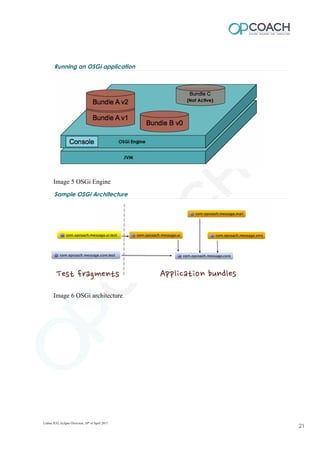
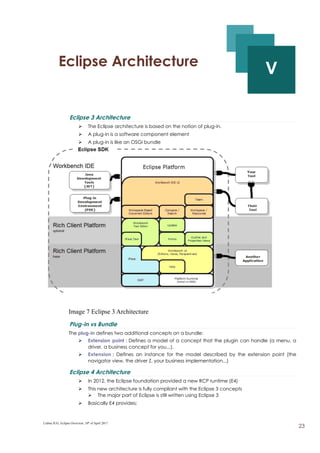
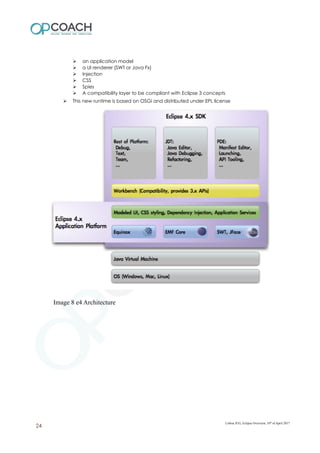
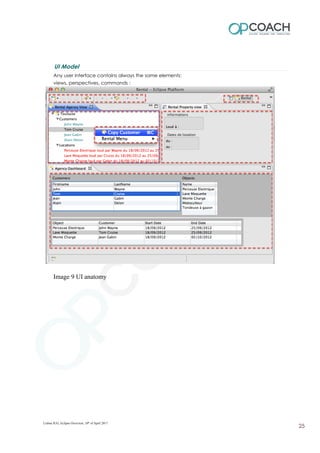
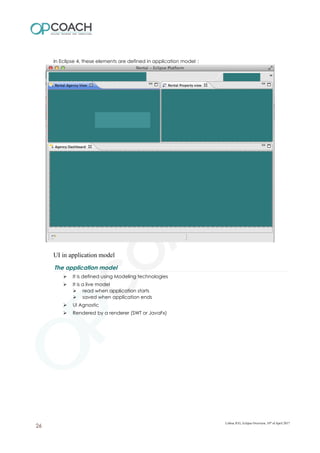
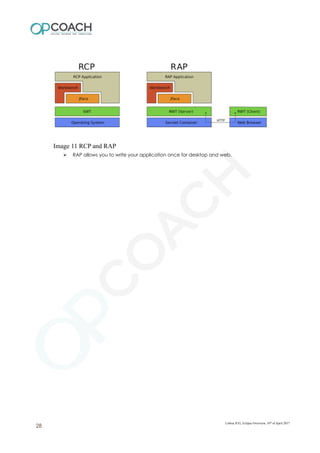
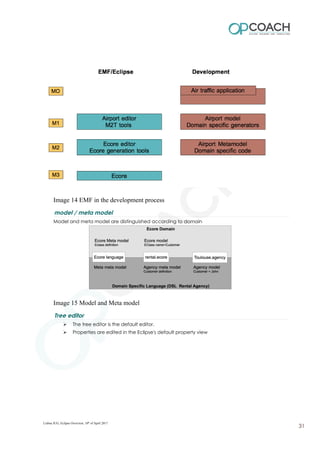
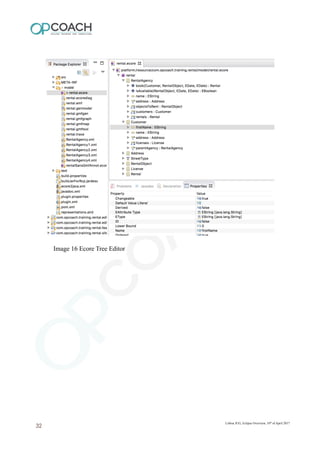
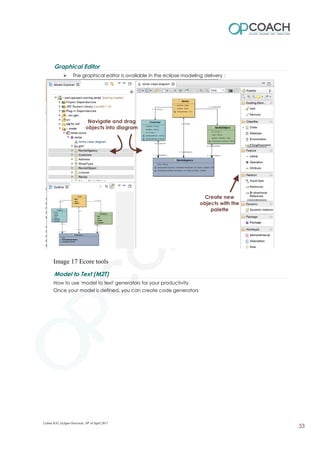
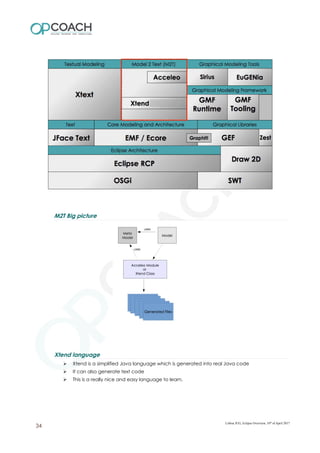
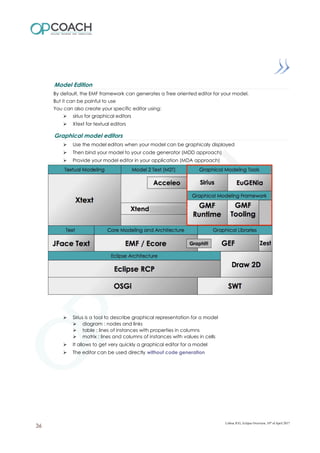
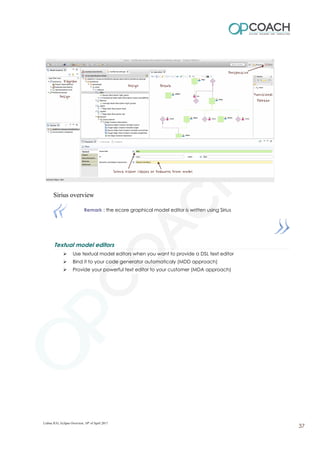
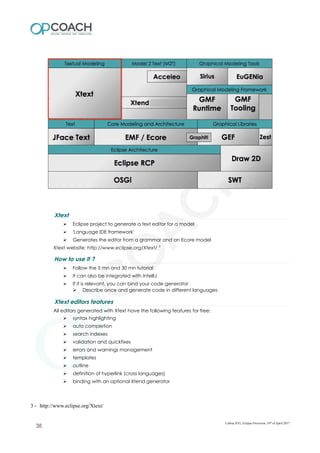
