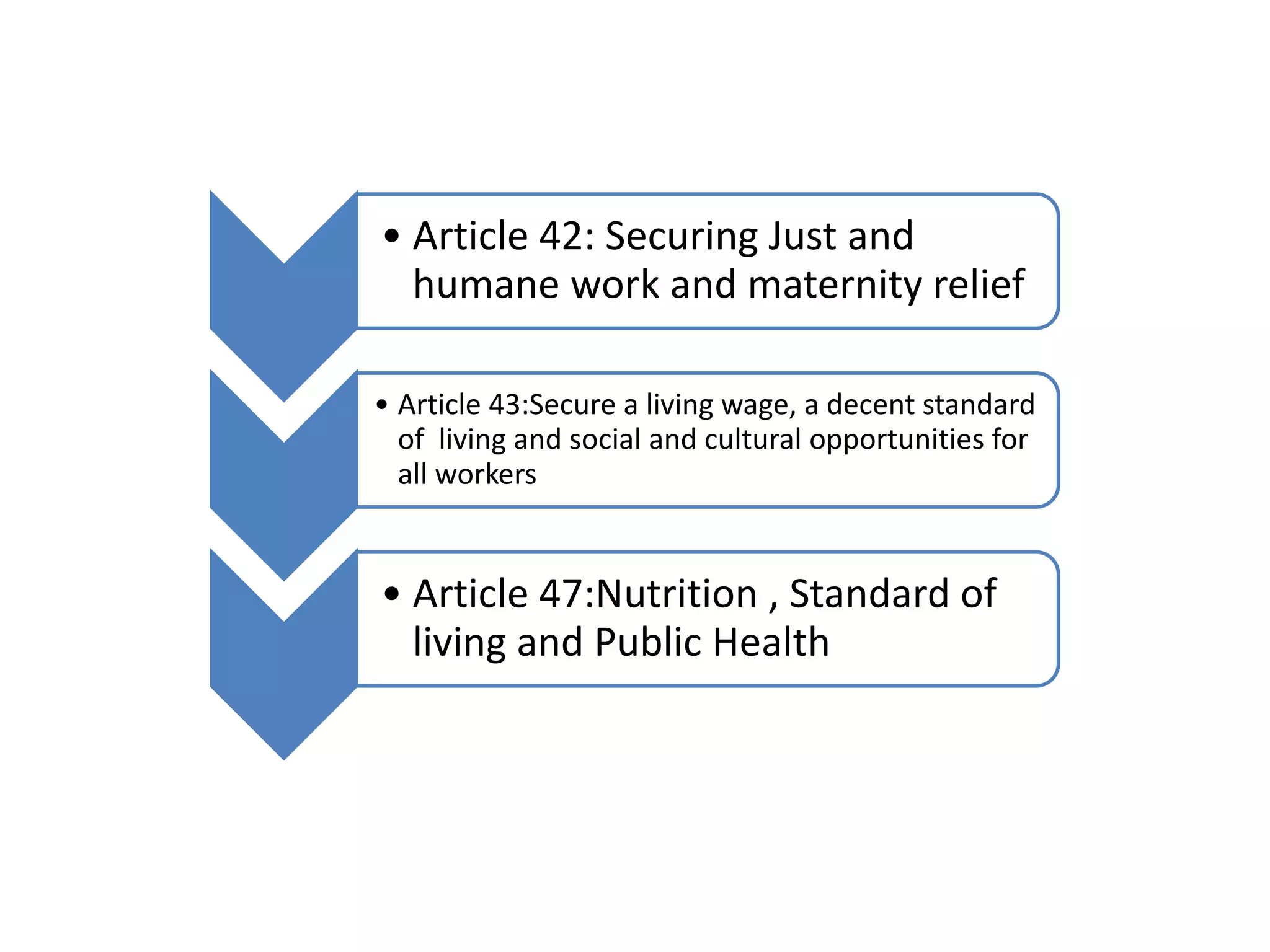
This document summarizes the key principles found in the Directive Principles of State Policy section of the Indian constitution. It divides the principles into three categories: socialist, Gandhian, and liberal intellectual. Under socialist principles, it outlines articles related to justice, livelihood, equal pay, child welfare, legal aid, unemployment assistance, education, working conditions, and public health. Gandhian principles reference local self-governance, cottage industries, and prohibiting intoxicants and cattle slaughter. Liberal intellectual principles cover a uniform civil code, education, wildlife/environment, historical sites, an independent judiciary, and international peace.