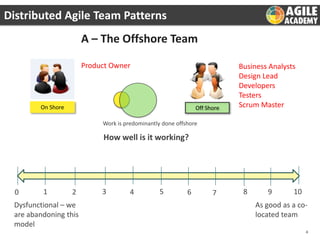
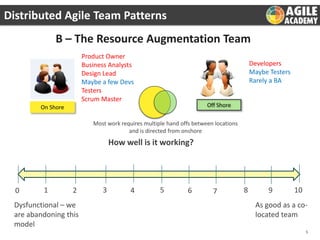
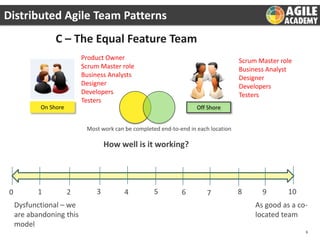
The document discusses the challenges and principles of distributed agile teams, emphasizing the importance of collaboration, knowledge sharing, and agility across multiple locations. It presents different team models and outlines best practices for successful distributed agile environments, including stable team structures, effective communication, and continuous improvement metrics. Additionally, it highlights the need for a shared agile mindset among team members to enhance productivity and ownership.