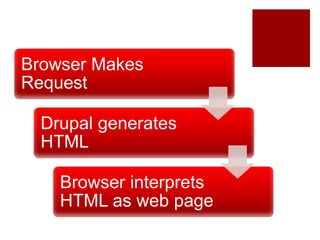
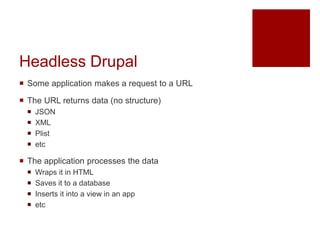
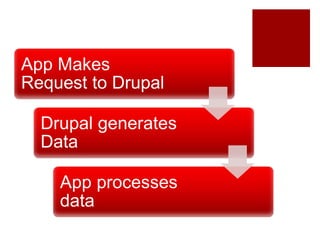
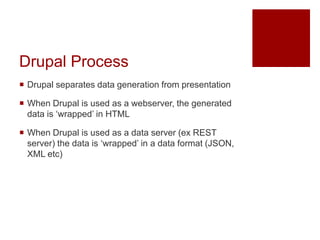
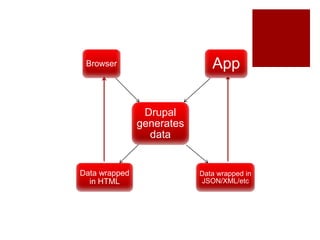
The document discusses using headless Drupal as a data server, detailing how browsers and applications interact with it for data retrieval in formats like JSON and XML. It covers the advantages and disadvantages of using headless Drupal with web and mobile applications, emphasizing faster data transfer and the separation of data generation from presentation. It also highlights features of Drupal 7 and 8's services modules, including authentication methods and custom extensibility.