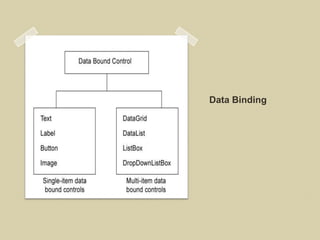
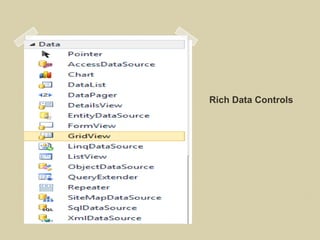
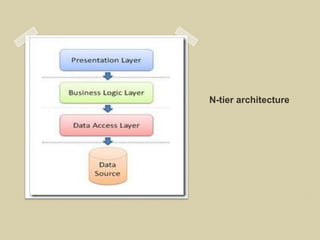
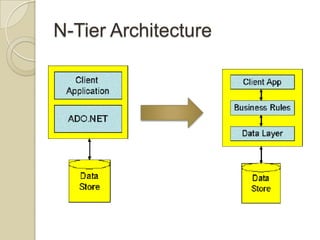
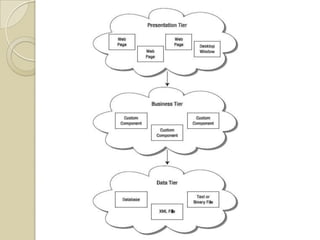
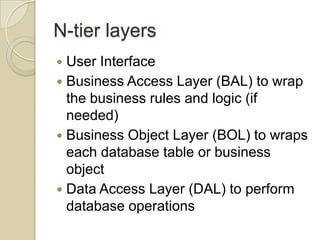
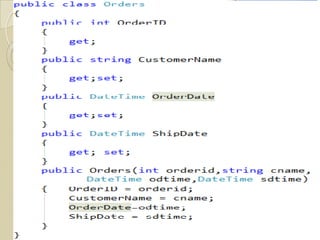
The document discusses ASP.NET 4.0 and covers topics like data binding, rich data controls, and n-tier architecture. It provides information on programatic and declarative data binding. Rich data controls like GridViews can be bound to data. N-tier architecture separates the user interface, business logic, and data access layers. This improves maintenance and flexibility. Data source controls allow binding database queries to controls without code.
















![REFERENCES
[1] Beginning ASP.NET 4 In C# 2010, Matthew
Macdonald, Apress
[2] Web Application Architecture
Principles, Protocols And Practices, Leon Shklar
And Richard Rosen, Wiley
[3] Professional AS P.NE T 4 In C# And VB, Bill
Evjen, Scott Hanselman And Devin Rader, Wiley
[4] Pro ASP.NET In C# 2010, Fourth
Edition,matthew Macdonald, Adam Freeman, And
Mario Szpuszta, Apress](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asp-net-lect4-130212112729-phpapp01/85/ASP-NET-Lecture-4-28-320.jpg)