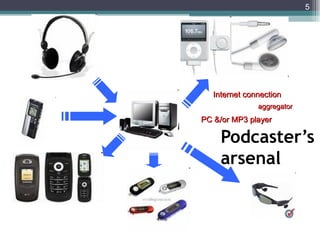
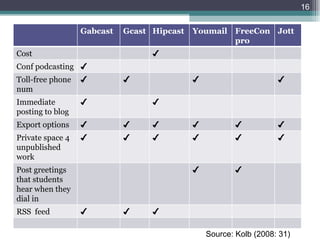
This document provides an outline of a workshop on podcasting presented by Prof Dick Ng'ambi at CPUT on March 13, 2012. The workshop covered what podcasting is, who is doing it, how it works, why it is significant, potential downsides, implications for teaching and learning, pedagogical rationale, and where podcasting is headed. Key points include that podcasting allows audio files to be automatically downloaded to portable devices; anyone can create podcasts; and it gives educators new ways to deliver content to students and meet them online.