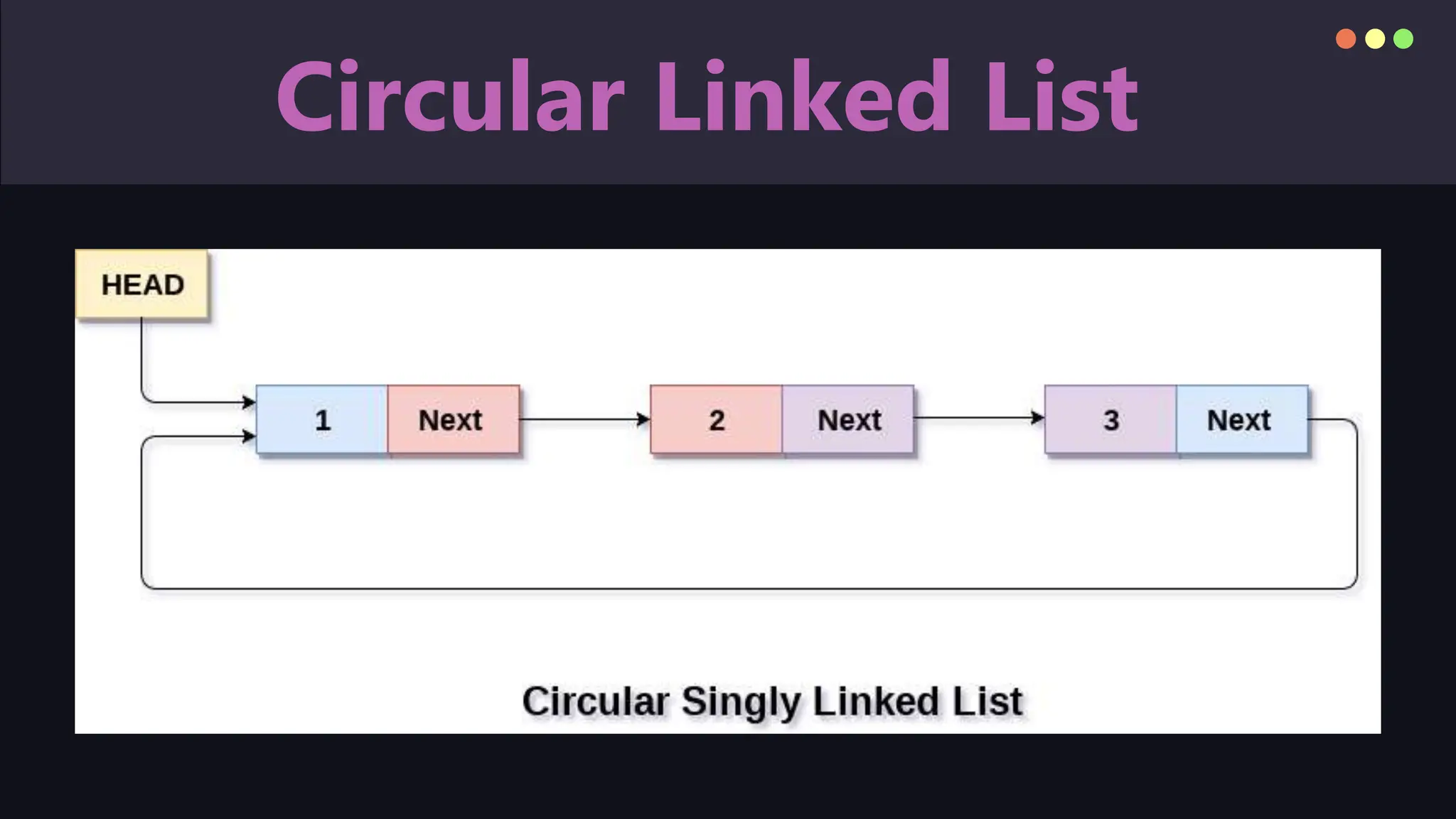
A linked list is a linear data structure consisting of nodes that contain data and pointers to the next node, allowing efficient insertion and deletion. While linked lists are flexible in size and facilitate constant-time modifications, they have drawbacks such as increased memory usage and sequential access. Variants include singly linked lists, doubly linked lists, and circular linked lists, each with distinct properties and applications.