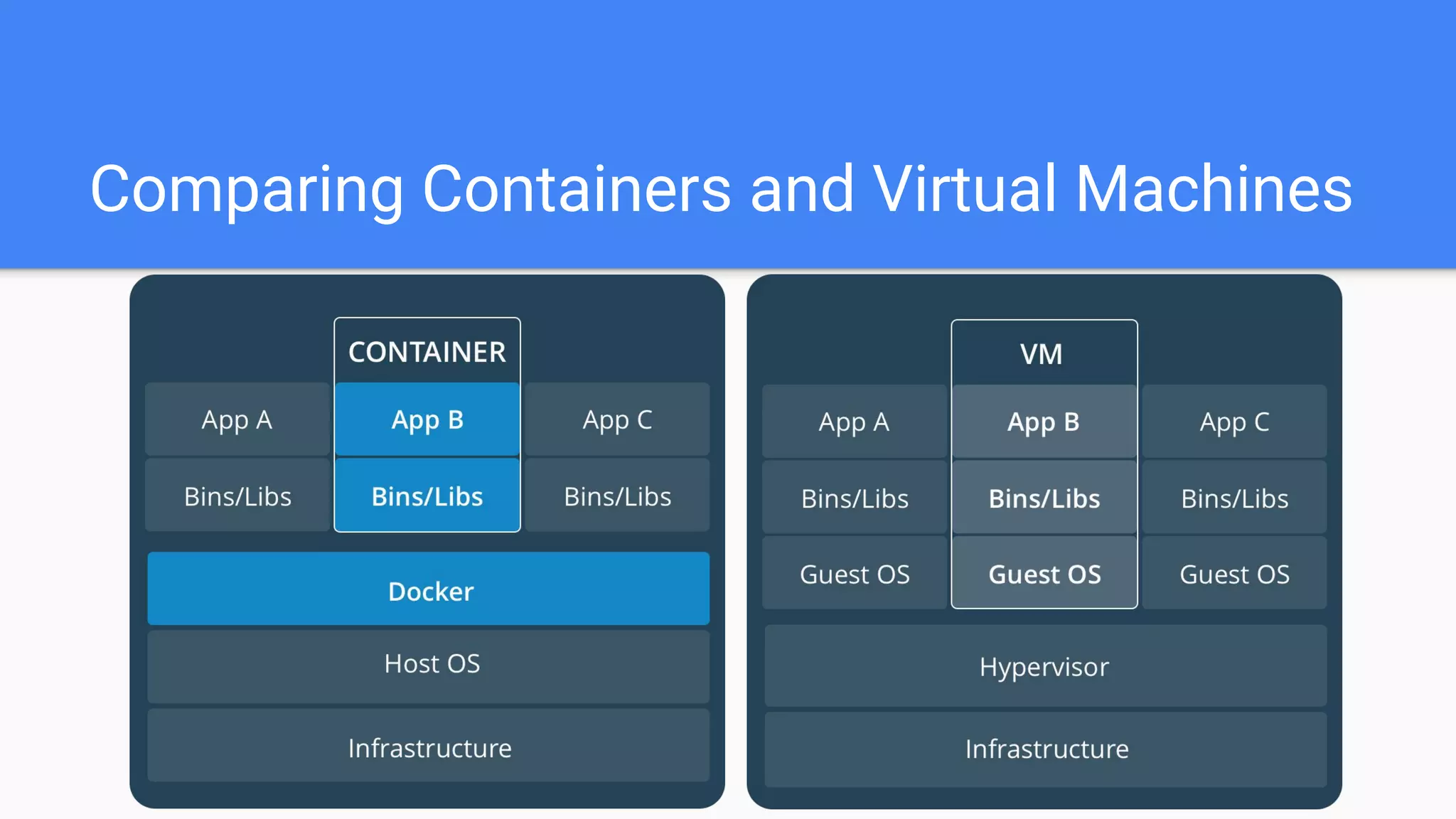
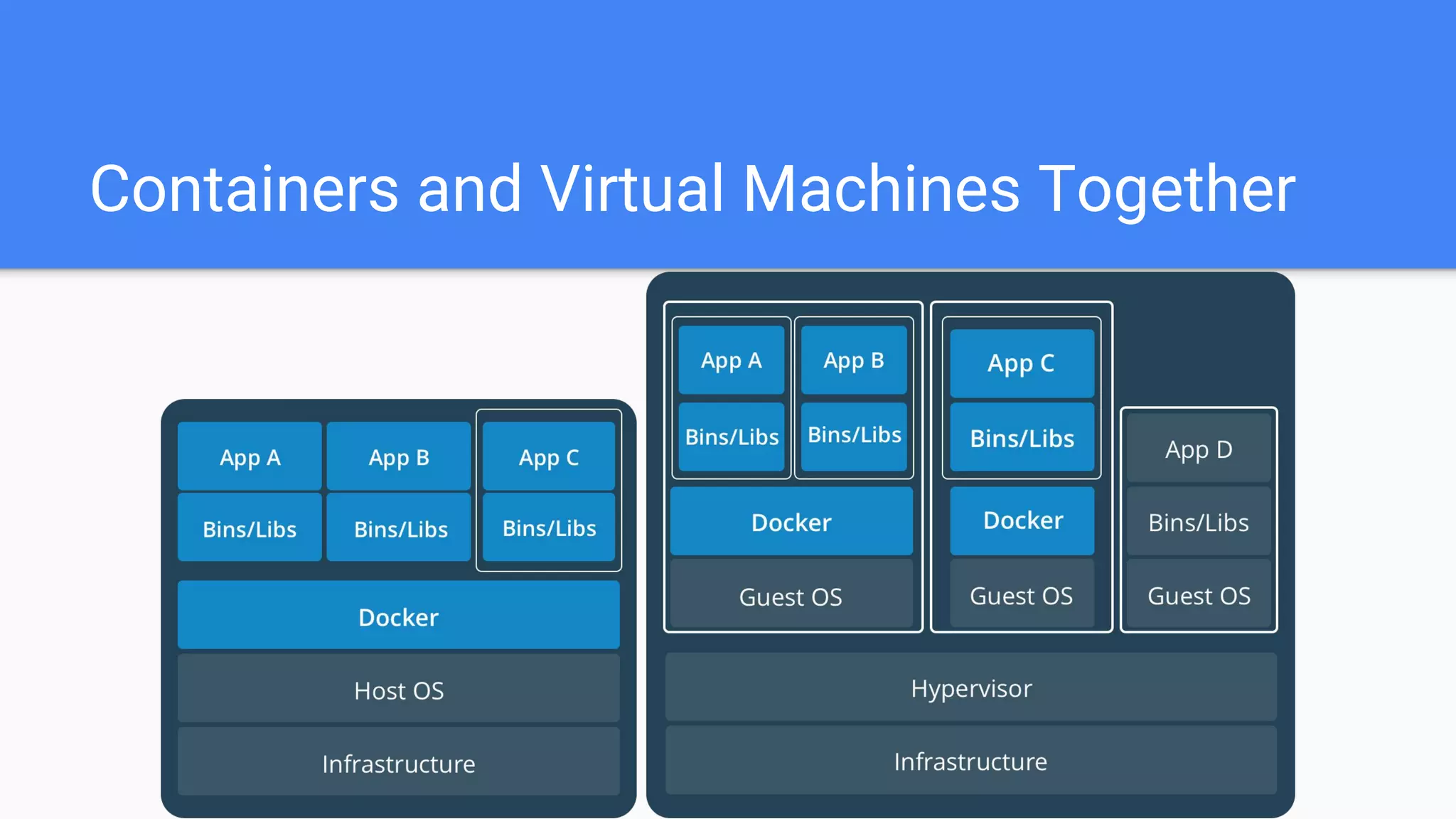
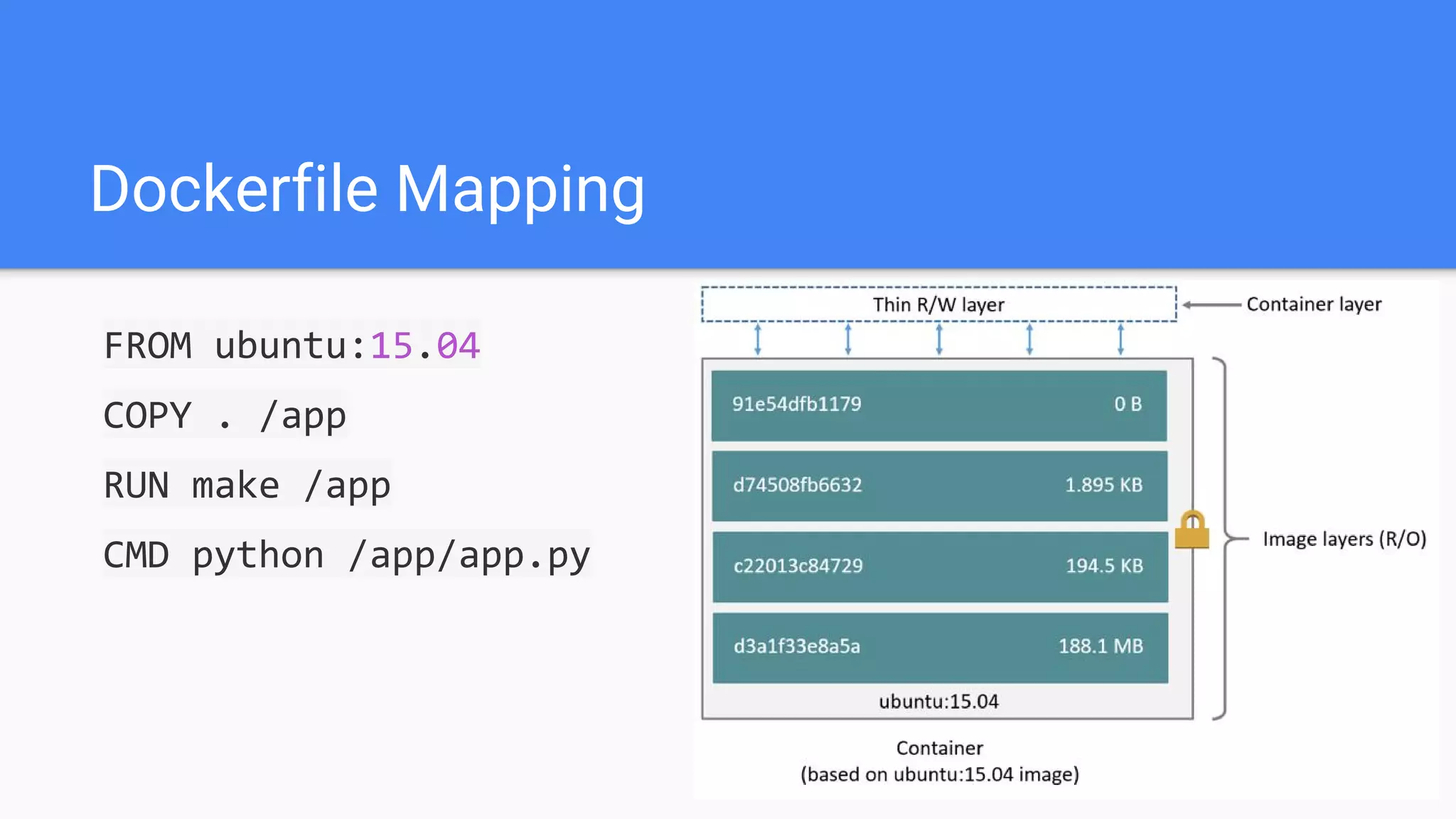
