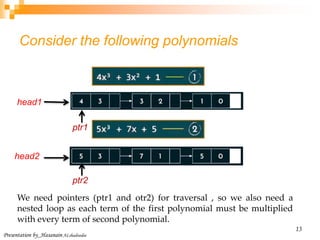
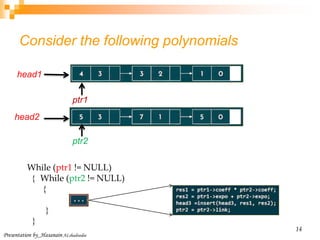
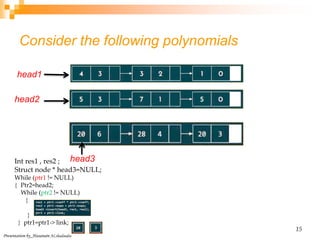
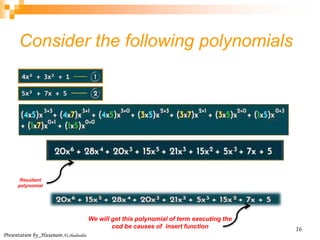
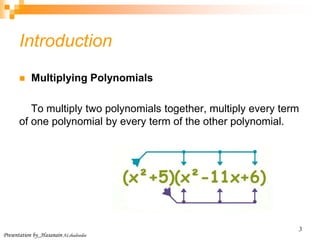
This document discusses multiplying two polynomials using a divide-and-conquer approach. It presents a naive O(n^2) method and then describes how to divide the polynomials into even and odd powers to perform the multiplication in O(n log n) time using recursion. The key steps are: (1) Express each polynomial as the sum of even and odd powers. (2) Multiply the even and odd parts separately. (3) Combine the results. Programming data structures like linked lists are also presented to efficiently represent and multiply the polynomials.


![Divide-and-Conquer
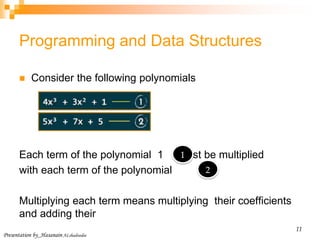
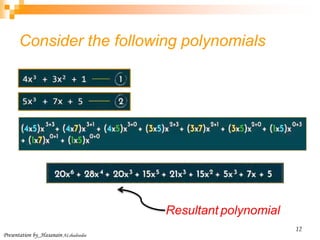
Multiply two polynomials
Problem
Given two polynomials represented by two arrays, write a function that
multiplies given two polynomials.
Input: A[] = {10, 5, 11}
B[] = {3, 2, 1}
Output: prod C[] = 10 X + 5 x1 + 11 x2
3 X + 2 x1 + 1 x2
= 30 + 10 * 2x1 + 10 * 1x1 + 5x1 * 3+ 5x1 * 2x1 + 5x1 * 1x2 + 11x2 * 3 +
11x2 * 2x1 + 11x2 * 1x2
polynomials
Presentation by_Hasanain ALshadoodee
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/divide-and-conquermultiplytwopolynomials-211221191010/85/Divide-and-conquer-multiply-two-polynomials-4-320.jpg)

![Algoritham
1) Create a product array prod[] of size m+n-1.
2) Initialize all entries in prod[] as 0.
3) Traverse array A[] and do following for every element A[i]
Traverse array B[] and do following for every element B[j]
so prod[i+j] = prod[i+j] + A[i] * B[j]
4) Return prod[].
Presentation by_Hasanain ALshadoodee
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/divide-and-conquermultiplytwopolynomials-211221191010/85/Divide-and-conquer-multiply-two-polynomials-6-320.jpg)