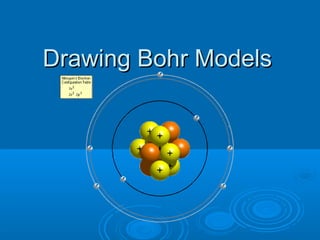
Bohr models are used to predict an element's reactivity by examining its valence electrons, which are the electrons in the outermost energy level. To draw a Bohr model, you draw the nucleus and write the number of protons and neutrons, then draw energy levels and fill them with electrons in pairs according to set rules about how many electrons each level can hold. The document then provides examples of drawing Bohr models for various elements by first determining protons, neutrons, and electrons, and using that information to draw the model.