1) This document discusses screening and diagnosis of diabetes, including definitions, criteria for testing asymptomatic adults, methods of testing such as fasting plasma glucose and oral glucose tolerance tests, use of HbA1c for diagnosis, and classification of diabetes types.
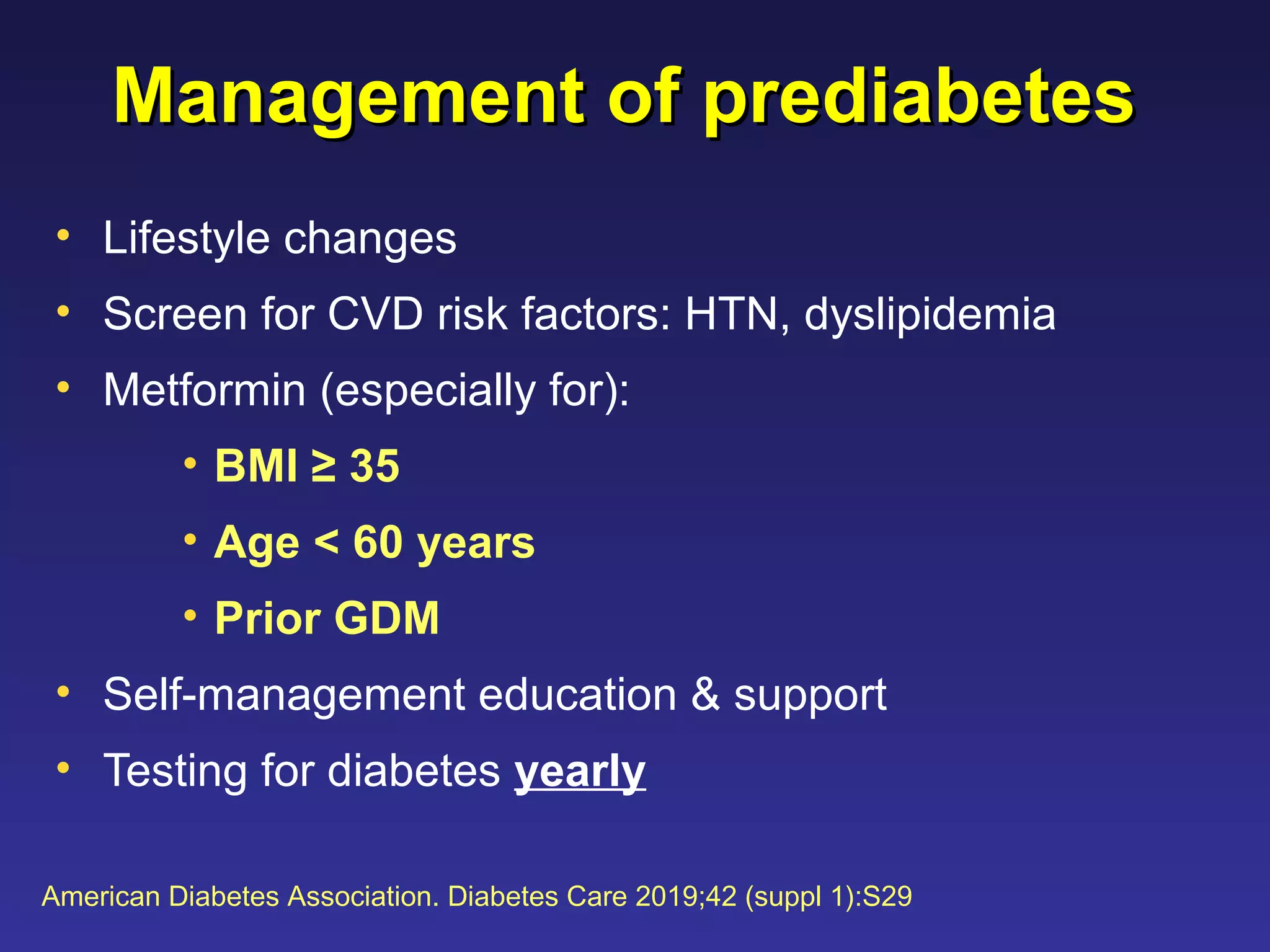
2) Prediabetes, defined as impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance, increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Lifestyle changes and metformin can prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.
3) Diabetes causes serious complications affecting the eyes, kidneys, nerves, heart and blood vessels due to damage to both small and large blood vessels if not properly managed.










![mal:
< 5.6 mmol (100 mg)
betes:
≥ 7 mmol (126 mg)
aired fasting glucose (IFG) [Prediabetes]:
5.6 to 6.9 mmol (100-125 mg)
Fasting plasmaglucose
American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2019;42 (suppl 1):S13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofdm-p-190126164832/75/Diabetes-screening-diagnosis-11-2048.jpg)













![Group on lifestyle changes:
Weight loss of 7 %
Structured exercise program
[moderate intensity]
(150 min./week)
Diabetes prevention program
Risk of DM ↓ by 58 %
• Group on Metformin
Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group.
N Engl J Med 2002; 346:393.
Risk of DM ↓ by 31 %
Persons with prediabetes (mainly IGT)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofdm-p-190126164832/75/Diabetes-screening-diagnosis-25-2048.jpg)