Embed presentation
Download to read offline
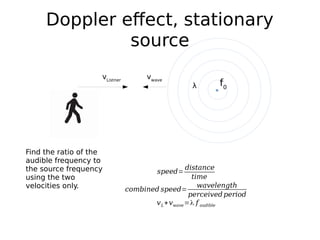
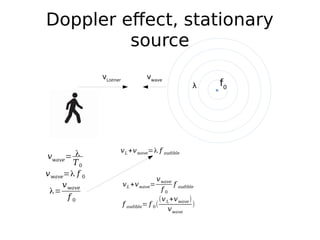
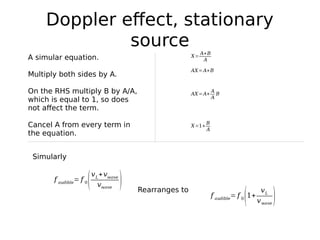
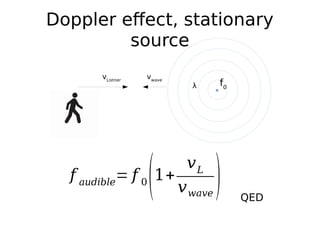

This document discusses the Doppler effect for sound waves emitted by a stationary source, such as a police siren, as perceived by a moving listener. It shows that the frequency perceived by the listener (f audible) can be calculated as the source frequency (f0) multiplied by 1 plus the ratio of the listener's velocity (vL) to the velocity of the sound waves (vwave). This calculation holds that the perceived frequency is higher than the actual frequency when the listener is moving towards the source and lower when moving away.




