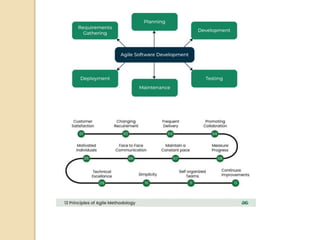
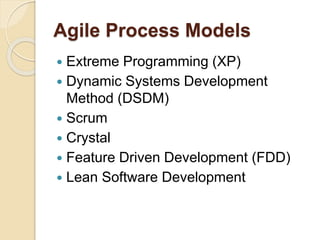
The document provides an overview of agile software development, highlighting its focus on flexibility, collaboration, and customer satisfaction based on the agile manifesto. It outlines the agile development process, including stages from requirements gathering to maintenance, and describes various models like scrum and extreme programming. Additionally, it discusses the advantages and disadvantages of agile development, emphasizing faster time-to-market and improved customer satisfaction alongside challenges such as lack of planning and difficulty in estimating effort.