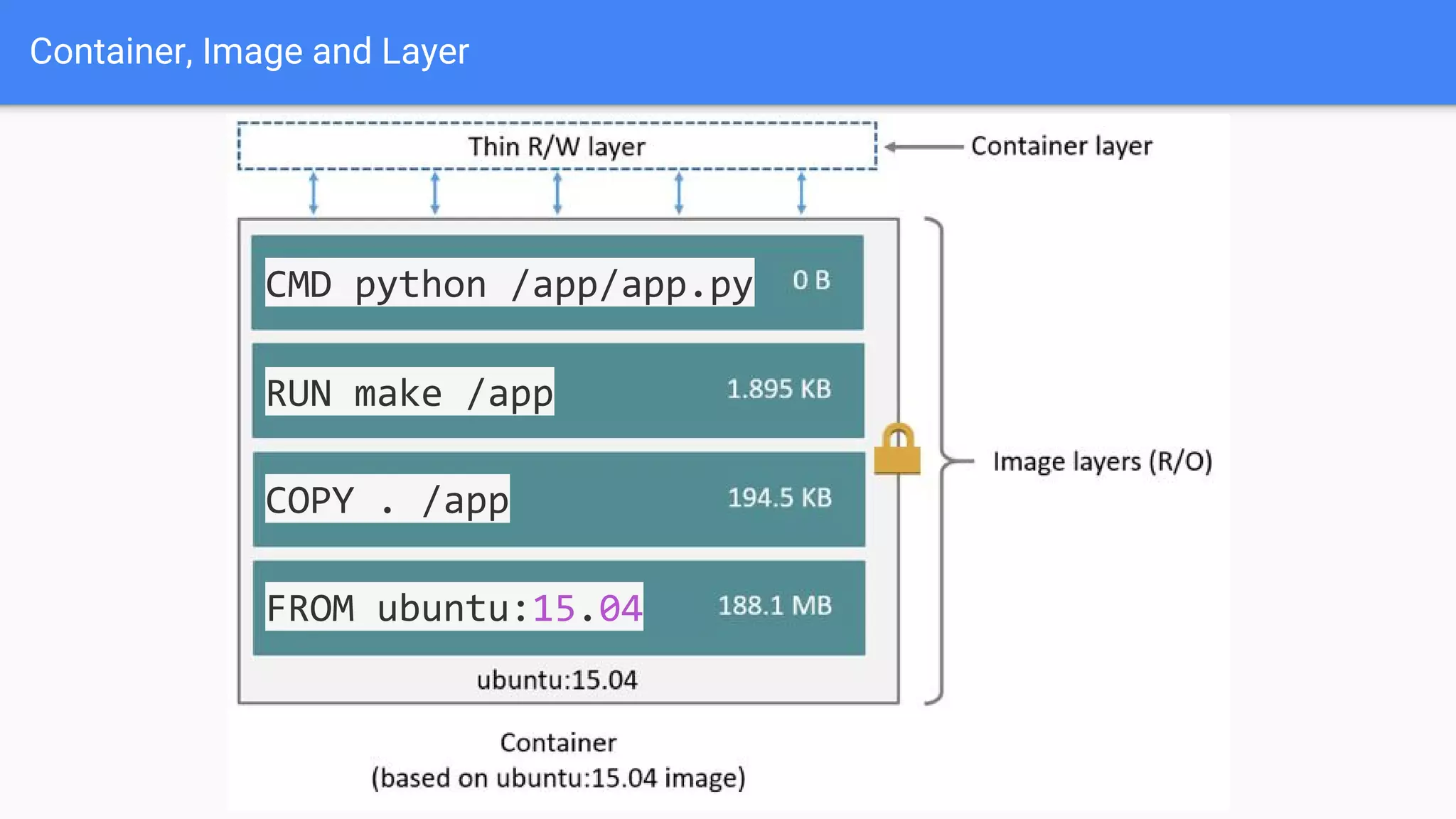
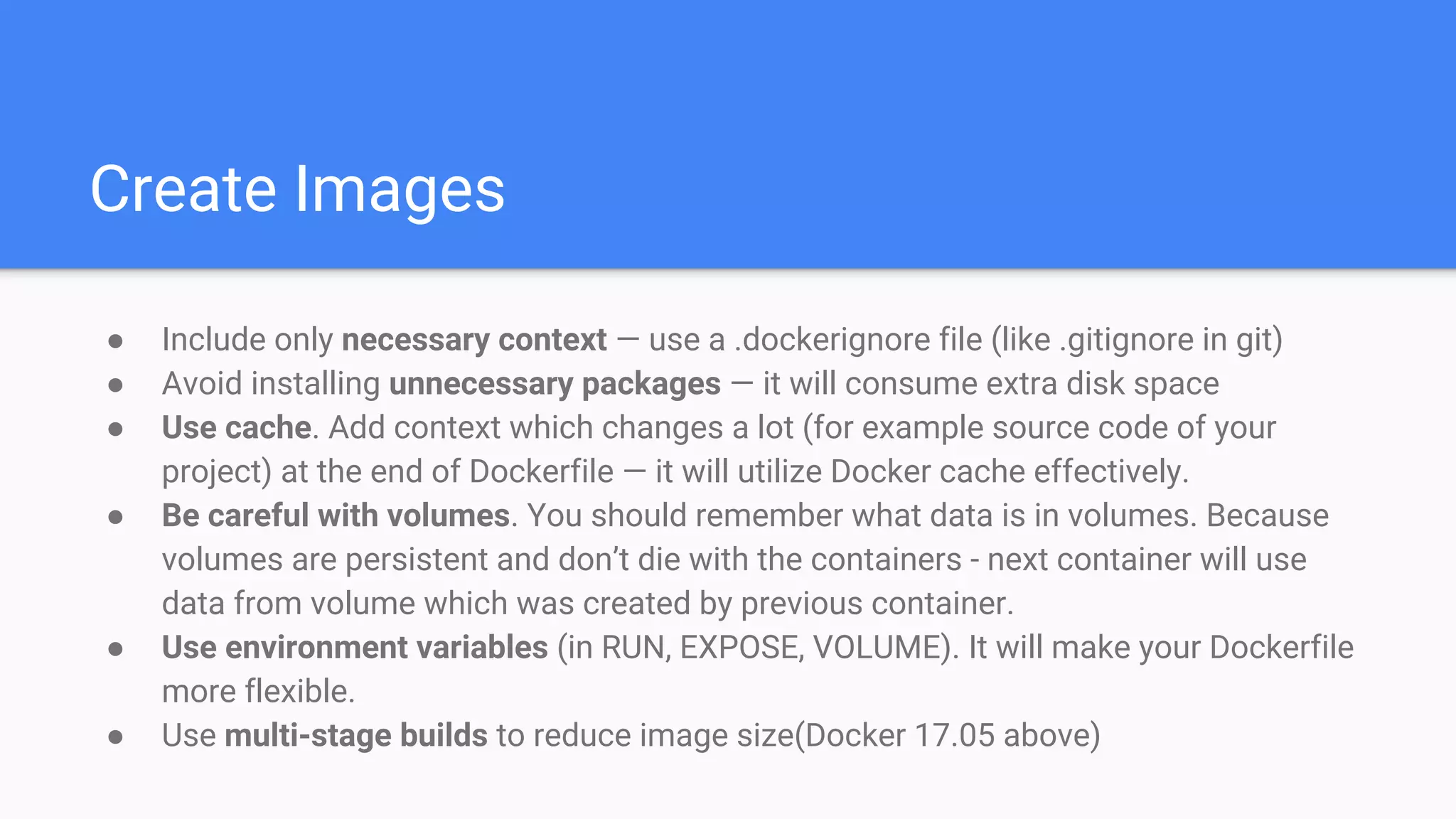
Docker is a container management service that isolates applications from the system, ensuring consistent behavior across different environments. It offers benefits like faster development, easy application encapsulation, and simplified monitoring and scaling. The document includes best practices for creating Docker images and containers, emphasizing the importance of efficiency and data management.