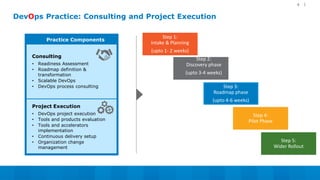
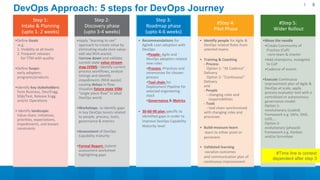
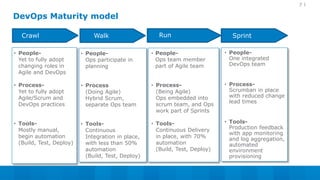
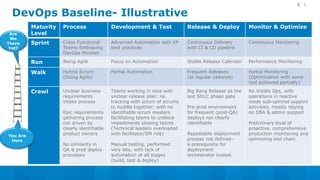
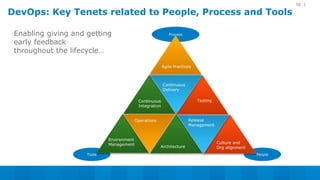
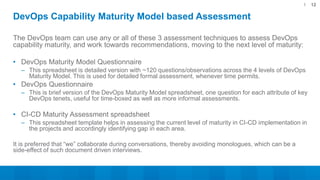
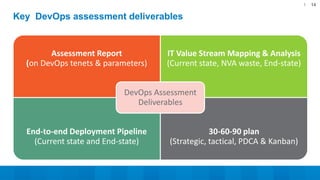
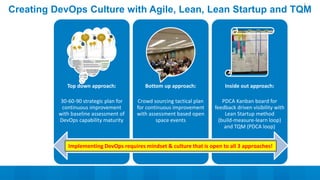
The document outlines a 5-step DevOps assessment and improvement process: 1) Intake and planning, 2) Discovery, 3) Roadmap development, 4) Piloting improvements, and 5) Wider rollout. It describes assessing an organization's DevOps capability maturity across people, processes, and tools. Deliverables include an assessment report, value stream map, deployment pipeline diagrams, and a 30-60-90 day continuous improvement plan. The key takeaway is that DevOps requires an open culture embracing Agile, Lean, and continuous feedback across stakeholders.