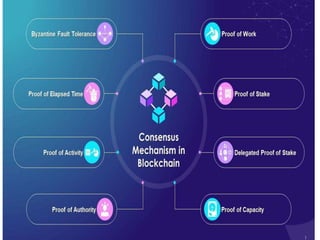
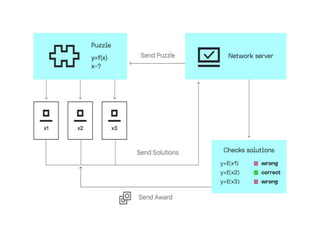
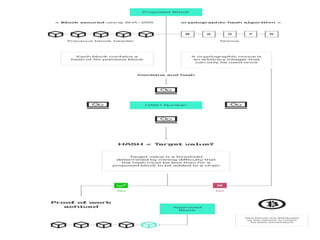
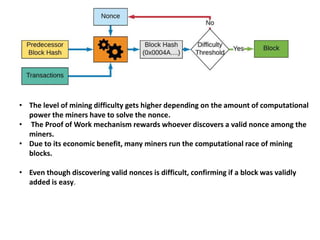
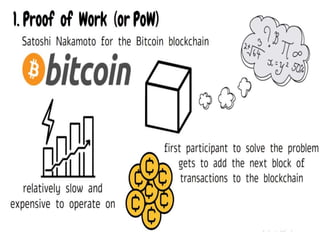
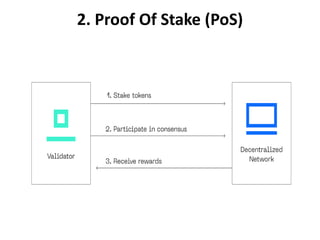
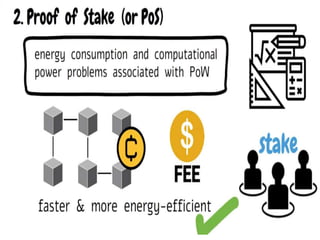
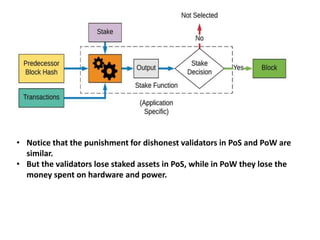
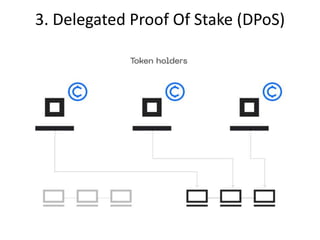
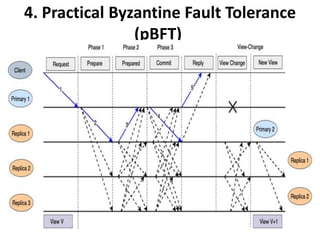
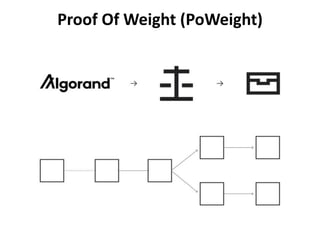
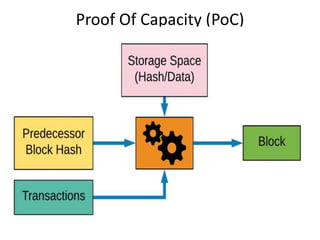
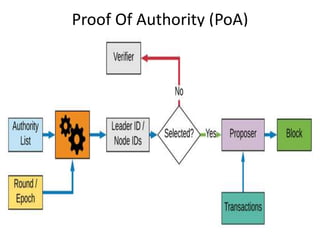
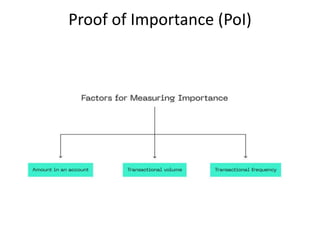
The document discusses various consensus mechanisms used in blockchain networks. It describes Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (pBFT), Proof of Weight (PoWeight), Proof of Capacity (PoC), Proof of Authority (PoA), and Proof of Importance (PoI). For each mechanism it provides details on how it works and its advantages and disadvantages.