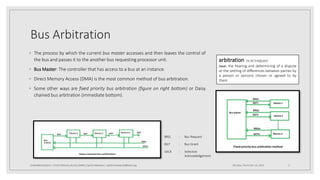
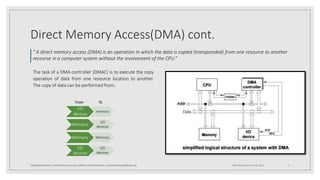
The document provides an overview of Direct Memory Access (DMA), explaining its function and significance in embedded systems. It describes DMA as a method that enables data transfer from peripherals to memory without CPU involvement, thus eliminating interrupt latency. The document also outlines three DMA modes: burst mode, cycle stealing mode, and transparent mode.