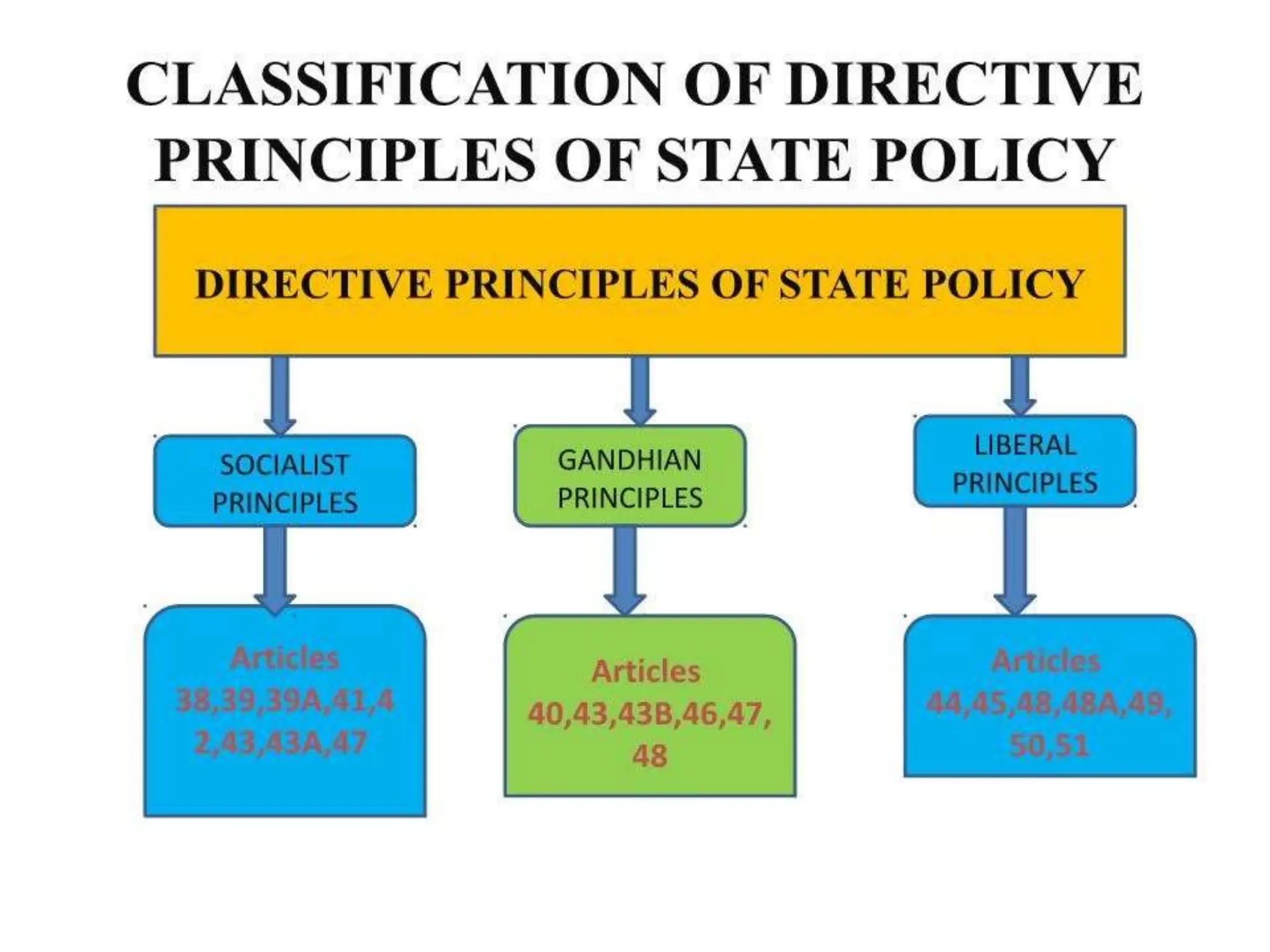
The document discusses the Directive Principles of State Policy in the Constitution of India, which serve as guidelines for state governance aimed at establishing a just society. It outlines socialistic, Gandhian, and liberal-intellectual principles that promote social and economic justice, self-governance, education, and environmental protection. These principles, while not legally enforceable, are fundamental to law-making and policy implementation in India.