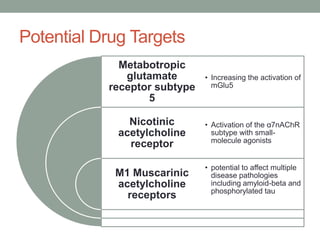
This document discusses Alzheimer's disease and potential drug targets and strategies. It begins by introducing Alzheimer's disease and some of its key characteristics like memory loss and neuronal cell dysfunction. It then discusses amyloid beta and its role in Alzheimer's disease pathology. Several current and potential drug targets are mentioned, like acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptors. The document also discusses using biomarkers from sources like platelets and CSF to aid diagnosis and validate drug targets. Methodologies like proteomics and various assays are mentioned for identifying these biomarkers. Overall the goal is to identify novel targets and strategies to enhance cognition and slow disease progression.