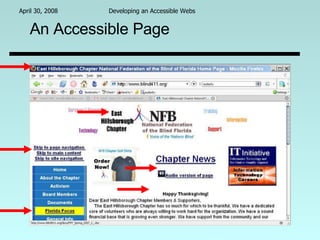
This document discusses developing accessible websites for people with disabilities. It notes that 20% of the population has a disability and outlines guidelines for making web content usable by people who are blind, have low vision, are deaf or hard of hearing, or have other disabilities. The document recommends conforming to standards like W3C's Web Content Accessibility Guidelines, understanding why the guidelines exist, and using good coding practices to ensure accessibility for all users.
![Developing an Accessible Web Arnold Bailey [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devaccweb-1209582499650330-9/75/Developing-an-Accessible-Web-1-2048.jpg)