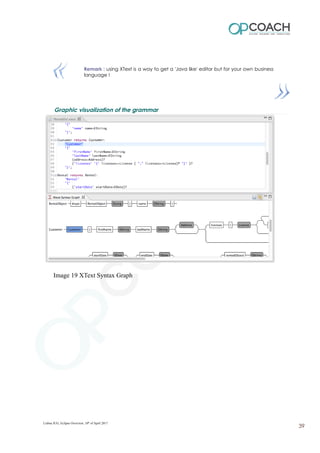
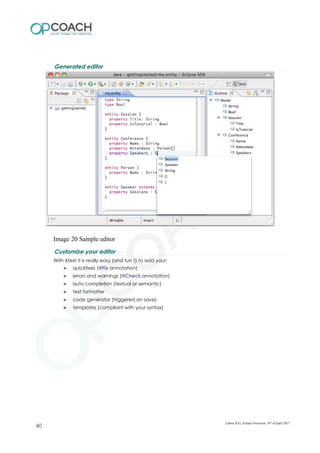
The document provides an overview of Eclipse including:
1) An introduction to the Eclipse Foundation, Eclipse IDE, OSGi architecture, and Eclipse modeling projects.
2) Details about the Eclipse ecosystem including strategic members, technical groups, and key figures.
3) Explanations of the Eclipse IDE, OSGi specification, Eclipse architecture including Eclipse 3 and Eclipse 4, and modeling projects including EMF and M2T generators.