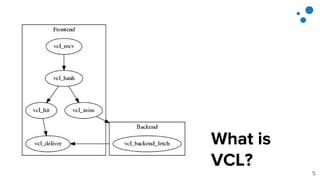
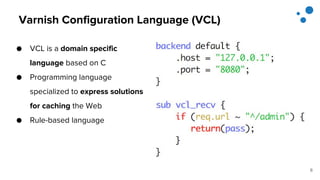
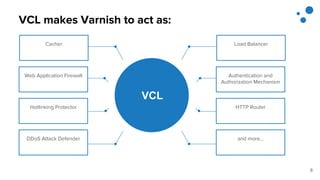
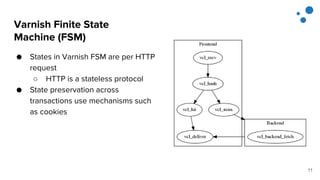
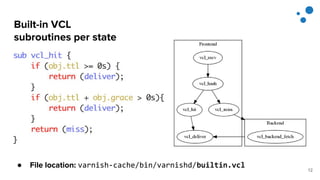
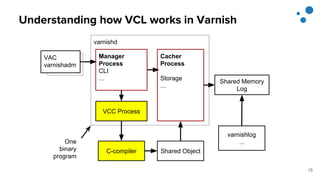
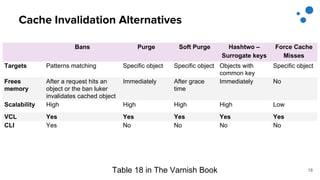
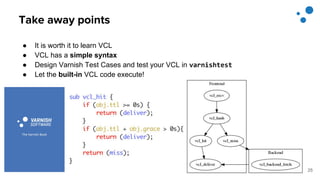
This document discusses Varnish Configuration Language (VCL), a domain-specific language used to configure Varnish caching. It motivates learning VCL by explaining how it allows customizing Varnish behavior. It then covers VCL characteristics, how VCL works within Varnish's finite state machine, best practices for designing and testing VCL, and common VCL mistakes. The overall message is that VCL is worth learning as it provides powerful customization but requires careful design and testing to avoid errors.