This document summarizes a presentation on integrating values and ethics into post-secondary teaching. The presentation covers:
1) The nature of the problem in teaching values with examples from an educator and social trends.
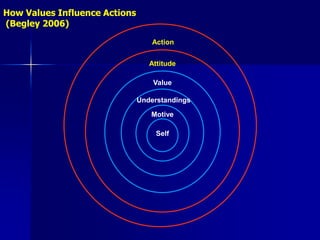
2) Key processes and concepts around values including where they come from, how they influence actions, and problems like hardening of attitudes.
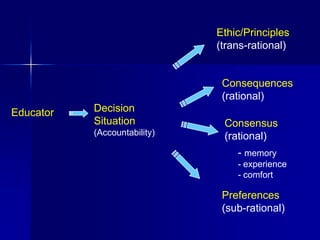
3) The context of teaching values through expert advice on development, the purposes of education, and three ways ethics relate to teaching strategies like case studies.
4) Resources for teaching values like a values audit process, journals, and annotated lists.