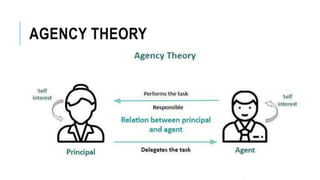
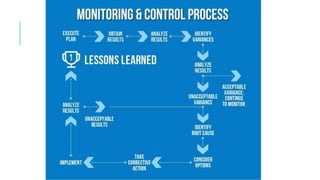
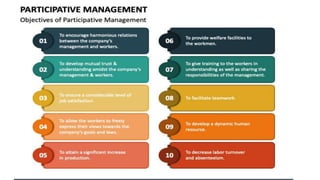
This document discusses several topics related to management control including agency theory, control mechanisms, participative management, and performance measurement. It provides definitions and explanations of key concepts. Agency theory examines the relationship between principals and agents and how their differing priorities can be resolved. Control mechanisms aim to regulate processes and include monitoring and incentive contracting. Participative management involves employees in decision-making to improve commitment and initiatives. Performance measurement assesses how well an organization's strategy is being implemented. The document also addresses morale, resistance to change, and potential reasons why participative management may fail.