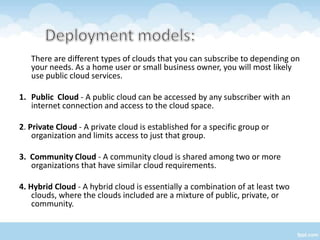
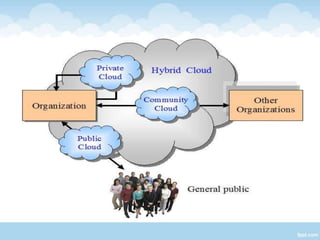
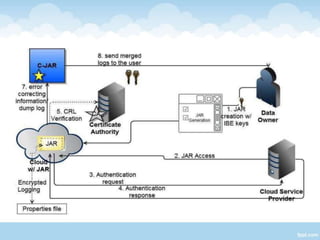
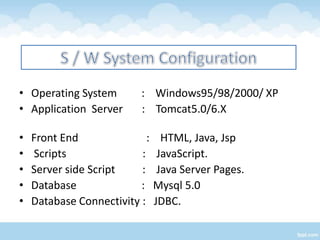
The document proposes a Cloud Information Accountability (CIA) framework to provide end-to-end accountability for data stored in the cloud. The CIA framework uses a logger component associated with each user's data to log all access and encrypt the logs. It also includes a log harmonizer that periodically collects encrypted logs and allows users to retrieve logs on demand for auditing purposes. The framework aims to enable data owners to track how their data is used while maintaining lightweight and decentralized logging.