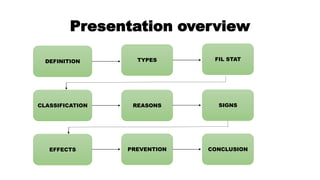
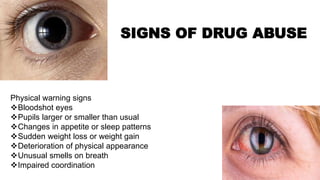
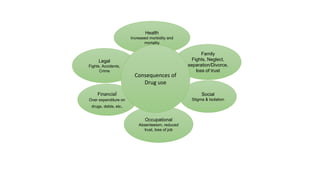
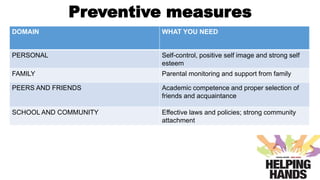
The document provides an overview of drug abuse, defining it as the repeated use of substances despite harmful consequences, and highlighting statistics such as age, sex ratio, and drug types. It classifies drugs into categories such as depressants, stimulants, hallucinogens, and others, while discussing the signs, effects, and preventive measures related to drug abuse. The conclusion emphasizes the complex nature of addiction and the challenges in identifying and addressing it.