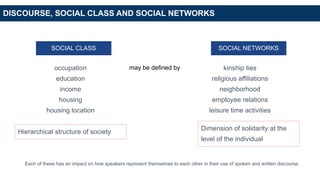
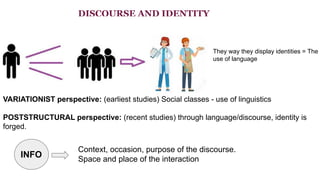
Discourse communities share common goals, communication mechanisms, information exchange, genres, terminology, and expertise. Speech communities interact using shared languages and varieties, recognizing appropriate language contexts. Membership in discourse and speech communities is defined by language, social factors like class, networks, geography, culture, politics, ethnicity, age, race, and gender. Language choice depends on domains, social contexts, topics, formality, and audience. Social class, networks, and identities are constructed through language use and negotiation across interactions and situations. Online identities are crafted through symbolic interaction. Academic writing identities are challenging for second language learners. Ideology is often hidden in framing, emphasis, presupposition.