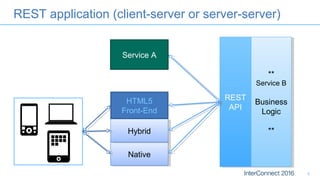
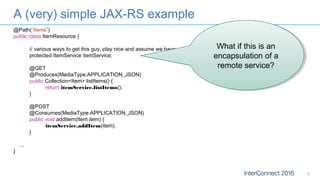
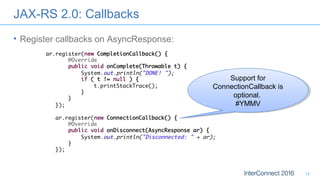
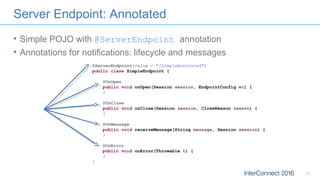
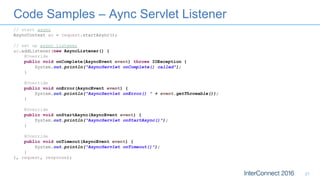
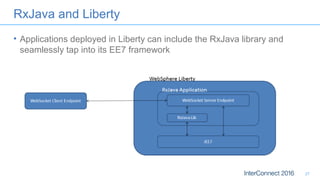
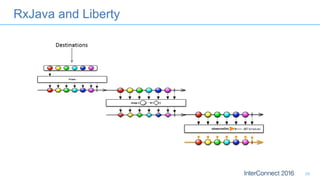
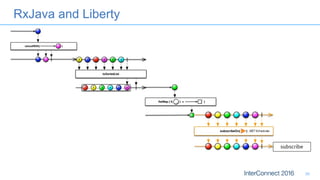
The document discusses developing responsive applications using Java EE7, highlighting technologies such as JAX-RS 2.0 for asynchronous processing, WebSocket API, and non-blocking I/O from Servlet 3.1. It emphasizes the benefits of these technologies in maximizing resource utilization and enabling real-time updates through reactive programming with libraries like RxJava. Additionally, it provides code examples demonstrating the implementation of asynchronous processing, WebSocket endpoints, and non-blocking I/O in Java EE environments.