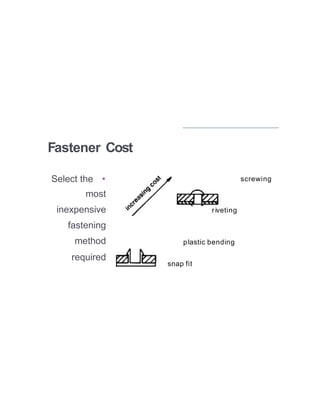
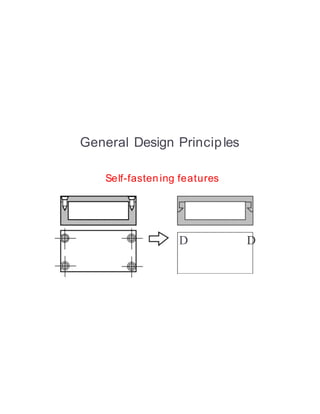
DFM is the design of parts for ease of manufacturing to reduce costs, while DFA focuses on ease of assembly. Both aim to lower material, overhead, and labor expenses. DFM objectives include estimating manufacturing costs, reducing component and production support costs. DFA assists with minimum cost assembly by reducing parts and operations. Key differences are that DFA only considers assembly costs while DFM reduces overall production costs, and DFA favors complex individual parts while DFM prioritizes simple manufacturing.